|
Venix
Venix is a discontinued version of the Unix operating system for low-end computers, developed by VenturCom, a "company that specialises in the skinniest implementations of Unix".VenturCom ships real-time Venix/386. Computer Business Review, 1 February 1990. Retrieved 23 March 2013. Overview A working version of Venix/86 for the IBM PC XT was demoed at Comdex in May 1983. It was based on Version 7 Unix with some enhancements from BSD (notably vi, more and csh) and custom inter-process communication mechanisms. It was the first licensed UNIX operating system available for the IBM PC and its compatibles, supported read/write access to a separate DOS/FAT-partition and could run in as little as 128 KB (256 KB - 512 KB recommended). In September 1984, Venix/86 Encore was released; it supported a number of early PC-compatibles, including the AT&T 6300, the Zenith 150, the (first) NCR PC, and the Texas Instruments Professional Computer. Venix Encore, which then became Venix 2.0, was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DEC Professional (computer)
The Professional 325 (PRO-325), Professional 350 (PRO-350), and Professional 380 (PRO-380) are PDP-11 compatible microcomputers introduced in 1982 by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) as high-end competitors to the IBM PC. History Like the cosmetically similar Rainbow 100 and DECmate II (also introduced at that time), the PRO series uses the LK201 keyboard and 400KB single-sided quad-density floppy disk drives (known as RX50), and offers a choice of color or monochrome monitors. For DEC, none of the three would be favorably received, and the industry instead standardized on Intel 8088-based IBM PC compatibles which are all binary program compatible with each other. In some ways, the PDP-11 microprocessors are technically superior to the Intel-based chips. While the 8088 is restricted to 1MB of memory because of its 20-bit address bus, DEC microprocessors are capable of accessing 4MB with their 22-bit addressing (although direct addressing of memory is limited in both approaches ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PRO-380
The Professional 325 (PRO-325), Professional 350 (PRO-350), and Professional 380 (PRO-380) are PDP-11 compatible microcomputers introduced in 1982 by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) as high-end competitors to the IBM PC. History Like the cosmetically similar Rainbow 100 and DECmate II (also introduced at that time), the PRO series uses the LK201 keyboard and 400KB single-sided quad-density floppy disk drives (known as RX50), and offers a choice of color or monochrome monitors. For DEC, none of the three would be favorably received, and the industry instead standardized on Intel 8088-based IBM PC compatibles which are all binary program compatible with each other. In some ways, the PDP-11 microprocessors are technically superior to the Intel-based chips. While the 8088 is restricted to 1MB of memory because of its 20-bit address bus, DEC microprocessors are capable of accessing 4MB with their 22-bit addressing (although direct addressing of memory is limited in both approaches ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AT&T 6300
The Olivetti M24 is a computer that was sold by Olivetti in 1983 using the Intel 8086 CPU. The system was sold in the United States under its original name by Docutel/Olivetti of Dallas. AT&T and Xerox bought rights to rebadge the system as the AT&T PC 6300 and the Xerox 6060 series, respectively. (AT&T owned 25% of Olivetti around this time.) The AT&T 6300, launched in June 1984, was AT&T's first attempt to compete in the PC compatible market. It was also available in France as the PERSONA 1600, built by LogAbax. Versions The initial 1984 US version named AT&T 6300 came with either one or two 360 KB 5.25" floppy drives; a hard disk was not offered. In Europe, Olivetti launched a 10 MHz version: the Olivetti M24 SP, announced in November 1985, a contender for the title of "highest clocked 8086 computer" as its processor was the fastest grade of 8086-2, rated for a maximum speed of exactly the same 10 MHz. To support this, the motherboard now featured a switchab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VenturCom
Ardence was a software company headquartered in Waltham, Massachusetts with representatives in Washington, D.C.; Virginia Beach, VA; Chicago, IL; Denton, TX; and in Europe, the Middle East, Africa and India. It developed a software-streaming product and an embedded OEM development platform. It was founded in 1980 as VenturCom. On December 20, 2006, Citrix Systems Inc. announced an agreement to acquire Ardence. In 2008, some former Ardence executives acquired the Ardence programs from Citrix and formed IntervalZero. History VenturCom was founded in 1980, by Marc H. Meyer, Doug Mook, Bill Spencer and Myron Zimmerman. The company changed its name to Ardence in 2004. On December 20, 2006, Citrix Systems Inc. announced an agreement to acquire Ardence. In 2008, a group of former Ardence executives founded IntervalZero and acquired the Ardence embedded software business from Citrix. Citrix retained a minority ownership the firm. Products The enterprise software-streaming product deplo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advanced Debugger
The advanced debugger adb is the standard UNIX debugger found on Solaris 1 and 2, HP-UX, SCO and Venix. It is the successor of a debugger called db. Overview The initial version was written by Stephen R. Bourne. ADB is the standard debugger on Solaris and the Solaris kernel debugger ''kadb'' that was introduced with SunOS-3.5 (1986) is a minor variant of adb. A version of ADB was integrated into the BSD kernel as a kernel debugger. On Solaris, ADB was replaced by the Modular Debugger mdb with Solaris 8 (2000) and the ADB command-line interface A command-line interpreter or command-line processor uses a command-line interface (CLI) to receive commands from a user in the form of lines of text. This provides a means of setting parameters for the environment, invoking executables and pro ... now is emulated by mdb when it is called as adb. Mdb has become OpenSource with OpenSolaris. See also * DBX, the symbolic debugger References External linksA Tutorial Introduction to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Equipment Corporation
Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC ), using the trademark Digital, was a major American company in the computer industry from the 1960s to the 1990s. The company was co-founded by Ken Olsen and Harlan Anderson in 1957. Olsen was president until forced to resign in 1992, after the company had gone into precipitous decline. The company produced many different product lines over its history. It is best known for the work in the minicomputer market starting in the mid-1960s. The company produced a series of machines known as the PDP line, with the PDP-8 and PDP-11 being among the most successful minis in history. Their success was only surpassed by another DEC product, the late-1970s VAX "supermini" systems that were designed to replace the PDP-11. Although a number of competitors had successfully competed with Digital through the 1970s, the VAX cemented the company's place as a leading vendor in the computer space. As microcomputers improved in the late 1980s, especially wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rainbow 100
The Rainbow 100 is a microcomputer introduced by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) in 1982. This desktop unit had a monitor similar to the VT220 and a dual-CPU box with both Zilog Z80 and Intel 8088 CPUs. The Rainbow 100 was a triple-use machine: VT100 mode (industry standard terminal for interacting with DEC's own VAX), 8-bit CP/M mode (using the Z80), and CP/M-86 or MS-DOS mode using the 8088. Models The Rainbow came in three models, the 100A, 100B and 100+. The "A" model was the first released, followed later by the "B" model. The most noticeable differences between the two models were the firmware and slight hardware changes. The systems were referred to with model numbers ''PC-100A'' and ''PC-100B'' respectively; later were also designated ''PC-100B2''. The system included a user-changeable ROM chip in a special casing to support their keyboard layout and language of the boot screen. On the 100A, the ROMs only supported three languages. The Rainbow did not have an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PDP-11
The PDP-11 is a series of 16-bit minicomputers sold by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) from 1970 into the 1990s, one of a set of products in the Programmed Data Processor (PDP) series. In total, around 600,000 PDP-11s of all models were sold, making it one of DEC's most successful product lines. The PDP-11 is considered by some experts to be the most popular minicomputer. The PDP-11 included a number of innovative features in its instruction set and additional general-purpose registers that made it much easier to program than earlier models in the PDP series. Further, the innovative Unibus system allowed external devices to be easily interfaced to the system using direct memory access, opening the system to a wide variety of peripherals. The PDP-11 replaced the PDP-8 in many real-time computing applications, although both product lines lived in parallel for more than 10 years. The ease of programming of the PDP-11 made it very popular for general-purpose computing uses also. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microcomputer
A microcomputer is a small, relatively inexpensive computer having a central processing unit (CPU) made out of a microprocessor. The computer also includes memory and input/output (I/O) circuitry together mounted on a printed circuit board (PCB). Microcomputers became popular in the 1970s and 1980s with the advent of increasingly powerful microprocessors. The predecessors to these computers, mainframes and minicomputers, were comparatively much larger and more expensive (though indeed present-day mainframes such as the IBM System z machines use one or more custom microprocessors as their CPUs). Many microcomputers (when equipped with a keyboard and screen for input and output) are also personal computers (in the generic sense). An early use of the term ''personal computer'' in 1962 predates microprocessor-based designs. ''(See "Personal Computer: Computers at Companies" reference below)''. A ''microcomputer'' used as an embedded control system may have no human-readable input ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
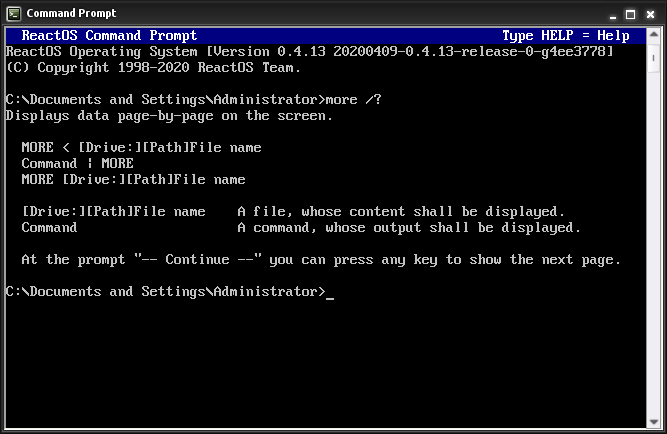
More (command)
In computing, more is a command to view (but not modify) the contents of a text file one screen at a time. It is available on Unix and Unix-like systems, DOS, Digital Research FlexOS, IBM/Toshiba 4690 OS, IBM OS/2, Microsoft Windows and ReactOS. Programs of this sort are called ''pagers''. more is a very basic pager, originally allowing only forward navigation through a file, though newer implementations do allow for limited backward movement. History The more command was originally written by Daniel Halbert, a graduate student at the University of California, Berkeley, in 1978. It was later expanded on by Eric Shienbrood, Geoff Peck (added underlining, single spacing) and John Foderaro (added -c, more environment variable history). It was first included in 3.0 BSD, and has since become a standard program in all Unix systems. less, a similar command with the extended capability of allowing both forward and backward navigation through the file, was written by Mark Nudelman betwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NCR Corporation
NCR Corporation, previously known as National Cash Register, is an American software, consulting and technology company providing several professional services and electronic products. It manufactures self-service kiosks, point-of-sale terminals, automated teller machines, cheque processing systems, and barcode scanners. NCR was founded in Dayton, Ohio, in 1884 and acquired by AT&T in 1991. A restructuring of AT&T in 1996 led to NCR's re-establishment on 1 January 1997, as a separate company and involved the spin-off of Lucent Technologies from AT&T. In June 2009 the company sold most of the Dayton properties and moved its headquarters to the Atlanta metropolitan area in unincorporated Gwinnett County, Georgia, near Duluth. In early January 2018, the new NCR Global Headquarters opened in Midtown Atlanta near Technology Square (adjacent to the Georgia Institute of Technology). History Early years The company began as the National Manufacturing Company of Dayton, Ohio, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ZP-150
The ZP-150 was one of the earliest commercially available laptops. It was released in late 1984 by Zenith Data Systems. Market life The ZP-150 was offered for when bundled with the Microsoft Works software, but could be found in the Fall 1985 Heathkit catalog for . The price came down to in the Winter 1986 edition of the same catalog and in the Fall 1987 edition, as it was being phased out with the release of the Z-181 and Z-183. The main target market was the U.S. government and "the mobile executive", for on-site applications. Its relatively small dimensions and light weight allowed it to be easily carried in a standard briefcase or the included carrying case. Hardware specifications *Weight: *Dimensions: 13"W × 11.1"D × 1.8"H *RAM: 32K, expandable to 416K *ROM: 224K, plus 2 sockets for software expansion * CPU: Intel 80C88 *Power: 12VDC or 10 AA alkaline batteries (providing 15 hours run-time w/o modem), plus internal nickel-cadmium battery for retaining memory whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)