|
Vartry River
The River Vartry (; ) is a river in County Wicklow, Ireland, and an important water source for the city of Dublin.Dublin on a knife-edge when it comes to water supply ''Irish Times'' March 10, 2018 Name The river first appears in 12th-century records with the name ''Fertir'' or ''Fortir''. This is believed to derive from an term meaning "fortress", perhaps referring to a at Glasnamullen. Similar placenames are found at Forther, Forthar, |
Ashford, County Wicklow
Ashford (), historically known as ''Ballymacahara'' (), is a village in County Wicklow, Ireland. It lies on the River Vartry and at the meeting of the R772, R763 and R764 regional roads. The village was formerly on the main Dublin–Wexford route, the N11, but was bypassed by the new N11 in 2004. As of the 2016 census, the village had a population of 1,425 people. Geography Ashford is about north of Rathnew, which is on the outskirts of the county town of Wicklow. Amenities The Mount Usher Gardens and Arboretum are located at the end of the village nearer Wicklow Town. The gardens were previously owned and operated by Madelaine Jay and the Jay family, but recently the gardens and shopping courtyard were leased to the Avoca Handweavers company, which originated in Avoca, County Wicklow, and which was owned and operated by the Pratt family for many generations, but sold to U.S. multinational corporation Aramark in 2015. There are a number of shops in the village centre, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finnegans Wake
''Finnegans Wake'' is a novel by Irish writer James Joyce. It is well known for its experimental style and reputation as one of the most difficult works of fiction in the Western canon. It has been called "a work of fiction which combines a body of fables ... with the work of analysis and deconstruction". Written in Paris over a period of seventeen years and published in 1939, ''Finnegans Wake'' was Joyce's final work. The entire book is written in a largely idiosyncratic language, which blends standard English words with neologistic portmanteau words, Irish mannerisms and puns in multiple languages to unique effect. Many critics believe the technique was Joyce's attempt to recreate the experience of sleep and dreams, reproducing the way concepts, people and places become amalgamated in dreaming. It is an attempt by Joyce to combine many of his aesthetic ideas, with references to other works and outside ideas woven into the text; Joyce declared that "Every syllable can be just ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulysses (novel)
''Ulysses'' is a Literary modernism, modernist novel by Irish literature, Irish writer James Joyce. Parts of it were first serialized in the American journal ''The Little Review'' from March 1918 to December 1920, and the entire work was published in Paris by Sylvia Beach on 2 February 1922, Joyce's 40th birthday. It is considered one of the most important works of modernist literature and has been called "a demonstration and summation of the entire movement." According to Declan Kiberd, "Before Joyce, no writer of fiction had so foregrounded the process of thinking". ''Ulysses'' chronicles the appointments and encounters of the itinerant Leopold Bloom in Dublin in the course of an ordinary day, 16 June 1904. Ulysses is the Latinisation of names, Latinised name of Odysseus, the hero of Homer's epic poem the ''Odyssey'', and the novel establishes a series of parallels between the poem and the novel, with structural correspondences between the characters and experiences of Bloom an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Joyce
James Augustine Aloysius Joyce (2 February 1882 – 13 January 1941) was an Irish novelist, poet, and literary critic. He contributed to the Modernism, modernist avant-garde movement and is regarded as one of the most influential and important writers of the 20th century. Joyce's novel ''Ulysses (novel), Ulysses'' (1922) is a landmark in which the episodes of Homer's ''Odyssey'' are paralleled in a variety of literary styles, particularly Stream of consciousness (narrative mode), stream of consciousness. Other well-known works are the short-story collection ''Dubliners'' (1914), and the novels ''A Portrait of the Artist as a Young Man'' (1916) and ''Finnegans Wake'' (1939). His other writings include three books of poetry, a play, letters, and occasional journalism. Joyce was born in Dublin into a middle-class family. He attended the Jesuit Clongowes Wood College in County Kildare, then, briefly, the Christian Brothers-run O'Connell School. Despite the chaotic family life impose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vartry Reservoir
Vartry Reservoir ( ga, Taiscumar Fheartraí) is a reservoir at Roundwood in County Wicklow, Ireland. The water is piped from Vartry to a large open service reservoir in Stillorgan in the southern suburbs of Dublin. The reservoir is operated by Irish Water. Image of Dublin City Council sign at the reservoir The original (lower) reservoir was completed in 1863 and has a capacity of 11.3 billion litres and a maximum depth of 18.3 metres. A second embankment, 3.5 km upstream, was completed in 1923 to form the upper reservoir. This has a capacity of 5.6 billion litres and a maximum depth of 13.4 metres. History The Vartry Reservoir scheme involved the partial redirection and damming of the Vartry River, the building of a series of water piping and filtering systems (and related public works) to carry freshwater to the city. Between 1862 and 1868 the lower reservoir was formed by constructing an earthen dam An embankment dam is a large artificial dam. It is typicall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roundwood
Roundwood, historically known as Tóchar ( ga, an Tóchar , meaning 'the causeway'), is a village in County Wicklow, Ireland. It was listed as having a population of 948 in the 2016 census. Geography Roundwood is located where the R755 road joins the R764 and R765. The R755 is part of the main route from Dublin to Glendalough in the Wicklow Mountains. At 238 metres above sea level, Roundwood is one of the highest villages in Ireland. Vartry Reservoir Lakes (reservoirs built in the 1860s) are close by. History Roundwood has a close association with two former Presidents of Ireland, Seán T. O'Kelly who lived locally, and Erskine Hamilton Childers, who, with other family members, is buried in Derrylossary Anglican churchyard near the village. Sport The local Gaelic football and ladies' Gaelic football club is An Tóchar GAA. Twin towns — sister cities Roundwood is twinned with the village of Spézet, in Brittany, northwestern France France (), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sand Spit
A spit or sandspit is a deposition bar or beach landform off coasts or lake shores. It develops in places where re-entrance occurs, such as at a cove's headlands, by the process of longshore drift by longshore currents. The drift occurs due to waves meeting the beach at an oblique angle, moving sediment down the beach in a zigzag pattern. This is complemented by longshore currents, which further transport sediment through the water alongside the beach. These currents are caused by the same waves that cause the drift. Hydrology and geology Where the direction of the shore inland ''re-enters'', or changes direction, for example at a headland, the longshore current spreads out or dissipates. No longer able to carry the full load, much of the sediment is dropped. This is called deposition. This submerged bar of sediment allows longshore drift or littoral drift to continue to transport sediment in the direction the waves are breaking, forming an above-water spit. Without the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N11 Road (Ireland)
The N11 road is a national primary road in Ireland, running for along the east side of Ireland from Dublin to Wexford. It passes close to Bray, Greystones, Wicklow, Arklow, Gorey, and Enniscorthy. Beyond Wexford, the route continues to Rosslare as the N25. The road forms part of European route E01. As of July 2019 the N11/M11 is of dual carriageway or motorway standard from Dublin as far as Oilgate in County Wexford. The road is a busy commuter route, being the only dual carriageway passing through the south eastern suburbs of Dublin, as well as close to the many commuter towns along the east coast as far south as Gorey. Summer Friday and Sunday evenings also see very heavy traffic as Dubliners decamp to and return from their many holiday home locations along the Co. Wicklow and Co. Wexford coastlines. Original route out of and into Dublin The N11 commenced where it met the N4 on the south end of ''O'Connell Bridge'' in Dublin city centre. The route proceeded along '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Sugar Loaf
Great Sugar Loaf () at , is the 404th–highest peak in Ireland on the Arderin scale, however, being below 600 m it does not rank on the Vandeleur-Lynam or Hewitt scales.Mountainviews, (September 2013), "A Guide to Ireland's Mountain Summits: The Vandeleur-Lynams & the Arderins", Collins Books, Cork, The mountain is in the far northeastern section of the Wicklow Mountains, in Ireland, and overlooks the village of Kilmacanogue. The profile of the mountain means it can be mistaken for a dormant volcano. It owes its distinctive shape, however, to the erosion-resistant metamorphosed deep-sea sedimentary deposit from which its quartzite composition was derived. Naming According to Irish academic Paul Tempan, the term "sugarloaf" is widely applied in Britain and Ireland to hills of conical form, in much the same way that the name pain de sucre is used in France. Tempan also notes that there is a widespread misconception that the term refers to a kind of bread, when it refers in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Wicklow
County Wicklow ( ; ga, Contae Chill Mhantáin ) is a county in Ireland. The last of the traditional 32 counties, having been formed as late as 1606, it is part of the Eastern and Midland Region and the province of Leinster. It is bordered by the Irish Sea to the east and the counties of Wexford to the south, Carlow to the southwest, Kildare to the west, and South Dublin and Dún Laoghaire–Rathdown to the north. Wicklow is named after its county town of Wicklow, which derives from the name ( Old Norse for "Vikings' Meadow"). Wicklow County Council is the local authority for the county, which had a population of 155,258 at the 2022 census. Colloquially known as the "Garden of Ireland" for its scenerywhich includes extensive woodlands, nature trails, beaches, and ancient ruins while allowing for a multitude of walking, hiking, and climbing optionsit is the 17th largest of Ireland's 32 counties by area and the 15th largest by population. It is also the fourth largest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
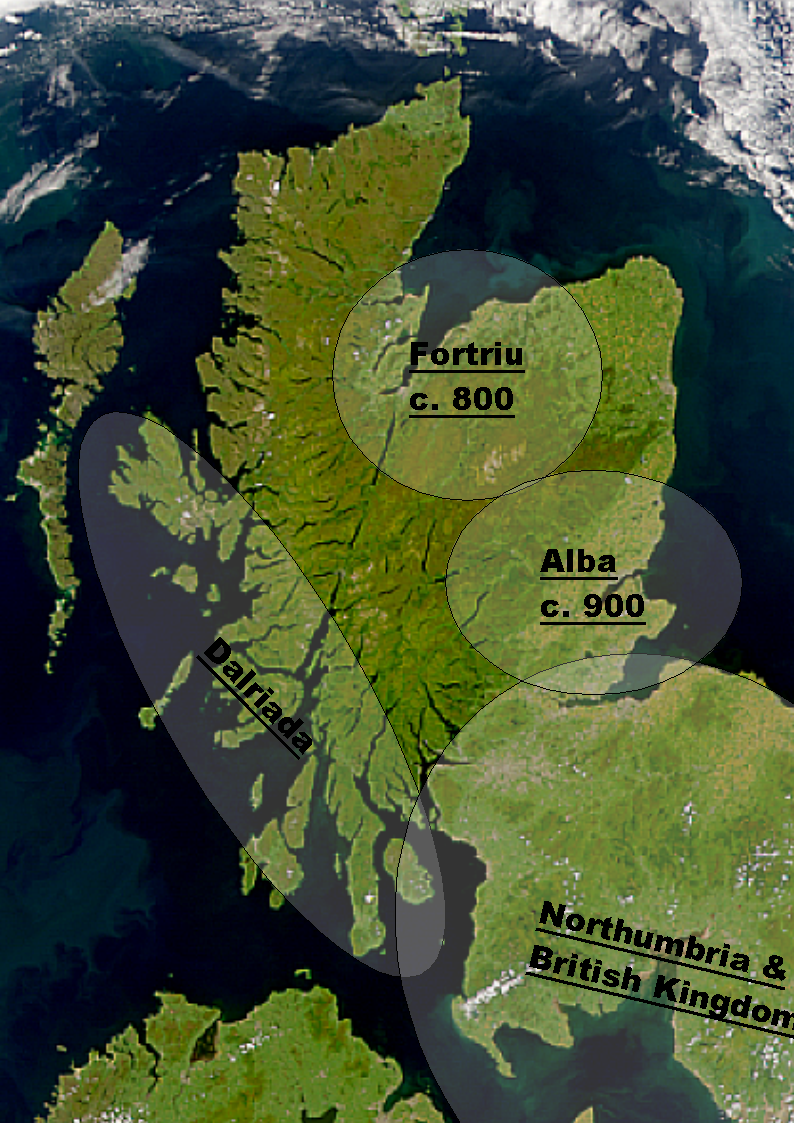
Fortriu
Fortriu ( la, Verturiones; sga, *Foirtrinn; ang, Wærteras; xpi, *Uerteru) was a Pictish kingdom that existed between the 4th and 10th centuries. It was traditionally believed to be located in and around Strathearn in central Scotland, but is more likely to have been based in the north, in the Moray and Easter Ross area. ''Fortriu'' is a term used by historians as it is not known what name its people used to refer to their polity. Historians also sometimes use the name synonymously with Pictland in general. Name The people of Fortriu left no surviving indigenous writings and the name they used to describe themselves is unrecorded. They were first documented in the late 4th century by the Roman historian Ammianus Marcellinus, who referred to them in Latin as the ''Verturiones (or Vecturiones)''. The Latin root ''verturio'' has been connected etymologically by John Rhys with the later Welsh word ''gwerthyr'', meaning "fortress", suggesting that both came from a Common Britto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |