|
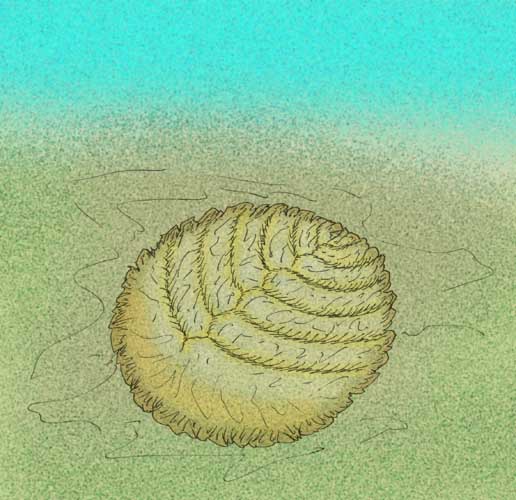
Vendiidae
Vendiamorpha is a class of extinct animals within the Ediacaran phylum Proarticulata. The typical vendiamorph had an oval-shaped or round-shaped body divided completely into segmented isomers, that were arranged alternately in two rows with reference to the longitudinal axis of the body. Description The phenomenon of left-right alternating segments is called ''glide reflection symmetry'', and is a diagnostic feature of proarticulatans. Transverse elements decrease in size from one end to the other and are inclined in the same direction. The larger isomers cover the smaller ones externally and the first isomer is much larger than the rest. Typically, the first few, or largest isomers are fused together to form a headshield-like structure, leading some researchers to have originally considered them to be ancestral or related to arthropods, though, overwhelming evidence of them being proarticulatans have since led researchers to discard this hypothetical relationship. Som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paravendia
''Paravendia'' is an extinct genus of proarticulate vendiamorph that lived in the Ediacaran period, about 553 million years ago. It shares the Vendiidae family with ''Vendia'' and ''Karakhtia''. It is a monotypic genus, with the species ''Paravendia janae''. Description It is an animal that presents 'bilateral' symmetry, similar in appearance to the previously mentioned genus '' Vendia '', with new isomers replacing the older ones. Distribution Ediacaran of the Russian Federation (Arkhangelsk). See also *List of ediacaran genera This is a list of all described Ediacaran genera, including the Ediacaran biota. It contains 227 genera. References {{reflist, 30em * Ediacaran The Ediacaran Period ( ) is a geological period that spans 96 million years from the end ... References Notes Zakrevskaya, Maria. Paleoecological reconstruction of the Ediacaran benthic macroscopic communities of the White Sea (Russia). Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology 15 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vendiamorpha
Vendiamorpha is a class of extinct animals within the Ediacaran phylum Proarticulata. The typical vendiamorph had an oval-shaped or round-shaped body divided completely into segmented isomers, that were arranged alternately in two rows with reference to the longitudinal axis of the body. Description The phenomenon of left-right alternating segments is called ''glide reflection symmetry'', and is a diagnostic feature of proarticulatans. Transverse elements decrease in size from one end to the other and are inclined in the same direction. The larger isomers cover the smaller ones externally and the first isomer is much larger than the rest. Typically, the first few, or largest isomers are fused together to form a headshield-like structure, leading some researchers to have originally considered them to be ancestral or related to arthropods, though, overwhelming evidence of them being proarticulatans have since led researchers to discard this hypothetical relationship. Som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vendiidae
Vendiamorpha is a class of extinct animals within the Ediacaran phylum Proarticulata. The typical vendiamorph had an oval-shaped or round-shaped body divided completely into segmented isomers, that were arranged alternately in two rows with reference to the longitudinal axis of the body. Description The phenomenon of left-right alternating segments is called ''glide reflection symmetry'', and is a diagnostic feature of proarticulatans. Transverse elements decrease in size from one end to the other and are inclined in the same direction. The larger isomers cover the smaller ones externally and the first isomer is much larger than the rest. Typically, the first few, or largest isomers are fused together to form a headshield-like structure, leading some researchers to have originally considered them to be ancestral or related to arthropods, though, overwhelming evidence of them being proarticulatans have since led researchers to discard this hypothetical relationship. Som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proarticulata
Proarticulata is a proposed phylum of extinct, bilaterally symmetrical animals known from fossils found in the Ediacaran (Vendian) marine deposits, and dates to approximately . The name comes from the Greek () = "before" and Articulata, i.e. prior to animals with true segmentation such as annelids and arthropods. This phylum was established by Mikhail A. Fedonkin in 1985 for such animals as '' Dickinsonia'', ''Vendia'', ''Cephalonega'', ''Praecambridium'' and currently many other Proarticulata are described (see list). Due to their simplistic morphology, their affinities and mode of life are subject to debate. They are almost universally considered to be metazoans, and due to possessing a clear central axis have been suggested to be stem-bilaterians. In the traditional interpretation, the Proarticulatan body is divided into transverse articulation (division) into isomers as distinct from the transverse articulation segments in annelids and arthropods, as their individual isome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karakhtia Nessovi
''Karakhtia nessovi'' is a species of Proarticulate from the Ediacaran period, around 555 Million Years Ago. K. nessovi is the only species in the genus ''Karakhtia''. The genus Haootia has been compared minorly to ''Karakhtia'' in the way that the fossils of ''Haootia'' superficially resemble the crumpled margins of ''Karakhtia''. See also * Vendiamorpha * Vendia ''Vendia'' is a genus of oval-shaped, Ediacaran fossils ranging from 4.5 to 12.5 mm long. The body is completely segmented into isomers, which are arranged alternately in two rows longitudinal to the axis of the body. The larger isomers cov ... * List of ediacaran genera References Vendiamorpha Ediacaran life Ediacaran Proarticulata Enigmatic prehistoric animal genera Taxa described in 2004 {{Ediacaran-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proarticulata
Proarticulata is a proposed phylum of extinct, bilaterally symmetrical animals known from fossils found in the Ediacaran (Vendian) marine deposits, and dates to approximately . The name comes from the Greek () = "before" and Articulata, i.e. prior to animals with true segmentation such as annelids and arthropods. This phylum was established by Mikhail A. Fedonkin in 1985 for such animals as '' Dickinsonia'', ''Vendia'', ''Cephalonega'', ''Praecambridium'' and currently many other Proarticulata are described (see list). Due to their simplistic morphology, their affinities and mode of life are subject to debate. They are almost universally considered to be metazoans, and due to possessing a clear central axis have been suggested to be stem-bilaterians. In the traditional interpretation, the Proarticulatan body is divided into transverse articulation (division) into isomers as distinct from the transverse articulation segments in annelids and arthropods, as their individual isome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vendia
''Vendia'' is a genus of oval-shaped, Ediacaran fossils ranging from 4.5 to 12.5 mm long. The body is completely segmented into isomers, which are arranged alternately in two rows longitudinal to the axis of the body. The larger isomers cover the smaller ones externally but the posterior ends of all the isomers remain free. The transverse elements decrease in size from anterior to posterior and are all inclined in the same direction. The fossil bears a depression along a body that is interpreted as a digestive-distributive system that consists of a simple axial tube and short lateral appendages located along the borders between the isomers. Except for the first isomer of ''Vendia rachiata'', all the isomers have one lateral appendage. The first species, ''V. sokolovi'', was originally found in a core from a Yarensk borehole in the south of Arkhangelsk Oblast of Russia in beginning of the 1960s V. V. Menner. (1963). "The Other Problematical Organic Remains". In: "Stratigrap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karakhtia
''Karakhtia nessovi'' is a species of Proarticulate from the Ediacaran period, around 555 Million Years Ago. K. nessovi is the only species in the genus ''Karakhtia''. The genus Haootia has been compared minorly to ''Karakhtia'' in the way that the fossils of ''Haootia'' superficially resemble the crumpled margins of ''Karakhtia''. See also * Vendiamorpha * Vendia * List of ediacaran genera This is a list of all described Ediacaran genera, including the Ediacaran biota. It contains 227 genera. References {{reflist, 30em * Ediacaran The Ediacaran Period ( ) is a geological period that spans 96 million years from the end ... References Vendiamorpha Ediacaran life Ediacaran Proarticulata Enigmatic prehistoric animal genera Taxa described in 2004 {{Ediacaran-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ediacaran
The Ediacaran Period ( ) is a geological period that spans 96 million years from the end of the Cryogenian Period 635 million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Cambrian Period 538.8 Mya. It marks the end of the Proterozoic Eon, and the beginning of the Phanerozoic Eon. It is named after the Ediacara Hills of South Australia. The Ediacaran Period's status as an official geological period was ratified in 2004 by the International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS), making it the first new geological period declared in 120 years. Although the period takes its name from the Ediacara Hills where geologist Reg Sprigg first discovered fossils of the eponymous Ediacaran biota in 1946, the type section is located in the bed of the Enorama Creek within Brachina Gorge in the Flinders Ranges of South Australia, at . The Ediacaran marks the first appearance of widespread multicellular fauna following the end of Snowball Earth glaciation events, the so-called Ediacaran biota, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Ediacaran Genera ...
This is a list of all described Ediacaran genera, including the Ediacaran biota. It contains 227 genera. References {{reflist, 30em * Ediacaran The Ediacaran Period ( ) is a geological period that spans 96 million years from the end of the Cryogenian Period 635 million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Cambrian Period 538.8 Mya. It marks the end of the Proterozoic Eon, and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Leicester
, mottoeng = So that they may have life , established = , type = public research university , endowment = £20.0 million , budget = £326 million , chancellor = David Willetts , vice_chancellor = Nishan Canagarajah , head_label = Visitor , head = The King , academic_staff = 1,705 (2018/19) , administrative_staff = 2,205 (2018/19) , students = () , undergrad = () , postgrad = () , city = Leicester , country = England, UK , coordinates = , campus = Urban parkland , colours = , website = , logo = UniOfLeicesterLogo.svg , logo_size = 250px , affiliations = ACUAMBA EMUA EUA Sutton 30 M5 UniversitiesUniversities UK The University of Leicester ( ) is a public research university based in Leicester, England. The main campus is south of the city centre, adjacent to Victoria Park. The university's predecessor, University College, Leicester, gained university status in 1957. The university had an income of £323.1 million in 2019/20, of which £5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudofossil
Pseudofossils are inorganic objects, markings, or impressions that might be mistaken for fossils. Pseudofossils may be misleading, as some types of mineral deposits can mimic lifeforms by forming what appear to be highly detailed or organized structures. One common example is when manganese oxides crystallize with a characteristic treelike or dendritic pattern along a rock fracture. The formation of frost dendrites on a window is another common example of this crystal growth. Concretions are sometimes thought to be fossils, and occasionally one contains a fossil, but are generally not fossils themselves. Chert or flint nodules in limestone can often take forms that resemble fossils. Background Pyrite disks or spindles are sometimes mistaken for fossils of sand dollars or other forms (see marcasite). Cracks, bumps, gas bubbles, and such can be difficult to distinguish from true fossils. Specimens that cannot be attributed with certainty to either fossils or pseudofossils are treated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |