|
Vautrin Lud
Vautrin is a character from the novels of French writer Honoré de Balzac in the '' La Comédie humaine'' series. His real name is Jacques Collin . He appears in the novels '' Le Père Goriot'' (Father Goriot, 1834/35) under the name Vautrin, and in '' Illusions perdues'' (Lost illusions, 1837–1843) and '' Splendeurs et misères des courtisanes'' (Scenes from a Courtesan's Life, 1838–1844), the sequel of ''Illusions perdues'', under the name of Abbé Carlos Herrera. In prison, he got the nickname "Trompe-la-Mort" ("Dodgedeath" or "Cheats-Death"), because he managed to avoid the death sentence repeatedly. Background By the time the ''Comédie humaine'' series begins, Jacques Collin is an escaped convict and criminal mastermind fleeing from the police. The character first appears in the La Comédie humaine series using the name of Vautrin, so he is usually referred to in literary criticism under this name. Balzac was inspired to the character by Eugène François Vidocq ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canon (fiction)
In fiction, canon is the material accepted as officially part of the story in an individual universe of that story by its fan base. It is often contrasted with, or used as the basis for, works of fan fiction. The alternative terms mythology, timeline, universe and continuity are often used, with the first of these being used especially to refer to a richly detailed fictional canon requiring a large degree of suspension of disbelief (e.g. an entire imaginary world and history), while the latter two typically refer to a single arc where all events are directly connected chronologically. Other times, the word can mean "to be acknowledged by the creator(s)". Origin The use of the word "canon" originated in reference to a set of texts derived from Biblical canon, the set of books regarded as scripture, as contrasted with non-canonical Apocrypha. The term was first used by analogy in the context of fiction to refer to the Sherlock Holmes stories and novels, written by Sir Arthur Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Théâtre Récamier
The théâtre Récamier was a Parisian Theater (building), theatre located at 3 rue Récamier in the 7th arrondissement of Paris, inaugurated in 1908 and closed in 1978. History Originally, it was an entertainment venue built by Charles Blondel for the Ligue de l'enseignement on the location of the convent chapel of the Abbaye-aux-Bois. From October 1959 to May 1961, the théâtre Récamier serves as second room of the Théâtre national populaire, TNP directed by Jean Vilar and located at palais de Chaillot. In December 1965, Louis Aragon set up there the soirée " Six poètes et une musique de maintenant " (Six poets and a music of our time) in order to introduce new poets (Jacques Garelli, Pierre Lartigue, Jacques Roubaud, André Libérati, Maurice Régnaut and Bernard Vargaftig). After the May 1968 events in France, the venue housed the Jean-Louis Barrault, compagnie Renaud-Barrault expelled from the Théâtre de l'Odéon. This troupe stayed in the place until 1975 when A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
André Charpak
André Charpak (4 September 1928 – 23 June 2006) was a Polish-born French actor, dialoguist, film director and screenwriter. A brother of the physicist Georges Charpak"La Vie à fil tendu", Georges Charpak (with D. Saudinos), , 1993 he was an alumnus of the prestigious Lycée Henri-IV where he earned his Baccalauréat. Filmography ;Director and screenwriter * 1964: ''Mayeux le bossu'' (short film) with Jacques Dufilho * 1964 : ''La Vie normale'' * 1967: '' Le Crime de David Levinstein'' * 1970: ''La Provocation'' * 1973: ''William Conrad'' (téléfilm) with Pierre Boulle ;Actor * 1958 : ''En bordée'' by Pierre Chevalier * 1961: '' Sur la Piste...'' (''Les Cinq Dernières Minutes'', n°19), by Claude Loursais * 1962: '' Paludi'' (telefilm) * 1965: '' La Dame de pique'' by Léonard Keigel * 1967 : '' Le Crime de David Levinstein'' * 1970 : ''La Provocation'' with Jean Marais * 1973 : ''William Conrad'' (telefilm) * 1973 : ''Le Feu sous la neige'' (telefilm) * 1973: '' L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Le Contrat De Mariage
''Le Contrat de mariage'' (English: ''A Marriage Contract'' or ''A Marriage Settlement'') is an 1835 novel by French French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to: * Something of, from, or related to France ** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents ** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ... author Honoré de Balzac (1799–1850) and included in the ''Scènes de la vie privée'' section of his novel sequence '' La Comédie humaine''. Set in Bordeaux, it describes the marriage of a Parisian gentleman, Paul de Manerville, to the beautiful but spoiled Spanish heiress, Natalie Evangelista. Plot summary Paul de Manerville is a gentleman born of wealth and nobility who decides, over the objections of his worldly friend de Marsay, to give up his elegant bachelor's life and get married at the age of twenty-seven. He falls in love with a beautiful girl named Natalie Evangelista, the daughter of a proud Spanis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Cousine Bette
''La Cousine Bette'' (, ''Cousin Bette'') is an 1846 novel by French author Honoré de Balzac. Set in mid-19th-century Paris, it tells the story of an unmarried middle-aged woman who plots the destruction of her extended family. Bette works with Valérie Marneffe, an unhappily married young lady, to seduce and torment a series of men. One of these is Baron Hector Hulot, husband to Bette's cousin Adeline. He sacrifices his family's fortune and good name to please Valérie, who leaves him for a well-off merchant named Crevel. The book is part of the ''Scènes de la vie parisienne'' section of Balzac's novel sequence ''La Comédie humaine'' ("The Human Comedy"). In the 1840s, a serial format is known as the '' roman-feuilleton'' was highly popular in France, and the most acclaimed expression of it was the socialist writing of Eugène Sue. Balzac wanted to challenge Sue's supremacy, and prove himself the most capable ''feuilleton'' author in France. Writing quickly and with intense ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guillotine
A guillotine is an apparatus designed for efficiently carrying out executions by beheading. The device consists of a tall, upright frame with a weighted and angled blade suspended at the top. The condemned person is secured with stocks at the bottom of the frame, positioning the neck directly below the blade. The blade is then released, swiftly and forcefully decapitating the victim with a single, clean pass so that the head falls into a basket or other receptacle below. The guillotine is best known for its use in France, particularly during the French Revolution, where the revolution's supporters celebrated it as the people's avenger and the revolution's opponents vilified it as the pre-eminent symbol of the violence of the Reign of Terror. While the name "guillotine" itself dates from this period, similar devices had been in use elsewhere in Europe over several centuries. The use of an oblique blade and the stocks set this type of guillotine apart from others. The display o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Villain
A villain (also known as a "black hat" or "bad guy"; the feminine form is villainess) is a stock character, whether based on a historical narrative or one of literary fiction. ''Random House Unabridged Dictionary'' defines such a character as "a cruelly malicious person who is involved in or devoted to wickedness or crime; scoundrel; or a character in a play, novel, or the like, who constitutes an important evil agency in the plot". The antonym of a villain is a hero. The villain's structural purpose is to serve as the opposition of the hero character and their motives or evil actions drive a plot along. In contrast to the hero, who is defined by feats of ingenuity and bravery and the pursuit of justice and the greater good, a villain is often defined by their acts of selfishness, evilness, arrogance, cruelty, and cunning, displaying immoral behavior that can oppose or pervert justice. Etymology The term ''villain'' first came into English from the Anglo-French and Old ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platonic Love
Platonic love (often lowercased as platonic love) is a type of love in which sexual desire or romantic features are nonexistent or has been suppressed or sublimated, but it means more than simple friendship. The term is derived from the name of Greek philosopher Plato, though the philosopher never used the term himself. Platonic love, as devised by Plato, concerns rising through levels of closeness to wisdom and true beauty, from carnal attraction to individual bodies to attraction to souls, and eventually, union with the truth. Platonic love is contrasted with romantic love. Classical philosophical interpretation Platonic love is examined in Plato's dialogue, the ''Symposium'', which has as its topic the subject of love, or more generally the subject of Eros. It explains the possibilities of how the feeling of love began and how it has evolved, both sexually and non-sexually, and defines genuine platonic love as inspiring a person's mind and soul and directing their att ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faust
Faust is the protagonist of a classic German legend based on the historical Johann Georg Faust ( 1480–1540). The erudite Faust is highly successful yet dissatisfied with his life, which leads him to make a pact with the Devil at a crossroads, exchanging his soul for unlimited knowledge and worldly pleasures. The Faust legend has been the basis for many literary, artistic, cinematic, and musical works that have reinterpreted it through the ages. "Faust" and the adjective "Faustian" imply sacrificing spiritual values for power, knowledge, or material gain. The Faust of early books—as well as the ballads, dramas, movies, and puppet-plays which grew out of them—is irrevocably damned because he prefers human knowledge over divine knowledge: "he laid the Holy Scriptures behind the door and under the bench, refused to be called doctor of theology, but preferred to be styled doctor of medicine". Plays and comic puppet theatre loosely based on this legend were popular throughout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Devil
A devil is the personification of evil as it is conceived in various cultures and religious traditions. It is seen as the objectification of a hostile and destructive force. Jeffrey Burton Russell states that the different conceptions of the devil can be summed up as 1) a principle of evil independent from God, 2) an aspect of God, 3) a created being turning evil (a ''fallen angel''), and 4) a symbol of human evil. Each tradition, culture, and religion with a devil in its mythos offers a different lens on manifestations of evil.Jeffrey Burton Russell, ''The Devil: Perceptions of Evil from Antiquity to Primitive Christianity'', Cornell University Press 1987 , pp. 41–75 The history of these perspectives intertwines with theology, mythology, psychiatry, art, and literature developing independently within each of the traditions. It occurs historically in many contexts and cultures, and is given many different names— Satan, Lucifer, Beelzebub, Mephistopheles, Iblis—and at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
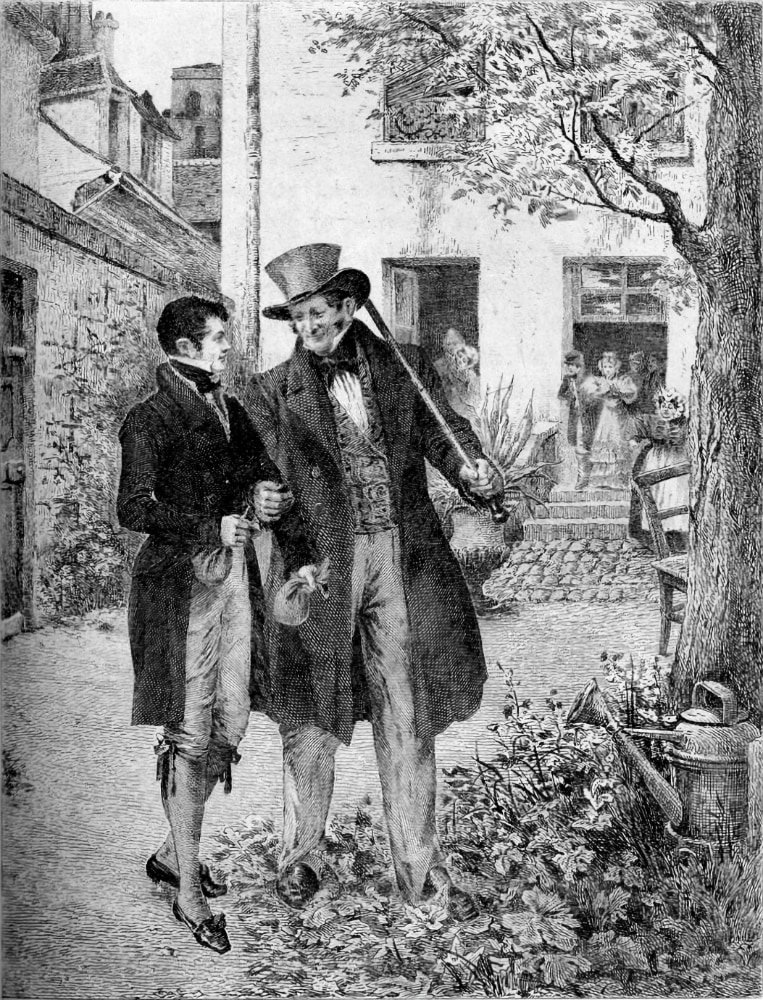



.png)
