|
Varali
Varali or Varaali (pronounced varāḷi) is a rāgam in Carnatic music (musical scale of South Indian classical music). It is classified either as the 39th mela kartha raga or as a ''janya'' rāgam (derived scale) of the 39th ''melakarta'' scale ''Jhalavarali''. Even though it is a mela kartha, the scale is most often rendered with a ''vakra'' scale (zig-zag notes) in the ascending scale.''Raganidhi'' by P. Subba Rao, Pub. 1964, The Music Academy of Madras It is a '' vivadi rāgam''. It is the 4th in the list of 5 ''Ghana'' rāgams (''Nata (raga)'', '' Gaula'', ''Arabhi'' and '' Shree ragam'' being the others).''Ragas in Carnatic music'' by Dr. S. Bhagyalekshmy, Pub. 1990, CBH Publications In olden times, this rāgam was called ''Varati'', and is said to be more than 1300 years old. It is with this name that it is referred in old musical texts like ''Sangita Makarandha'' and ''Sangita Ratnakara''. Structure and Lakshana ''Varali'' is an asymmetric rāgam due to the ''vakra pray ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pancharatna Kriti
The ''Pancharatna kritis'' (transliterated as ''Pañcaratna kṛti'') (Sanskrit: ''pancha'' "five" + ''ratna'' "gems") are a set of five ''kritis'' (songs) in Carnatic classical music, composed by the 18th-century Indian composer Tyagaraja. All the ''kritis'', as is the case with almost all of Tyagaraja's compositions, are penned in Telugu, except the first one, which is composed in Sanskrit. The songs are: " Jagadananda karaka", " Dudukugala Nanne", " Sadhinchene", " Kanakana Ruchira" and " Endaro Mahanubhavulu". Tyagaraja and the Pancharatna Kritis Tyagaraja lived in the late 18th century and early 19th century in Tiruvarur in present-day Thanjavur district in Tamil Nadu. His compositions are considered to be some of the finest in Carnatic music. Of the five ''Pancharatna Kritis'', four are in Telugu and one in Sanskrit. They are set to music in five ragas: Nata, Gaula, Arabhi, Varali and Sri. Composition The ''Pancharatna kritis'' were written in praise of the Hindu deity R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bhadrachala Ramadasu
Kancharla Gopanna ( te, కంచర్ల గోపన్న) ( – 1688), popularly known as Bhakta Ramadasu or Bhadrachala Ramadasu ( te, భద్రాచల రామదాసు), was a 17th-century devotee of the Hindu god Rama, a saint-poet and a composer of Carnatic music. He is a famous ''Vaggeyakara'' (classical composer) from the Telugu classical era. He was born in the village of Nelakondapalli in Khammam district, and orphaned as a teenager. He spent his later years in Bhadrachalam and 12 years in solitary confinement at the Golconda prison during the Qutb Shahi-rule. Different mythical stories about his life circulate in the Telugu tradition. He is renowned for constructing the famous Sita Ramachandraswamy Temple and pilgrimage center on the banks of river Godavari at Bhadrachalam. His devotional ''kirtana'' lyrics to Rama illustrate the classical Pallavi, Anupallavi and Caranam genre composed mostly in Telugu, some in Sanskrit and with occasional use of Tamil l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jhalavarali
Jhalavarali (pronounced , meaning ''A moon with the sun's heat''), is a ragam in Carnatic music (musical scale of South Indian classical music). It is the 39th ''Melakarta'' rāgam in the 72 ''melakarta'' rāgam system of Carnatic music. It is called in Muthuswami Dikshitar school of Carnatic music.''Sri Muthuswami Dikshitar Keertanaigal'' by Vidwan A Sundaram Iyer, Pub. 1989, Music Book Publishers, Mylapore, Chennai''Ragas in Carnatic music'' by Dr. S. Bhagyalekshmy, Pub. 1990, CBH Publications''Raganidhi'' by P. Subba Rao, Pub. 1964, The Music Academy of Madras Structure and Lakshana It is the 3rd rāgam in the 7th ''chakra Rishi''. The mnemonic name is ''Rishi-Go''. The mnemonic phrase is ''sa ra ga mi pa dha nu''. Its ' structure (ascending and descending scale) is as follows (see ''swaras'' in Carnatic music for details on below notation and terms): * : * : (the notes in this scale : ''shuddha rishabham, shuddha gandharam, prati madhyamam, shuddha dhaivatham, kakali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vivadi
In Hindustani classical music, ''vivadi'' ( sa, विवादि meaning "dissonant") refers to pitches that are not part of the ''arohana'' or '' avrohana'' of a given raga. In general, ''vivadi'' are not to be played during an improvisation on a given raga. So, for instance, if a raga had the structure S R G m P D N S', S' N D P m G R S; in that case, r, g, M, d and n would all be ''vivadi''. Although ''vivadi'' pitches are generally to be avoided during the playing of a given raga, they are occasionally added by skilled performers in order to introduce some color to an interpretation. In Carnatic music In Carnatic music, vivadi is used in ''vivadi swaram'', , ''vivadi ragam'', and by extension ''vivadi melakarta''. ''Vivadi'' term means going against the grain of thought or approach. Vivadi swaram A ''swaram'' is said to be ''vivadi'' in relationship with another swaram. There are twelve swarams in Indian classical music. But there are 16 notes. Thus some notes occupy t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shyama Shastri
Shyama Shastri (; 26 April 1762 – 1827) or Syama Sastri was a musician and composer of Carnatic music. He was the oldest among the Trinity of Carnatic music, Tyagaraja and Muthuswami Dikshitar being the other two. Early life and career Shyama Shastri, whose birth name was Venkata Subrahmanya, was born on 26 April 1762 in a Telugu Brahmin family. He was also known as one of the trinity of carnatic music. To later generations, he is better known by his adopted name Shyama Shastri or by his musical mudra (signature) Shyama Krishna. He was born in Tiruvarur, in what is now the state of Tamil Nadu. He received his instruction in the vedas, astrology, and other traditional subjects early on and learned music from his maternal uncle. He was later trained in music by Adiappayya, a noted durbar musician of Thanjavur. Although Śyāma Śastri did not compose as many ''kritis'' as his two prolific contemporaries, his compositions are still well known due to the literary, melodic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ganesha
Ganesha ( sa, गणेश, ), also known as Ganapati, Vinayaka, and Pillaiyar, is one of the best-known and most worshipped deities in the Hindu pantheon and is the Supreme God in Ganapatya sect. His image is found throughout India. Hindu denominations worship him regardless of affiliations. Devotion to Ganesha is widely diffused and extends to Jains and Buddhists and includes Nepal, Sri Lanka, Thailand, Indonesia (Java and Bali), Singapore, Malaysia, Philippines, and Bangladesh and in countries with large ethnic Indian populations including Fiji, Guyana, Mauritius, and Trinidad and Tobago. Although Ganesha has many attributes, he is readily identified by his elephant head. He is widely revered, more specifically, as the remover of obstacles and thought to bring good luck; the patron of arts and sciences; and the deva of intellect and wisdom. As the god of beginnings, he is honoured at the start of rites and ceremonies. Ganesha is also invoked as a patron of letters ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Purandara Dasa
Purandara Dasa (IAST: Purandara dāsa) ( 1470 – 1565) was a Haridasa philosopher and a follower of Madhwacharya 's Dwaitha philosophy -saint from present-day Karnataka, India. He was a composer, singer and one of the chief founding-proponents of Carnatic music (Karnataka classical music). In honor of his significant contributions to Carnatic music, he is widely referred to as the ''Pitamaha'' (''lit''. "father" or "grandfather") of Carnatic music. According to a legend, he is considered as an incarnation of Saint Narada. Purandara Dasa was a wealthy merchant of gold, silver and other miscellaneous jewellery from Karnataka, who gave away all his material riches to become a Haridasa (literally meaning a servant of Lord Hari or Lord Krishna), a devotional singer who made the difficult Sanskrit tenets of Bhagavata Purana available to everyone in simple and melodious songs. He was one of the most important music scholars of medieval India. He formulated the basic lessons of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papanasam Sivan
Paapanaasam Raamayya Sivan (26 September 1890 – 1 October 1973) was an Indian composer of Carnatic music and a singer. He was awarded the Madras Music Academy's Sangeetha Kalanidhi in 1971. He was also a film score composer in Kannada cinema as well as Tamil cinema in the 1930s and 1940s. Sivan was also known as Tamil Thyaagaraja. Using Classical South Indian as a base, Sivan created compositions popularised by M. K. Thyagaraja Bhagavathar, D. K. Pattammal, and M. S. Subbulakshmi. In 1962, he was awarded the Sangeet Natak Akademi Fellowship conferred by Sangeet Natak Akademi, India's National Academy for Music, Dance and Drama. Life Sivan's early years were spent in the Travancore area of Kerala. He was born at Polagam village in the district of Thanjavur, which was home to the musical trinity of Carnatic music. His given name was Ramaiya. In 1897, when he was 7, his father died. His mother Yogambal, along with her sons, left Thanjavur and moved to Travancore (now Thiruva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kshetrajna
Kshetrajna (Devnagari: क्षेत्रज्ञ) means the one who knows the field of the body, soul, physical matter. It is the conscious principle in the corporeal frame. In the thirteenth chapter of the Bhagavad Gita, Krishna explains the distinction between the Kshetra and the Kshetrajna. Overview The Kshetra or the field refers to the body which is material, mutable, transitory and perishable, the Kshetrajna refers to the conscious knower of the body who is of the same essence as Knowledge, immutable, eternal and imperishable, the knower of the body is the soul residing in the body. Kshetra is Prakrti or matter which is insentient, and the knower of the Kshetra is the Purusha who is sentient. True knowledge is knowing and understanding both these two factors, the insentient and sentient. The knowledge of Prakrti only, is called the Apara Vidya or Lower knowledge, and that pertaining to the Purusha is called the Para Vidya or Higher knowledge. in the Bhagavad Gita, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swathi Thirunal
( ml, സ്വാതി തിരുനാള് രാമവർമ്മ) (16 April 1813 – 26 December 1846) was the Maharaja of the Kingdom of Travancore. He is also considered as a brilliant music composer and is credited with over 400 classical compositions in both Carnatic and Hindustani style.http://print.achuth.googlepages.com/SwathiThirunalandSciencev3.0.pdf A well-formulated code of laws, courts of justice, introduction of English education, construction of an observatory, installation of the first Government printing press, establishment of the first manuscripts library were amongst the many initiatives taken by Svāti Tirunāḷ, as a King, to modernise Travancore. Early life Svāti Tirunāḷ was born into the Venad dynasty of the Matrilineal royal family of Travancore, which is now a part of Kerala, on 16 April 1813. He was the second child of Queen Gowri Lakshmi Bayi who ruled Travancore from 1811 to 1815, and Raja Raja Varma Koil Thampuran of C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muthuswami Dikshitar
Muthuswami Dikshitar (Mudduswamy Dikshitar)(, 24 March 1776 – 21 October 1835), mononymously Dikshitar, was a South Indian poet, singer and veena player, and a legendary composer of Indian classical music, who is considered one of the musical trinity of Carnatic music. Muthuswami Dikshitar was born on 24 March 1775 in Tiruvarur near Thanjavur, in what is now the state of Tamil Nadu in India, to a family that is traditionally traced back to Virinichipuram in the northern boundaries of the state. His compositions, of which around 500 are commonly known, are noted for their elaborate and poetic descriptions of Hindu gods and temples and for capturing the essence of the raga forms through the vainika (veena) style that emphasises gamakas. They are typically in a slower speed (chowka kala). He is also known by his signature name of Guruguha which is also his mudra (and can be found in each of his songs). His compositions are widely sung and played in classical concerts of Carnatic mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
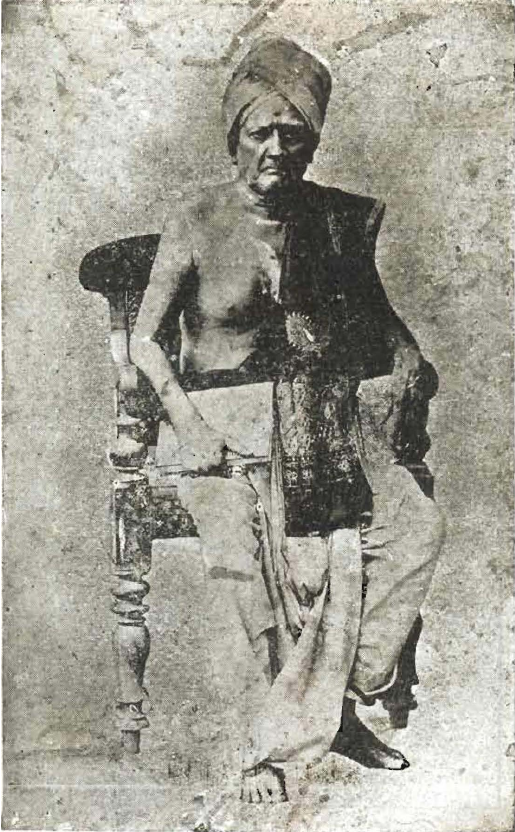
Tyagaraja
Thyagaraja (Telugu: త్యాగరాజ) (4 May 1767 – 6 January 1847), also known as Thyāgayya and in full as Kakarla Thyagabrahmam, was a composer and vocalist of Carnatic music, a form of Indian classical music. Tyagaraja and his contemporaries, Shyama Shastri and Muthuswami Dikshitar, are regarded as the Trinity of Carnatic music. Thyagaraja composed thousands of devotional compositions, most in Telugu and in praise of Lord Rama, many of which remain popular today, the most popular being "Nagumomu". Of special mention are five of his compositions called the ''Pancharatna Kritis'' ( "five gems"), which are often sung in programs in his honour, and ''Utsava Sampradaya Krithis'' ( Festive ritual compositions), which are often sung to accompany temple rituals. Tyagaraja lived through the reigns of four kings of the Maratha dynasty — Tulaja II (1763–1787), Amarasimha (1787–1798), Serfoji II (1798–1832) and Sivaji II (1832–1855), although he served none of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)