|
Veglie
Veglie ( Salentino: ) is a town and ''comune'' in the Italian province of Lecce in the Apulia region of south-east Italy. Veglie is west of Lecce and east of the sea, the Gulf of Taranto. It is bounded by the ''comuni'' of Campi Salentina, Carmiano, Leverano, Nardò, Novoli and Salice Salentino. History Veglie was founded around the 10th century. Francesco Ribezzo thinks that the name ''Veglie'' comes from pre-Messapic ''vel'', of Mediterranean origin, meaning "elevation". A tomb found in Via Novoli in 1957 dates back to Messapic times. It is displayed in a provincial museum. Economy Its main industries are agriculture, which features olive and wine Wine is an alcoholic drink typically made from Fermentation in winemaking, fermented grapes. Yeast in winemaking, Yeast consumes the sugar in the grapes and converts it to ethanol and carbon dioxide, releasing heat in the process. Different ... production and manufacturers. Ice cream is also produced in the villa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Novoli
Novoli (Salentino: ) is a town and ''comune'' in the Italian province of Lecce in the Apulia region of south-east Italy. Bounding communes * Arnesano *Campi Salentina * Carmiano *Lecce *Trepuzzi *Veglie Population History The population grew until the 1951 census, after the increasing trend, the population fell slowly mainly by emigration to other parts of Italy Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical re .... External linksOfficial site References Cities and towns in Apulia Localities of Salento {{Puglia-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leverano
Leverano (Salentino: ) is a town and ''comune'' in the province of Lecce in the southeastern part of the Apulia region of south-east Italy. It is bounded by the ''comuni'' of Arnesano, Carmiano, Copertino, Nardò and Veglie. History Leverano was severely destroyed by the Ostrogoth Totila, it was also destroyed by the Arabs in the 9th century. A tower was later built in 1220 and it protected against pirate raids. The tower is built with Norman architecture. Leverano DOC The area around Leverano produces both red, white and ''rose'' Italian DOC wine, though the region produces vastly more red wine than anything else. The grapes are limited to a harvest yield of 15 tonnes/ha. Red wines must have a finished alcohol level of at least 12% and are composed of at least 65% Negroamaro and up to 35% of the assorted blend of Malvasia, Sangiovese and Montepulciano. White wines must have a minimum alcohol level of at least 11% and be composed by at least 65% Malvasia bianca with Trebbiano ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carmiano
Carmiano (Salentino: ) is a town and ''comune'' in the province of Lecce in the Apulia region of south-east Italy. Carmiano is in the heart of the province of Lecce and Salento. It is located east of the Ionian Sea (Porto Cesareo) and west of the Adriatic Sea ( San Cataldo). Geography The commune is located in the area called the Valle della Cupa or the Cupa Valley and is situated northwest of the Salentino cape. The terrain is mainly flat and features olive crops as well as fruits and vegetables along with cattle and others. Bounding communes are Arnesano, Novoli and Veglie. History The origin of the communal name probably comes from the colour "carminium" (red). Another possibility is that it came from a name of the Roman Centurion "Carminius" who was assigned to the Roman Senate; the land at the time was in the area of Salento. References Cities and towns in Apulia Localities of Salento Carmeiano Carmeiano Carmiano ( Salentino: ) is a town and ''comune'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nardò
Nardò ( la, Neritum or ; cms, Nareton) is a town and ''comune'' in the southern Italian region of Apulia, in the Province of Lecce. Lies on a lowland area placed at south-west of its Province, its border includes part of the Ionian coast of Salento. For centuries, it had been one of the central cities of the Byzantine Empire, until 1497, when the ducal House of Acquaviva acquired it under their domain. During those years it became the main cultural hotspot of Salento, seat of many Universities, Academies, literary and philosophical studies: it was given the name of ''Nuoua Atene litterarum''. With almost 32.000 inhabitants and 190 squared kilometres of land, it is the second largest and most populated city among those in the Province, right after Lecce, and also one of the most culturally active towns of Salento. The Old Town is particularly rich with palaces, churches, chapels and other architectural details shaped accordingly to the principles of Lecce's Baroque style. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Language
Greek ( el, label=Modern Greek, Ελληνικά, Elliniká, ; grc, Ἑλληνική, Hellēnikḗ) is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages, native to Greece, Cyprus, southern Italy (Calabria and Salento), southern Albania, and other regions of the Balkans, the Black Sea coast, Asia Minor, and the Eastern Mediterranean. It has the longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning at least 3,400 years of written records. Its writing system is the Greek alphabet, which has been used for approximately 2,800 years; previously, Greek was recorded in writing systems such as Linear B and the Cypriot syllabary. The alphabet arose from the Phoenician script and was in turn the basis of the Latin, Cyrillic, Armenian, Coptic, Gothic, and many other writing systems. The Greek language holds a very important place in the history of the Western world. Beginning with the epics of Homer, ancient Greek literature includes many works of lasting impo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provinces Of Italy
The provinces of Italy ( it, province d'Italia) are the second-level administrative divisions of the Italy, Italian Republic, on an intermediate level between a municipality () and a regions of Italy, region (). Since 2015, provinces have been classified as "institutional bodies of second level". There are currently 107 institutional bodies of second level in Italy, including 80 ordinary provinces, 2 autonomous provinces, 4 regional decentralization entities, 6 free municipal consortia, and 14 Metropolitan cities of Italy, metropolitan cities, as well as the Aosta Valley region (which also exercises the powers of a province). Italian provinces (with the exception of the current Sardinian provinces) correspond to the NUTS statistical regions of Italy, NUTS 3 regions. Overview A province of the Italian Republic is composed of many municipalities (). Usually several provinces together form a region; the region of Aosta Valley is the sole exception—it is not subdivided into prov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wine
Wine is an alcoholic drink typically made from fermented grapes. Yeast consumes the sugar in the grapes and converts it to ethanol and carbon dioxide, releasing heat in the process. Different varieties of grapes and strains of yeasts are major factors in different styles of wine. These differences result from the complex interactions between the biochemical development of the grape, the reactions involved in fermentation, the grape's growing environment (terroir), and the wine production process. Many countries enact legal appellations intended to define styles and qualities of wine. These typically restrict the geographical origin and permitted varieties of grapes, as well as other aspects of wine production. Wines not made from grapes involve fermentation of other crops including rice wine and other fruit wines such as plum, cherry, pomegranate, currant and elderberry. Wine has been produced for thousands of years. The earliest evidence of wine is from the Caucasus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olive
The olive, botanical name ''Olea europaea'', meaning 'European olive' in Latin, is a species of small tree or shrub in the family Oleaceae, found traditionally in the Mediterranean Basin. When in shrub form, it is known as ''Olea europaea'' 'Montra', dwarf olive, or little olive. The species is cultivated in all the countries of the Mediterranean, as well as in Australia, New Zealand, North and South America and South Africa. ''Olea europaea'' is the type species for the genus ''Olea''. The olive's fruit, also called an "olive", is of major agricultural importance in the Mediterranean region as the source of olive oil; it is one of the core ingredients in Mediterranean cuisine. The tree and its fruit give their name to the plant family, which also includes species such as lilac, jasmine, forsythia, and the true ash tree. Thousands of cultivars of the olive tree are known. Olive cultivars may be used primarily for oil, eating, or both. Olives cultivated for consumption ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
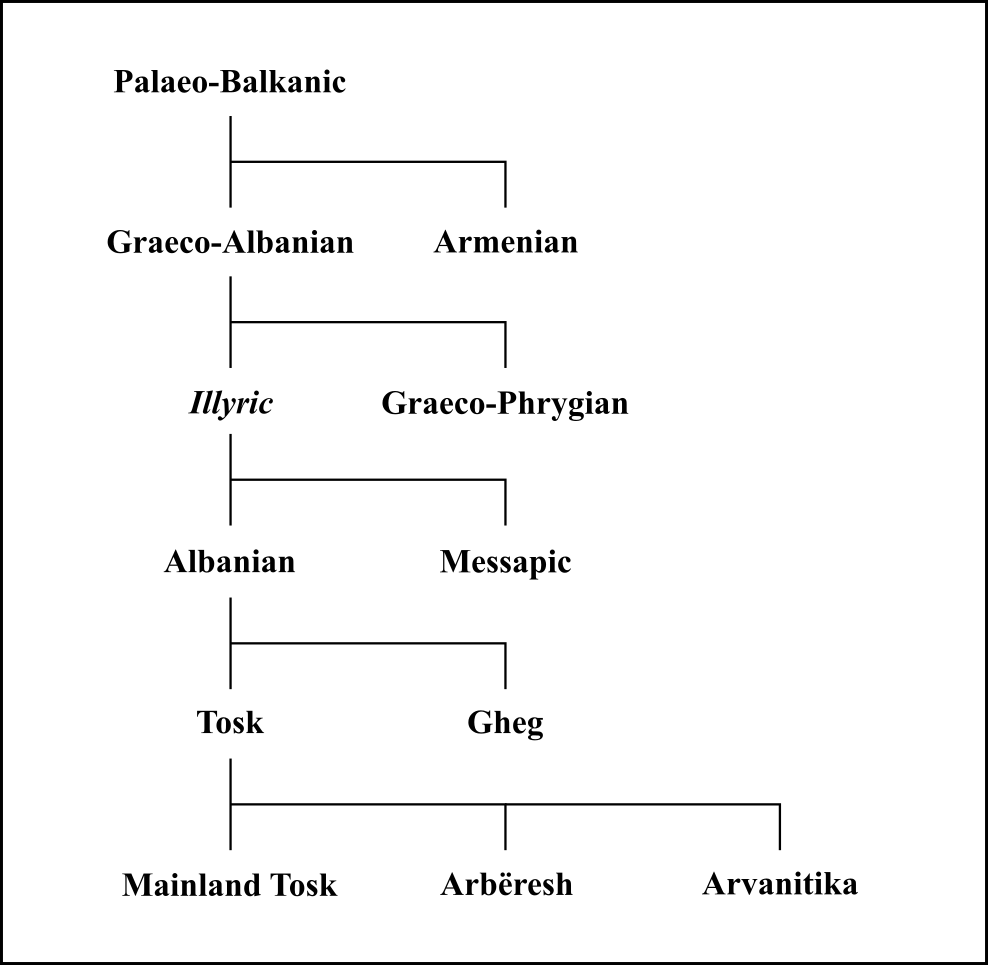
Messapic
Messapic (; also known as Messapian; or as Iapygian) is an extinct Indo-European language of the southeastern Italian Peninsula, once spoken in Apulia by the Iapygian peoples of the region: the ''Calabri'' and ''Salentini'' (known collectively as the Messapii), the Peucetians and the Daunians. Messapic was the pre-Roman, non- Italic language of Apulia. It has been preserved in about 600 inscriptions written in an alphabet derived from a Western Greek model and dating from the mid-6th to at least the 2nd century BC, when it went extinct following the Roman conquest of the region. Name The term 'Messapic' or 'Messapian' is traditionally used to refer to a group of languages spoken by the Iapygians, a "relatively homogeneous linguistic community" of non- Italic-speaking tribes (Messapians, Peucetians and Daunians) dwelling in the region of Apulia before the Roman conquest. However, some scholars have argued that the term 'Iapygian languages' should be preferred for referring to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francesco Ribezzo
Francesco, the Italian (and original) version of the personal name "Francis", is the most common given name among males in Italy. Notable persons with that name include: People with the given name Francesco * Francesco I (other), several people * Francesco Barbaro (other), several people * Francesco Bernardi (other), several people *Francesco di Giorgio Martini (1439-1501), Italian architect, engineer and painter * Francesco Berni (1497–1536), Italian writer * Francesco Canova da Milano (1497–1543), Italian lutenist and composer * Francesco Primaticcio (1504–1570), Italian painter, architect, and sculptor * Francesco Albani (1578–1660), Italian painter * Francesco Borromini (1599–1667), Swiss sculptor and architect * Francesco Cavalli (1602–1676), Italian composer * Francesco Maria Grimaldi (1618–1663), Italian mathematician and physicist * Francesco Bianchini (1662–1729), Italian philosopher and scientist * Francesco Galli Bibiena (1659 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulf Of Taranto
The Gulf of Taranto ( it, Golfo di Taranto; Tarantino: ; la, Sinus Tarentinus) is a gulf of the Ionian Sea, in Southern Italy. The Gulf of Taranto is almost square, long and wide, making it the largest gulf in Italy, and it is delimited by the capes Santa Maria di Leuca (to the east, in Apulia) and Colonna (the ancient ''Lacinium'', to the west, in Calabria), encompassed by the three regions of Apulia, Basilicata and Calabria. The most important rivers are the Basento, the Sinni, and the Agri. The main cities on the gulf are Taranto and Gallipoli. Also the Greek colonies (Magna Graecia) of Kroton, Heraclea, Thurii, and Sybaris were founded on the Gulf of Taranto. Italy claims the whole gulf as national waters, thus closed to international traffic. This position, which is similar to that of Libya on the Gulf of Sidra, is not recognized by some other countries, such as the United States and the United Kingdom The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lecce
Lecce ( ); el, label=Griko, Luppìu, script=Latn; la, Lupiae; grc, Λουπίαι, translit=Loupíai), group=pron is a historic city of 95,766 inhabitants (2015) in southern Italy. It is the capital of the province of Lecce, the province of second-highest population in the region of Apulia, as well as one of that region's most important cities. It is the main city of the Salentine Peninsula, a sub-peninsula at the heel of the Italian Peninsula, and is over 2,000 years old. Because of the rich Baroque architectural monuments found in the city, Lecce is commonly nicknamed "The Florence of the South". In terms of industry, the "Lecce stone"—a particular kind of limestone—is one of the city's main exports, because it is very soft and workable, thus suitable for sculptures. Lecce is also an important agricultural centre, chiefly for its olive oil and wine production, as well as an industrial centre specializing in ceramic production. Lecce is home to the University of S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |