|
Vasography
Vasography is an X-ray study of the vas deferens to see if there is blockage, oftentimes in the context of male infertility. An incision is made in the scrotum, contrast is injected in the vas deferens, and X-rays are taken from different angles. Thus, it is an invasive procedure and carries risk of iatrogenic scarring and obstruction of the vas. Vasography has traditionally been considered the gold standard imaging modality for evaluating the seminal tract patency. To avoid performing an extra operation, vasography is encouraged to be done at the time of correction of the obstruction, and thus should not be done as an isolated outpatient procedure. History Vasography was first described by Belfield in 1913, where a vasotomy was initially done and the vas deferens was subsequently intubated. After almost 40 years of being overlooked, Boreau revived the procedure in the 1950s. Then, vasography was somewhat overused for various fertility disorders and other diseases such as tube ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasography 2
Vasography is an X-ray study of the vas deferens to see if there is blockage, oftentimes in the context of male infertility. An incision is made in the scrotum, contrast is injected in the vas deferens, and X-rays are taken from different angles. Thus, it is an invasive procedure and carries risk of iatrogenic scarring and obstruction of the vas. Vasography has traditionally been considered the gold standard imaging modality for evaluating the seminal tract patency. To avoid performing an extra operation, vasography is encouraged to be done at the time of correction of the obstruction, and thus should not be done as an isolated outpatient procedure. History Vasography was first described by Belfield in 1913, where a vasotomy was initially done and the vas deferens was subsequently intubated. After almost 40 years of being overlooked, Boreau revived the procedure in the 1950s. Then, vasography was somewhat overused for various fertility disorders and other diseases such as tube ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oligospermia
Terms oligospermia, oligozoospermia, and low sperm count refer to semen with a low concentration of sperm and is a common finding in male infertility. Often semen with a decreased sperm concentration may also show significant abnormalities in sperm morphology and motility (technically oligoasthenoteratozoospermia). There has been interest in replacing the descriptive terms used in semen analysis with more quantitative information. Diagnosis The diagnosis of oligozoospermia is based on one low count in a semen analysis performed on two occasions. For many decades sperm concentrations of less than 20 million sperm/ml were considered low or oligospermic, recently, however, the WHO reassessed sperm criteria and established a lower reference point, less than 15 million sperm/ml, consistent with the 5th percentile for fertile men. Sperm concentrations fluctuate and oligospermia may be temporary or permanent. Sources usually classify oligospermia in 3 classes: *Mild: concentrations 10 mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azoospermia
Azoospermia is the medical condition of a man whose semen contains no sperm. It is associated with male infertility, but many forms are amenable to medical treatment. In humans, azoospermia affects about 1% of the male population and may be seen in up to 20% of male infertility situations in Canada. In a non-pathological context, azoospermia is also the intended result of a successful vasectomy. Classification Azoospermia can be classified into three major types as listed. Many conditions listed may also cause various degrees of oligospermia rather than azoospermia. Pretesticular and testicular azoospermia are known as non-obstructive azoospermia, whereas post-testicular azoospermia is considered obstructive. Pretesticular Pretesticular azoospermia is characterized by inadequate stimulation of otherwise normal testicles and genital tract. Typically, follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) levels are low (hypogonadotropic) commensurate with inadequate stimulation of the testes to prod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compressive Fibrolipomatosis
In continuum mechanics, stress is a physical quantity. It is a quantity that describes the magnitude of forces that cause deformation. Stress is defined as ''force per unit area''. When an object is pulled apart by a force it will cause elongation which is also known as deformation, like the stretching of an elastic band, it is called tensile stress. But, when the forces result in the compression of an object, it is called compressive stress. It results when forces like tension or compression act on a body. The greater this force and the smaller the cross-sectional area of the body on which it acts, the greater the stress. Therefore, stress is measured in newton per square meter (N/m2) or pascal (Pa). Stress expresses the internal forces that neighbouring particles of a continuous material exert on each other, while strain is the measure of the deformation of the material. For example, when a solid vertical bar is supporting an overhead weight, each particle in the bar pushe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hematoma
A hematoma, also spelled haematoma, or blood suffusion is a localized bleeding outside of blood vessels, due to either disease or trauma including injury or surgery and may involve blood continuing to seep from broken capillary, capillaries. A hematoma is benign and is initially in liquid form spread among the tissues including in sacs between tissues where it may coagulate and solidify before blood is reabsorbed into blood vessels. An ecchymosis is a hematoma of the skin larger than 10 mm. They may occur among and or within many areas such as skin and other organs, connective tissues, bone, joints and muscle. A collection of blood (or even a hemorrhage) may be aggravated by anticoagulant medication (blood thinner). Blood seepage and collection of blood may occur if heparin is given via an Intramuscular injection, intramuscular route; to avoid this, heparin must be given intravenously or subcutaneous injection, subcutaneously. Signs and symptoms Some hematomas are visible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stenosis
A stenosis (from Ancient Greek στενός, "narrow") is an abnormal narrowing in a blood vessel or other tubular organ or structure such as foramina and canals. It is also sometimes called a stricture (as in urethral stricture). ''Stricture'' as a term is usually used when narrowing is caused by contraction of smooth muscle (e.g. achalasia, prinzmetal angina); ''stenosis'' is usually used when narrowing is caused by lesion that reduces the space of lumen (e.g. atherosclerosis). The term coarctation is another synonym, but is commonly used only in the context of aortic coarctation. Restenosis is the recurrence of stenosis after a procedure. Types The resulting syndrome depends on the structure affected. Examples of vascular stenotic lesions include: * Intermittent claudication (peripheral artery stenosis) * Angina ( coronary artery stenosis) * Carotid artery stenosis which predispose to (strokes and transient ischaemic episodes) * Renal artery stenosis The types of sten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibody
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of the pathogen, called an antigen. Each tip of the "Y" of an antibody contains a paratope (analogous to a lock) that is specific for one particular epitope (analogous to a key) on an antigen, allowing these two structures to bind together with precision. Using this binding mechanism, an antibody can ''tag'' a microbe or an infected cell for attack by other parts of the immune system, or can neutralize it directly (for example, by blocking a part of a virus that is essential for its invasion). To allow the immune system to recognize millions of different antigens, the antigen-binding sites at both tips of the antibody come in an equally wide variety. In contrast, the remainder of the antibody is relatively constant. It only occurs in a few varia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spermatid
The spermatid is the haploid male gametid that results from division of secondary spermatocytes. As a result of meiosis, each spermatid contains only half of the genetic material present in the original primary spermatocyte. Spermatids are connected by cytoplasmic material and have superfluous cytoplasmic material around their nuclei. When formed, ''early round spermatids'' must undergo further maturational events to develop into spermatozoa, a process termed spermiogenesis (also termed ''spermeteliosis''). The spermatids begin to grow a living thread, develop a thickened mid-piece where the mitochondria become localised, and form an acrosome. Spermatid DNA also undergoes packaging, becoming highly condensed. The DNA is packaged firstly with specific nuclear basic proteins, which are subsequently replaced with protamines during spermatid elongation. The resultant tightly packed chromatin is transcriptionally inactive. In 2016 scientists at Nanjing Medical University clai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
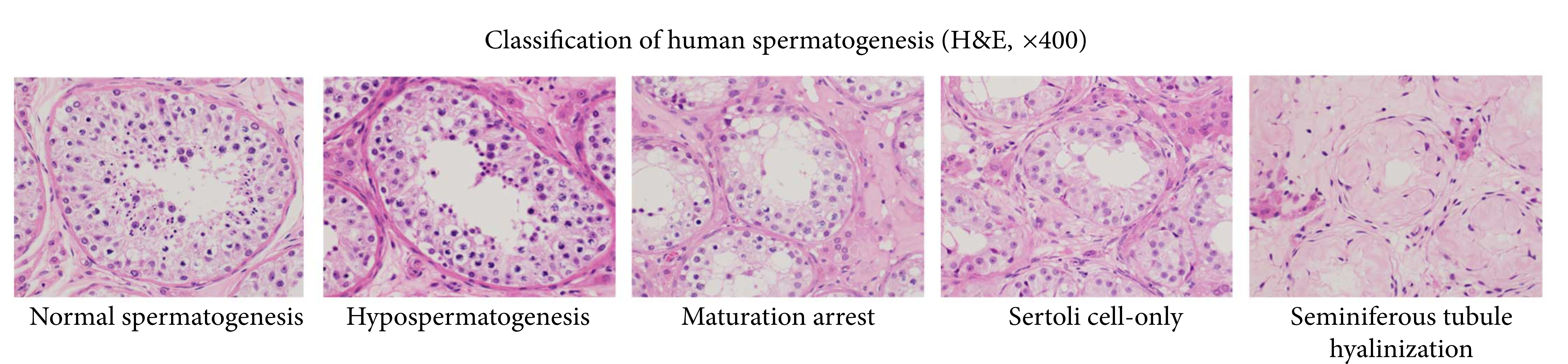
Spermatogenesis
Spermatogenesis is the process by which haploid spermatozoa develop from germ cells in the seminiferous tubules of the testis. This process starts with the mitotic division of the stem cells located close to the basement membrane of the tubules. These cells are called spermatogonial stem cells. The mitotic division of these produces two types of cells. Type A cells replenish the stem cells, and type B cells differentiate into primary spermatocytes. The primary spermatocyte divides meiotically (Meiosis I) into two secondary spermatocytes; each secondary spermatocyte divides into two equal haploid spermatids by Meiosis II. The spermatids are transformed into spermatozoa (sperm) by the process of spermiogenesis. These develop into mature spermatozoa, also known as sperm cells. Thus, the primary spermatocyte gives rise to two cells, the secondary spermatocytes, and the two secondary spermatocytes by their subdivision produce four spermatozoa and four haploid cells. Spermatozoa are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiologist. The process involves extraction of sample cells or tissues for examination to determine the presence or extent of a disease. The tissue is then fixed, dehydrated, embedded, sectioned, stained and mounted before it is generally examined under a microscope by a pathologist; it may also be analyzed chemically. When an entire lump or suspicious area is removed, the procedure is called an excisional biopsy. An incisional biopsy or core biopsy samples a portion of the abnormal tissue without attempting to remove the entire lesion or tumor. When a sample of tissue or fluid is removed with a needle in such a way that cells are removed without preserving the histological architecture of the tissue cells, the procedure is called a needle aspiration biopsy. Biopsies are most commonly performed for insight into possible cancerous or inflammatory conditions. History T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Testis
A testicle or testis (plural testes) is the male reproductive gland or gonad in all bilaterians, including humans. It is homologous to the female ovary. The functions of the testes are to produce both sperm and androgens, primarily testosterone. Testosterone release is controlled by the anterior pituitary luteinizing hormone, whereas sperm production is controlled both by the anterior pituitary follicle-stimulating hormone and gonadal testosterone. Structure Appearance Males have two testicles of similar size contained within the scrotum, which is an extension of the abdominal wall. Scrotal asymmetry, in which one testicle extends farther down into the scrotum than the other, is common. This is because of the differences in the vasculature's anatomy. For 85% of men, the right testis hangs lower than the left one. Measurement and volume The volume of the testicle can be estimated by palpating it and comparing it to ellipsoids of known sizes. Another method is to use caliper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemospermia
Hematospermia (also known as haematospermia, hemospermia, or haemospermia) is the presence of blood in ejaculation. It is most often a benign symptom. Among men age 40 or older, hematospermia is a slight predictor of cancer, typically prostate cancer. No specific cause is found in up to 70% of cases. Cause Though haematospermia may cause considerable distress to patients, it is often a benign and self-limiting condition caused by infections, particularly in younger patients. An isolated episode is usually considered benign and not likely to be associated with malignancy. Recurrent haematospermia may indicate a more serious underlying pathology particularly in patients over 40 years of age. Infection and inflammation Infection or inflammation is considered the most common cause of the condition. Implicated pathogens include; Gram-negative bacteria (often ''E. coli''), gonococci, '' T. pallidum'', ''C. trachomatis'', ''N. gonorrhoeae,'' echinococcus (rarely), HSV type 1 or 2, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |