|
Van Veen Grab Sampler
The Van Veen grab sampler is an instrument to sample sediment in water environments. Usually it is a clamshell bucket made of stainless steel. Up to 20 cm deep samples of roughly 0.1 m2 can be extracted with this instrument. It can be light-weight (roughly 5 kg) and low-tech. The smallest version even fits into hand luggage. The sampler was invented by Johan van Veen (a Dutch engineer) in 1933. A draw-back of the use of this sampler is that it tends to disturb the sediments more than a box corer does. Mechanism While letting the instrument down into the water, the two levers with buckets at their ends are spread like an open scissor. The levers are locked in this position, and unlocked on hitting the ground. When the rope is pulled upward again, the two buckets close and grab a sample from the sea floor. File:VanVeenGrab - Locked.jpg, Van Veen grab when it is locked, ready to be lowered to the floor File:VanVeenGrab - Unlocked.jpg, It is now unlocked after hitting the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Van Veen
Van Veen is a Dutch toponymic surname. Notable people with the surname include: * Anne van Veen (born 1983), Dutch cabaret artist, daughter of Herman * Anneloes van Veen (born 1990), Dutch competitive sailor * Babette van Veen (born 1968), Dutch actor and singer, daughter of Herman * Chris van Veen (1922–2009), Dutch State Secretary, minister and chairperson of VNO * Gertruida van Veen (1602-1643), Flemish painter * Gijsbert van Veen (1558–1630), Dutch painter and engraver, brother of Otto * Herman van Veen (born 1945), Dutch singer and actor * Jeroen van Veen (born 1969), Dutch pianist * Jeroen van Veen (born 1974), Dutch bassist * Johan van Veen (1893–1959), Dutch civil engineer who originated the Delta Works * José van Veen (born 1986), Dutch rower * Kevin van Veen (born 1991), Dutch footballer * Leo van Veen (born 1946), Dutch football player and coach * Maarten van Veen (born 1971), Dutch pianist and conductor * Maerten van Veen, better known as Maarten van Heems ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Floor
The seabed (also known as the seafloor, sea floor, ocean floor, and ocean bottom) is the bottom of the ocean. All floors of the ocean are known as 'seabeds'. The structure of the seabed of the global ocean is governed by plate tectonics. Most of the ocean is very deep, where the seabed is known as the abyssal plain. Seafloor spreading creates mid-ocean ridges along the center line of major ocean basins, where the seabed is slightly shallower than the surrounding abyssal plain. From the abyssal plain, the seabed slopes upward toward the continents and becomes, in order from deep to shallow, the continental rise, slope, and shelf. The depth within the seabed itself, such as the depth down through a sediment core, is known as the “depth below seafloor.” The ecological environment of the seabed and the deepest waters are collectively known, as a habitat for creatures, as the “ benthos.” Most of the seabed throughout the world's oceans is covered in layers of marine sedimen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Oceanography
Biological oceanography is the study of how organisms affect and are affected by the physics, chemistry, and geology of the oceanographic system. Biological oceanography may also be referred to as ocean ecology, in which the root word of ecology is ''Oikos'' (oικoσ), meaning ‘house’ or ‘habitat’ in Greek. With that in mind, it is of no surprise then that the main focus of biological oceanography is on the microorganisms within the ocean; looking at how they are affected by their environment and how that affects larger marine creatures and their ecosystem.Lalli, Carol M., and Timothy R. Parsons. "Introduction." Biological Oceanography: An Introduction. First Edition ed. Tarrytown, New York: Pergamon, 1993. 7-21. Print. Biological oceanography is similar to marine biology, but is different because of the perspective used to study the ocean. Biological oceanography takes a bottom-up approach (in terms of the food web), while marine biology studies the ocean from a top-down ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquatic Ecology
An aquatic ecosystem is an ecosystem formed by surrounding a body of water, in contrast to land-based terrestrial ecosystems. Aquatic ecosystems contain communities of organisms that are dependent on each other and on their environment. The two main types of aquatic ecosystems are marine ecosystems and freshwater ecosystems. Freshwater ecosystems may be lentic (slow moving water, including pools, ponds, and lakes); lotic (faster moving water, for example streams and rivers); and wetlands (areas where the soil is saturated or inundated for at least part of the time). Types Marine ecosystems Marine coastal ecosystem Marine surface ecosystem Freshwater ecosystems Lentic ecosystem (lakes) Lotic ecosystem (rivers) Wetlands Functions Aquatic ecosystems perform many important environmental functions. For example, they recycle nutrients, purify water, attenuate floods, recharge ground water and provide habitats for wildlife. Aquatic ecosystems are al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
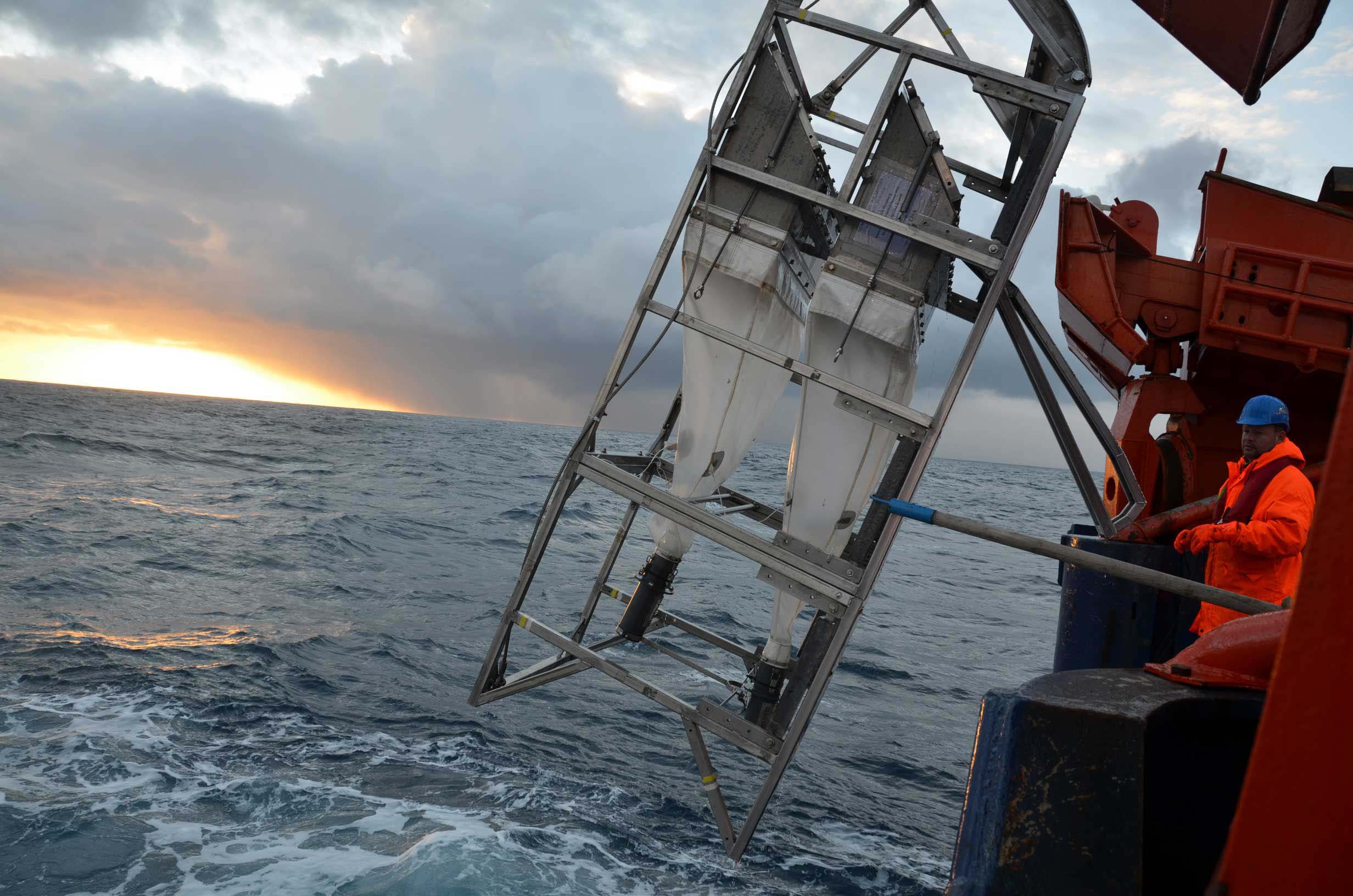
Epibenthic Sled
An epibenthic sled (or ''epibenthos sled/sledge'') is an instrument designed to collect benthic and benthopelagic faunas from the deep sea. The sled is made from a steel frame consisting of two skids and stabilizing planes to keep it from sinking too deep into the mud. Attached to the frame is a 1 mm mesh net to collect the samples. The sled is towed along the seafloor at the sediment water interface. The device has a mechanically operated door that is closed when the sled is mid water and opens when it reaches the seafloor. When the fauna is collected, the door closes again to preserve the sample on the long trek back through the water column. The door prevents washing of the sample and loss of organisms through turbulence generated as the net is lifted out. The epibenthic sled can also be used with external sensors and cameras. The sled is mostly used to collect epifauna, however some infauna can be gathered as well. There is an adjustable cutting bar mounted und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Young Grab
The Young grab, or the Young modified Van Veen grab sampler is an instrument to sample sediment in the ocean. It is a modified version of the Van Veen grab sampler, with a clamshell bucket made out of stainless steel mounted to a supporting frame. The sampling area extracted with this instrument can vary depending on its size. With the modifications this version of the Van Veen grab sampler is heavier than the traditional version. The frame allows for better stability and level sampling. Weights can be attached to the frame to ensure the bucket grabs sufficient sediment, or skids to ensure the gear does not sink too deep in soft sediments. A draw-back of the use of this sampler is that it tends to disturb the sediments more than a box corer does. This does also not allow for sampling of the water column, but only the benthic surface. Mechanism While letting the instrument down into the water, the two levers with buckets at their ends are spread like an open scissor. The levers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
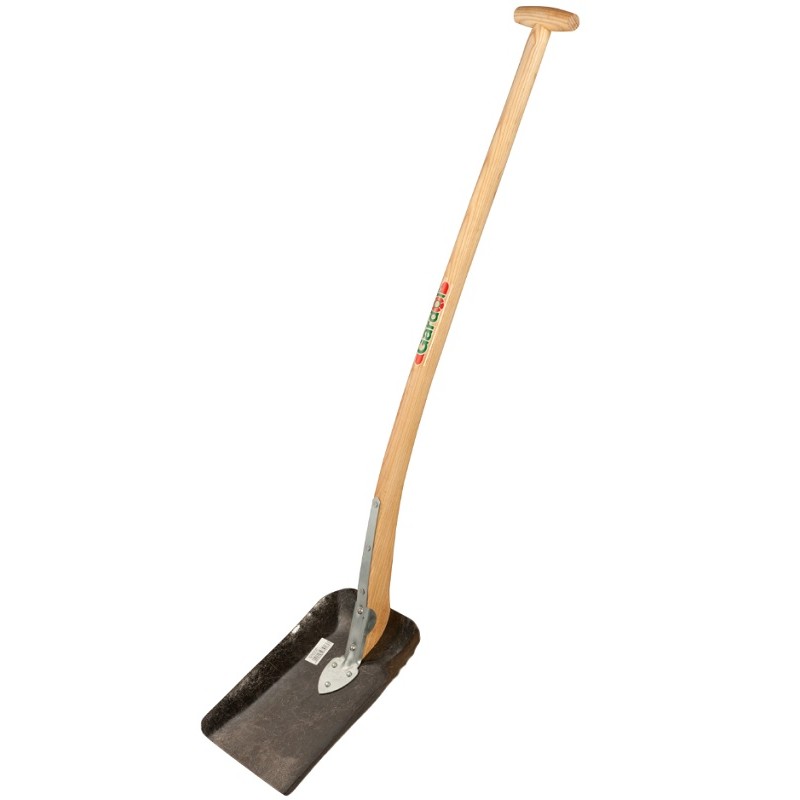
Shovels
A shovel is a tool used for digging, lifting, and moving bulk materials, such as soil, coal, gravel, snow, sand, or ore. Most shovels are hand tools consisting of a broad blade fixed to a medium-length handle. Shovel blades are usually made of sheet steel or hard plastics and are very strong. Shovel handles are usually made of wood (especially specific varieties such as ash or maple) or glass-reinforced plastic (fiberglass). Hand shovel blades made of sheet steel usually have a folded seam or hem at the back to make a socket for the handle. This fold also commonly provides extra rigidity to the blade. The handles are usually riveted in place. A T-piece is commonly fitted to the end of the handle to aid grip and control where the shovel is designed for moving soil and heavy materials. These designs can all be easily mass-produced. The term ''shovel'' also applies to larger excavating machines called power shovels, which serve the same purpose—digging, lifting, and moving mate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
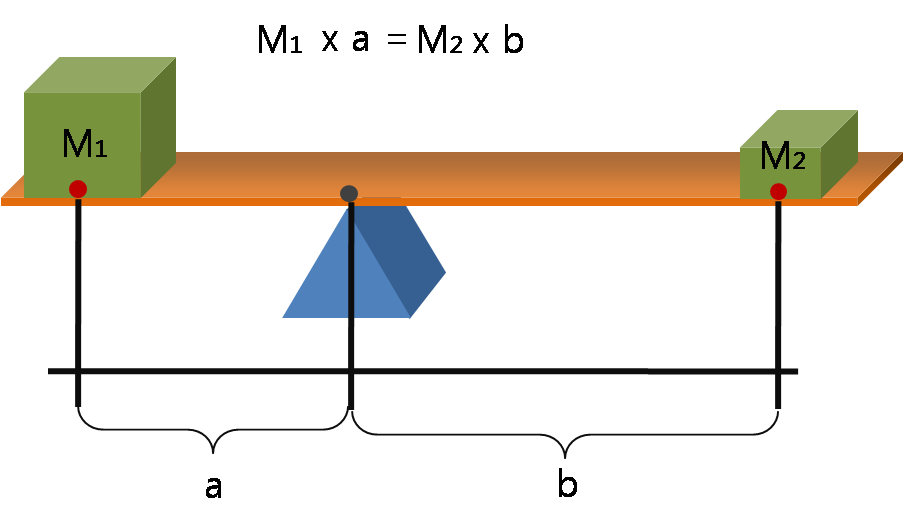
Lever
A lever is a simple machine consisting of a beam or rigid rod pivoted at a fixed hinge, or '' fulcrum''. A lever is a rigid body capable of rotating on a point on itself. On the basis of the locations of fulcrum, load and effort, the lever is divided into three types. Also, leverage is mechanical advantage gained in a system. It is one of the six simple machines identified by Renaissance scientists. A lever amplifies an input force to provide a greater output force, which is said to provide leverage. The ratio of the output force to the input force is the mechanical advantage of the lever. As such, the lever is a mechanical advantage device, trading off force against movement. Etymology The word "lever" entered English around 1300 from Old French, in which the word was ''levier''. This sprang from the stem of the verb ''lever'', meaning "to raise". The verb, in turn, goes back to the Latin ''levare'', itself from the adjective ''levis'', meaning "light" (as in "not heavy") ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sediment
Sediment is a naturally occurring material that is broken down by processes of weathering and erosion, and is subsequently transported by the action of wind, water, or ice or by the force of gravity acting on the particles. For example, sand and silt can be carried in suspension in river water and on reaching the sea bed deposited by sedimentation; if buried, they may eventually become sandstone and siltstone (sedimentary rocks) through lithification. Sediments are most often transported by water ( fluvial processes), but also wind ( aeolian processes) and glaciers. Beach sands and river channel deposits are examples of fluvial transport and deposition, though sediment also often settles out of slow-moving or standing water in lakes and oceans. Desert sand dunes and loess are examples of aeolian transport and deposition. Glacial moraine deposits and till are ice-transported sediments. Classification Sediment can be classified based on its grain size, grain sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Box Corer
The box corer is a marine geological sampling tool for soft sediments in lakes or oceans. It is deployed from a research vessel with a wire and suitable for any water depth. It is designed for a minimum of disturbance of the sediment surface by bow wave effects which is important for quantitative investigations of the benthic micro- to macrofauna, geochemical processes, sampling of bottom water or sedimentology. Construction The surface area of the box ranges between 200 cm2 and a quarter of a square meter (50x50 cm = 2,500 cm2); the penetration depth of 0.5 m can be controlled to prevent over-penetration in softer sediments. It allows for large sample sizes which optimizes deploy time and can satisfy sample requests for various investigations. Procedure The box is fixed at the lower end of a large plunger. To deploy the box corer an "A"-frame or a sliding beam with at least 3 m clearance is required. The corer is lowered vertically until it impacts with the seabed. At ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johan Van Veen
Johan van Veen ( Uithuizermeeden, 21 December 1893 – The Hague, 9 December 1959) was a Dutch hydraulic engineer. He is considered the father of the Delta Works. Education Johan van Veen was the fifth child of seven in a farming family. He was the brother of Marie van Veen, married to the artist Johan Dijkstra. In 1913, after high school graduation, he started his studies in Delft at the Technische Hoogeschool van Delft. He studied civil engineering. In 1919, he graduated as "ingenieur" (equivalent to M.Sc. in engineering). Provincial Water Authority Drenthe Van Veen worked as an engineer for the Drainage Department of the Provincial Water Authority of the Province of Drenthe. The task of this department was to develop plans to improve the drainage and road structure of the province. In turn, this would enlarge the agricultural yield and to transport the products in a more efficient way to the markets (in the western part of the Netherlands). During World War I, it became ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |