|
Vasanti N. Bhat-Nayak
Vasanti N. Bhat-Nayak was a mathematician whose research concerned balanced incomplete block designs, bivariegated graphs, graceful graphs, graph equations and frequency partitions. She earned a Ph.D. from the University of Mumbai in 1970 with the dissertation ''Some New Results in PBIBD Designs and Combinatorics''. S. S. Shrikhande Sharadchandra Shankar Shrikhande (19 October 1917 – 21 April 2020) was an Indian mathematician with notable achievements in combinatorial mathematics. He was notable for his breakthrough work along with R. C. Bose and E. T. Parker in their di ... was her advisor. After completing her doctorate, she remained on the faculty at the university, and eventually served as department head. References Indian combinatorialists University of Mumbai alumni Academic staff of the University of Mumbai Scientists from Mumbai Konkani people 20th-century Indian mathematicians Indian women mathematicians 20th-century Indian women scientists 20t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Mumbai
The University of Mumbai is a collegiate university, collegiate, State university (India), state-owned, Public university, public research university in Mumbai. The University of Mumbai is one of the largest universities in the world. , the university had 711 affiliated colleges. Ratan Tata is the appointed head of the advisory council. History In accordance with "Wood's despatch", drafted by Charles Wood, 1st Viscount Halifax, Sir Charles Wood in 1854, the University of Bombay was established in 1857 after the presentation of a petition from the Bombay Association to the British colonial government in India. The University of Mumbai was modelled on similar universities in the United Kingdom, specifically the University of London. The first departments established were the Faculty of Arts at Elphinstone College in 1835 and the Faculty of Medicine at Grant Medical College in 1845. Both colleges existed before the university was founded and surrendered their degree-granting priv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balanced Incomplete Block Design
In combinatorial mathematics, a block design is an incidence structure consisting of a set together with a family of subsets known as ''blocks'', chosen such that frequency of the elements satisfies certain conditions making the collection of blocks exhibit symmetry (balance). They have applications in many areas, including experimental design, finite geometry, physical chemistry, software testing, cryptography, and algebraic geometry. Without further specifications the term ''block design'' usually refers to a balanced incomplete block design (BIBD), specifically (and also synonymously) a 2-design, which has been the most intensely studied type historically due to its application in the design of experiments. Its generalization is known as a t-design. Overview A design is said to be ''balanced'' (up to ''t'') if all ''t''-subsets of the original set occur in equally many (i.e., ''λ'') blocks. When ''t'' is unspecified, it can usually be assumed to be 2, which means that ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bivariegated Graph
In graph theory, a bivariegated graph is a graph whose vertex set can be partitioned into two equal parts such that each vertex is adjacent to exactly one vertex from the other set not containing it.... In a bivarigated graph ''G'' with 2''n'' vertices, there exists a set of ''n'' independent edges such that no odd number of them lie on a cycle of ''G''. Examples The Petersen graph, shown below, is a bivariegated graph: if one partitions it into an outer pentagon and an inner five-point star, each vertex on one side of the partition has exactly one neighbor on the other side of the partition. More generally, the same is true for any generalized Petersen graph formed by connecting an outer polygon and an inner star with the same number of points; for instance, this applies to the Möbius–Kantor graph and the Desargues graph. Any hypercube graph, such as the four-dimensional hypercube shown below, is also bivariegated. However, the graph shown below is not bivariegated. Whate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graceful Graph
In graph theory, a graceful labeling of a graph with edges is a labeling of its vertices with some subset of the integers from 0 to inclusive, such that no two vertices share a label, and each edge is uniquely identified by the absolute difference between its endpoints, such that this magnitude lies between 1 and inclusive. Virginia Vassilevska, "Coding and Graceful Labeling of trees." SURF 2001PostScript/ref> A graph which admits a graceful labeling is called a graceful graph. The name "graceful labeling" is due to Solomon W. Golomb; this type of labeling was originally given the name β-labeling by Alexander Rosa in a 1967 paper on graph labelings.. A major conjecture in graph theory is the graceful tree conjecture or Ringel–Kotzig conjecture, named after Gerhard Ringel and Anton Kotzig, and sometimes abbreviated GTC. It hypothesizes that all trees are graceful. It is still an open conjecture, although a related but weaker conjecture known as "Ringel's conjecture" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graph Equations
In graph theory, Graph equations are equations in which the unknowns are graphs. One of the central questions of graph theory concerns the notion of isomorphism. We ask: When are two graphs the same? (i.e., graph isomorphism) The graphs in question may be expressed differently in terms of graph equations. What are the graphs ( solutions) ''G'' and ''H'' such that the line graph of ''G'' is same as the total graph of ''H''? (What are ''G'' and ''H'' such that ''L''(''G'') = '' T''(''H'') ?). For example, ''G'' = ''K''3, and ''H'' = ''K''2 are the solutions of the graph equation ''L''(''K''3) = ''T''(''K''2) and ''G'' = ''K''4, and ''H'' = ''K''3 are the solutions of the graph equation ''L''(''K''4) = ''T''(''K''3). Image: Complete graph K2.svg, :::K_2 Image: Complete graph K3.svg, :::K_3 Image: Complete graph K4.svg, :::K_4 Note that ''T''(''K''3) is a 4- regular graph on 6 vertices. Selected publications * Graph equations for line graphs and total graphs, DM Cvet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frequency Partition
In graph theory, a discipline within mathematics, the frequency partition of a graph ( simple graph) is a partition of its vertices grouped by their degree. For example, the degree sequence of the left-hand graph below is (3, 3, 3, 2, 2, 1) and its frequency partition is 6 = 3 + 2 + 1. This indicates that it has 3 vertices with some degree, 2 vertices with some other degree, and 1 vertex with a third degree. The degree sequence of the bipartite graph in the middle below is (3, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 1, 1, 1) and its frequency partition is 9 = 5 + 3 + 1. The degree sequence of the right-hand graph below is (3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 2) and its frequency partition is 7 = 6 + 1. Image:6n-graf.svg, A graph with frequency partition 6 = 3 + 2 + 1. Image:Simple-bipartite-graph.svg, A bipartite graph with frequency partition 9 = 5 + 3 + 1. Image:Nonplanar no subgraph K 3 3.svg, A graph with frequency partition 7 = 6 + 1. In general, there are many non-isomorphic graphs with a given frequency partition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Combinatorialists
Indian or Indians may refer to: Peoples South Asia * Indian people, people of Indian nationality, or people who have an Indian ancestor ** Non-resident Indian, a citizen of India who has temporarily emigrated to another country * South Asian ethnic groups, referring to people of the Indian subcontinent, as well as the greater South Asia region prior to the 1947 partition of India * Anglo-Indians, people with mixed Indian and British ancestry, or people of British descent born or living in the Indian subcontinent * East Indians, a Christian community in India Europe * British Indians, British people of Indian origin The Americas * Indo-Canadians, Canadian people of Indian origin * Indian Americans, American people of Indian origin * Indigenous peoples of the Americas, the pre-Columbian inhabitants of the Americas and their descendants ** Plains Indians, the common name for the Native Americans who lived on the Great Plains of North America ** Native Americans in the Uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Mumbai Alumni
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United States, the designation is reserved for colleges that have a graduate school. The word ''university'' is derived from the Latin ''universitas magistrorum et scholarium'', which roughly means "community of teachers and scholars". The first universities were created in Europe by Catholic Church monks. The University of Bologna (''Università di Bologna''), founded in 1088, is the first university in the sense of: *Being a high degree-awarding institute. *Having independence from the ecclesiastic schools, although conducted by both clergy and non-clergy. *Using the word ''universitas'' (which was coined at its foundation). *Issuing secular and non-secular degrees: grammar, rhetoric, logic, theology, canon law, notarial law.Hunt Janin: "The university i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academic Staff Of The University Of Mumbai
An academy ( Attic Greek: Ἀκαδήμεια; Koine Greek Ἀκαδημία) is an institution of secondary or tertiary higher learning (and generally also research or honorary membership). The name traces back to Plato's school of philosophy, founded approximately 385 BC at Akademia, a sanctuary of Athena, the goddess of wisdom and skill, north of Athens, Greece. Etymology The word comes from the ''Academy'' in ancient Greece, which derives from the Athenian hero, '' Akademos''. Outside the city walls of Athens, the gymnasium was made famous by Plato as a center of learning. The sacred space, dedicated to the goddess of wisdom, Athena, had formerly been an olive grove, hence the expression "the groves of Academe". In these gardens, the philosopher Plato conversed with followers. Plato developed his sessions into a method of teaching philosophy and in 387 BC, established what is known today as the Old Academy. By extension, ''academia'' has come to mean the accumulatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientists From Mumbai
A scientist is a person who conducts scientific research to advance knowledge in an area of the natural sciences. In classical antiquity, there was no real ancient analog of a modern scientist. Instead, philosophers engaged in the philosophical study of nature called natural philosophy, a precursor of natural science. Though Thales (circa 624-545 BC) was arguably the first scientist for describing how cosmic events may be seen as natural, not necessarily caused by gods,Frank N. Magill''The Ancient World: Dictionary of World Biography'', Volume 1 Routledge, 2003 it was not until the 19th century that the term ''scientist'' came into regular use after it was coined by the theologian, philosopher, and historian of science William Whewell in 1833. In modern times, many scientists have advanced degrees in an area of science and pursue careers in various sectors of the economy such as academia, industry, government, and nonprofit environments.'''' History The roles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
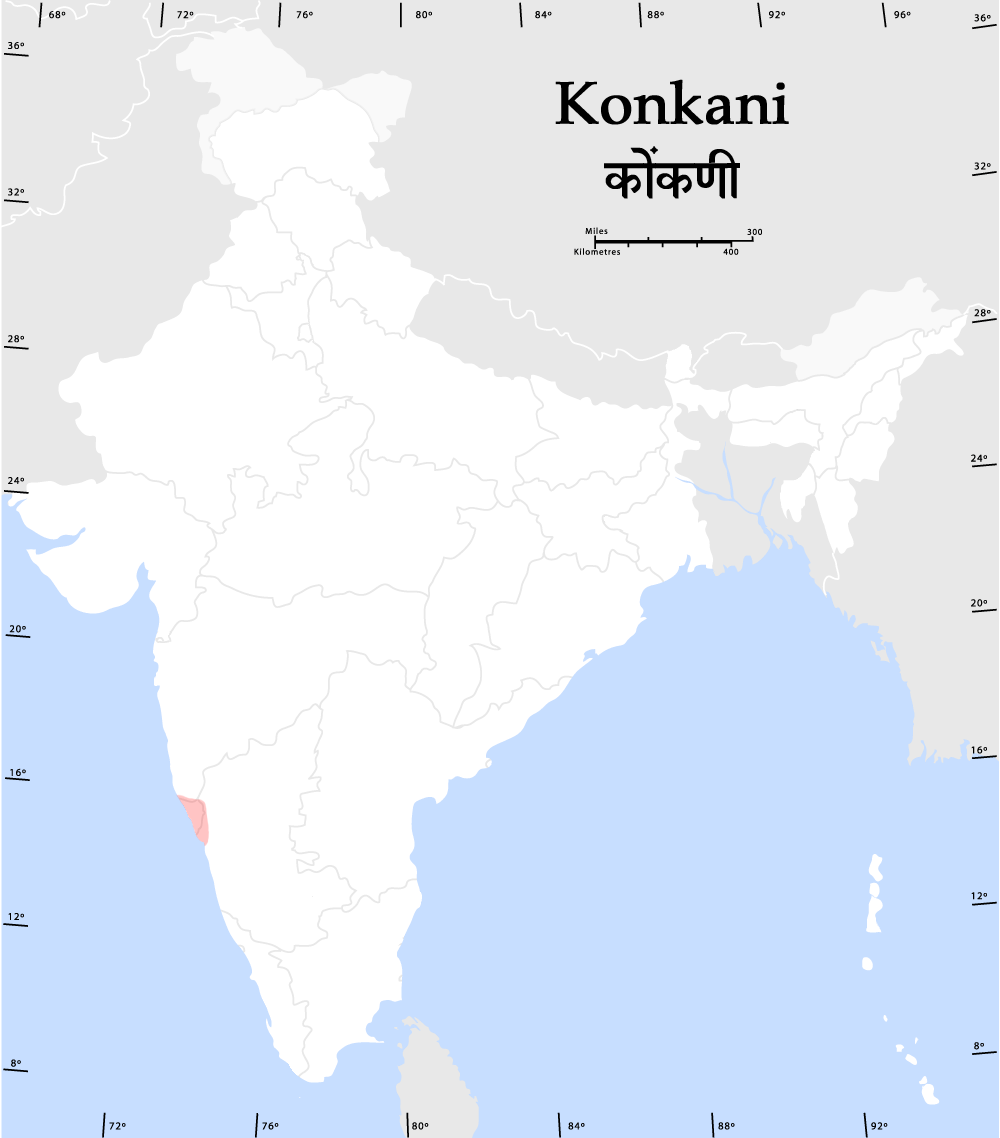
Konkani People
The Konkan people ( Konkani) Konkanis The Konkan people (Konkani language, Konkani) Konkanis The Konkan people (Konkani language, Konkani) Konkanis The Konkan people (Konkani language, Konkani) Konkanis The Konkan people (Konkani language, Konkani) Konkanis The Konkan people (Konkani language, Konkani) Konkanis The Konkan people (Konkani language, Konkani) Konkanis The Konkan people (Konkani language, Konkani) Konkanis The Konkan people (Konkani language, Konkani) Konkanis The Konkan people (Konkani language, Konkani) Konkanis The Konkan people (Konkani language, Konkani) Konkanis The Konkan people (Konkani language, Konkani) Konkanis The Konkan people (Konkani language, Konkani) Konkanis The Konkan people (Konkani language, Konkani) Konkanis The Konkan people (Konkani language, Konkani) Konkanis The Konkan people (Konkani language, Konkani) Konkanis The Konkan people ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |