|
Valve Audio Amplifier Technical Specification
Technical specifications and detailed information on the valve audio amplifier, including its development history. Circuitry and performance Characteristics of valves Valves (also known as vacuum tubes) are very high input impedance (near infinite in most circuits) and high-output impedance devices. They are also high-voltage / low-current devices. The characteristics of valves as gain devices have direct implications for their use as audio amplifiers, notably that power amplifiers need output transformers (OPTs) to translate a high-output-impedance high-voltage low-current signal into a lower-voltage high-current signal needed to drive modern low-impedance loudspeakers (cf. transistors and FETs which are relatively low voltage devices but able to carry large currents directly). Another consequence is that since the output of one stage is often at ~100 V offset from the input of the next stage, direct coupling is normally not possible and stages need to be coupled using a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
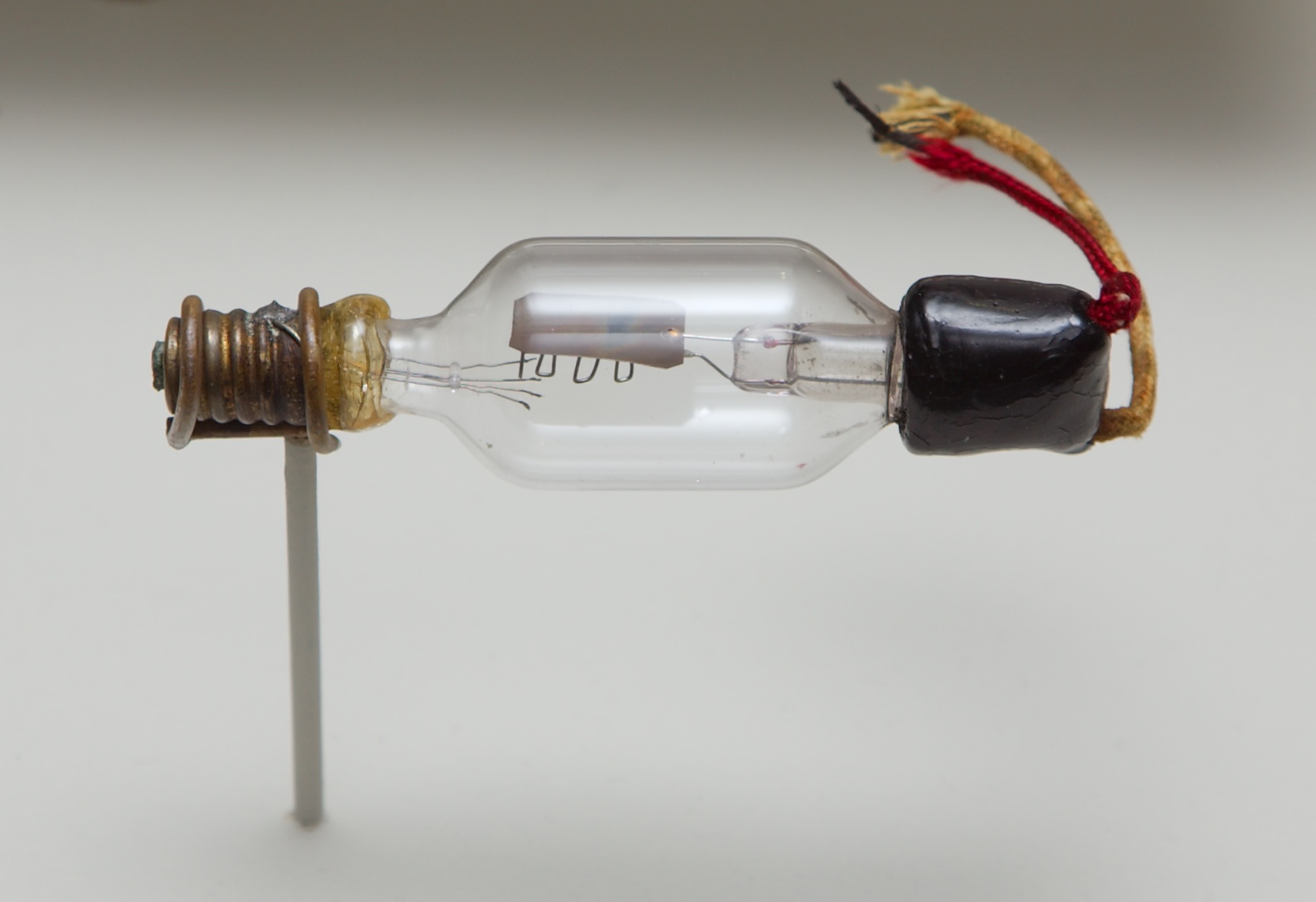
Vacuum Tube
A vacuum tube, electron tube, valve (British usage), or tube (North America), is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric voltage, potential difference has been applied. The type known as a thermionic tube or thermionic valve utilizes thermionic emission of electrons from a hot cathode for fundamental electronic functions such as signal amplifier, amplification and current rectifier, rectification. Non-thermionic types such as a vacuum phototube, however, achieve electron emission through the photoelectric effect, and are used for such purposes as the detection of light intensities. In both types, the electrons are accelerated from the cathode to the anode by the electric field in the tube. The simplest vacuum tube, the diode (i.e. Fleming valve), invented in 1904 by John Ambrose Fleming, contains only a heated electron-emitting cathode and an anode. Electrons can only flow in one direction through the device—fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Push–pull Output
A push–pull amplifier is a type of electronic circuit that uses a pair of active devices that alternately supply current to, or absorb current from, a connected load. This kind of amplifier can enhance both the load capacity and switching speed. Push–pull outputs are present in TTL and CMOS digital logic circuits and in some types of amplifiers, and are usually realized by a complementary pair of transistors, one dissipating or ''sinking'' current from the load to ground or a negative power supply, and the other supplying or ''sourcing'' current to the load from a positive power supply. A push–pull amplifier is more efficient than a single-ended "class-A" amplifier. The output power that can be achieved is higher than the continuous dissipation rating of either transistor or tube used alone and increases the power available for a given supply voltage. Symmetrical construction of the two sides of the amplifier means that even-order harmonics are cancelled, which can re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bandwidth (signal Processing)
Bandwidth is the difference between the upper and lower frequencies in a continuous band of frequencies. It is typically measured in hertz, and depending on context, may specifically refer to ''passband bandwidth'' or ''baseband bandwidth''. Passband bandwidth is the difference between the upper and lower cutoff frequencies of, for example, a band-pass filter, a communication channel, or a signal spectrum. Baseband bandwidth applies to a low-pass filter or baseband signal; the bandwidth is equal to its upper cutoff frequency. Bandwidth in hertz is a central concept in many fields, including electronics, information theory, digital communications, radio communications, signal processing, and spectroscopy and is one of the determinants of the capacity of a given communication channel. A key characteristic of bandwidth is that any band of a given width can carry the same amount of information, regardless of where that band is located in the frequency spectrum. For example, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
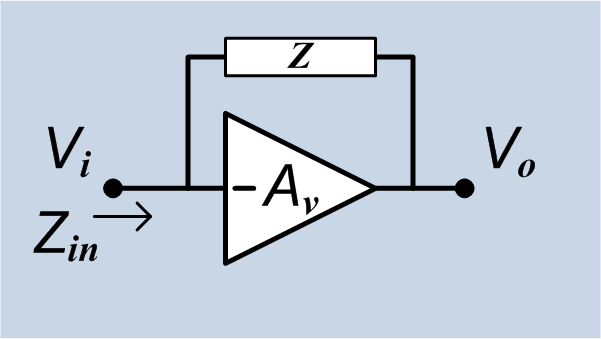
Miller Effect
In electronics, the Miller effect accounts for the increase in the equivalent input capacitance of an inverting voltage amplifier due to amplification of the effect of capacitance between the input and output terminals. The virtually increased input capacitance due to the Miller effect is given by :C_=C (1+A_v)\, where -A_v is the voltage gain of the inverting amplifier (A_v positive) and C is the feedback capacitance. Although the term ''Miller effect'' normally refers to capacitance, any impedance connected between the input and another node exhibiting gain can modify the amplifier input impedance via this effect. These properties of the Miller effect are generalized in the Miller theorem. The Miller capacitance due to parasitic capacitance between the output and input of active devices like transistors and vacuum tubes is a major factor limiting their gain at high frequencies. Miller capacitance was identified in 1920 in triode vacuum tubes by John Milton Miller. History The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valve Audio Amplifier Technical Specification
Technical specifications and detailed information on the valve audio amplifier, including its development history. Circuitry and performance Characteristics of valves Valves (also known as vacuum tubes) are very high input impedance (near infinite in most circuits) and high-output impedance devices. They are also high-voltage / low-current devices. The characteristics of valves as gain devices have direct implications for their use as audio amplifiers, notably that power amplifiers need output transformers (OPTs) to translate a high-output-impedance high-voltage low-current signal into a lower-voltage high-current signal needed to drive modern low-impedance loudspeakers (cf. transistors and FETs which are relatively low voltage devices but able to carry large currents directly). Another consequence is that since the output of one stage is often at ~100 V offset from the input of the next stage, direct coupling is normally not possible and stages need to be coupled using a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voltage Regulator
A voltage regulator is a system designed to automatically maintain a constant voltage. A voltage regulator may use a simple feed-forward design or may include negative feedback. It may use an electromechanical mechanism, or electronic components. Depending on the design, it may be used to regulate one or more AC or DC voltages. Electronic voltage regulators are found in devices such as computer power supplies where they stabilize the DC voltages used by the processor and other elements. In automobile alternators and central power station generator plants, voltage regulators control the output of the plant. In an electric power distribution system, voltage regulators may be installed at a substation or along distribution lines so that all customers receive steady voltage independent of how much power is drawn from the line. Electronic voltage regulators A simple voltage/current regulator can be made from a resistor in series with a diode (or series of diodes). Due to the loga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Grid
An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that can increase the magnitude of a signal (a time-varying voltage or current). It may increase the power significantly, or its main effect may be to boost the voltage or current (power, voltage or current amplifier). It is a two-port electronic circuit that uses electric power from a power supply to increase the amplitude of a signal applied to its input terminals, producing a greater amplitude signal at its output. The ratio of output to input voltage, current, or power is termed gain (voltage, current, or power gain). An amplifier, by definition has gain greater than unity (if the gain is less than unity, the device is an attenuator). An amplifier can either be a separate piece of equipment or an electrical circuit contained within another device. Amplification is fundamental to modern electronics, and amplifiers are widely used in almost all electronic equipment. Amplifiers can be categorize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triode
A triode is an electronic amplifying vacuum tube (or ''valve'' in British English) consisting of three electrodes inside an evacuated glass envelope: a heated filament or cathode, a grid, and a plate (anode). Developed from Lee De Forest's 1906 Audion, a partial vacuum tube that added a grid electrode to the thermionic diode (Fleming valve), the triode was the first practical electronic amplifier and the ancestor of other types of vacuum tubes such as the tetrode and pentode. Its invention founded the electronics age, making possible amplified radio technology and long-distance telephony. Triodes were widely used in consumer electronics devices such as radios and televisions until the 1970s, when transistors replaced them. Today, their main remaining use is in high-power RF amplifiers in radio transmitters and industrial RF heating devices. In recent years there has been a resurgence in demand for low power triodes due to renewed interest in tube-type audio systems by audiophi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buffer Amplifier
A buffer amplifier (sometimes simply called a buffer) is one that provides electrical impedance transformation from one circuit to another, with the aim of preventing the signal source from being affected by whatever currents (or voltages, for a current buffer) that the load may be produced with. The signal is 'buffered from' load currents. Two main types of buffer exist: the voltage buffer and the current buffer. Voltage buffer A voltage buffer amplifier is used to transfer a voltage from a first circuit, having a high output impedance level, to a second circuit with a low input impedance level. The interposed buffer amplifier prevents the second circuit from loading the first circuit unacceptably and interfering with its desired operation, since without the voltage buffer the voltage of the second circuit is influenced by output impedance of the first circuit (as it is larger than the input impedance of the second circuit). In the ideal voltage buffer in the diagram, the input re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transconductance
Transconductance (for transfer conductance), also infrequently called mutual conductance, is the electrical characteristic relating the current through the output of a device to the voltage across the input of a device. Conductance is the reciprocal of resistance. Transadmittance (or transfer admittance) is the AC equivalent of transconductance. Definition Transconductance is very often denoted as a conductance, ''g''m, with a subscript, m, for ''mutual''. It is defined as follows: :g_m = \frac For small signal alternating current, the definition is simpler: :g_m = \frac The SI unit for transconductance is the siemens, with the symbol S, as in conductance. Transresistance Transresistance (for transfer resistance), also infrequently referred to as mutual resistance, is the dual of transconductance. It refers to the ratio between a change of the voltage at two output points and a related change of current through two input points, and is notated as ''r''m: :r_m = \frac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amplifier
An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that can increase the magnitude of a signal (a time-varying voltage or current). It may increase the power significantly, or its main effect may be to boost the voltage or current (power, voltage or current amplifier). It is a two-port electronic circuit that uses electric power from a power supply to increase the amplitude of a signal applied to its input terminals, producing a greater amplitude signal at its output. The ratio of output to input voltage, current, or power is termed gain (voltage, current, or power gain). An amplifier, by definition has gain greater than unity (if the gain is less than unity, the device is an attenuator). An amplifier can either be a separate piece of equipment or an electrical circuit contained within another device. Amplification is fundamental to modern electronics, and amplifiers are widely used in almost all electronic equipment. Amplifiers can be categorize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
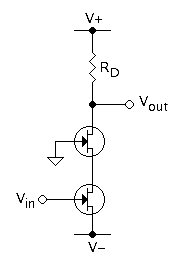
Cascode
The cascode is a two-stage amplifier that consists of a common-emitter stage feeding into a common-base stage. Compared to a single amplifier stage, this combination may have one or more of the following characteristics: higher input–output isolation, higher input impedance, high output impedance, higher bandwidth. In modern circuits, the cascode is often constructed from two transistors (BJTs or FETs), with one operating as a common emitter or common source and the other as a common base or common gate. The cascode improves input–output isolation (reduces reverse transmission), as there is no direct coupling from the output to input. This eliminates the Miller effect and thus contributes to a much higher bandwidth. History The use of a cascode (sometimes verbified to ''cascoding'') is a common technique for improving analog circuit performance, applicable to both vacuum tubes and transistors. The name "cascode" was coined in an article written by Frederick Vinton Hunt an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.gif)

.png)