|
Valery Troitskaya
Valeria Troitskaya (1917 - 2010) was a Russian geophysicist who is known for her work on Ultra Low Frequency (ULF) waves. Early life Troitskaya was born in Petrograd (today known as St. Petersburg) on November 15, 1917, during Soviet suppression. Even when young, her gifts were exceptional. She excelled in music (piano) and sports and became fluent in French and German in addition to her native Russian. Later she learned English. Her mastery of many languages gave her easy access to world communications. She was always well read in the popular literature of many countries as well as their scientific literature. In 1937 at a time of intense political persecution referred to as the Great Purge, her father was arrested by the Soviet secret police (KGB). Twenty-year-old Valeria managed to send a telegram to the dreaded Beria who was directing the ruthless extermination of large numbers of “enemies of the people”. Remarkably, her pleas on her father's behalf were successful i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), is the second-largest city in Russia. It is situated on the Neva River, at the head of the Gulf of Finland on the Baltic Sea, with a population of roughly 5.4 million residents. Saint Petersburg is the fourth-most populous city in Europe after Istanbul, Moscow and London, the most populous city on the Baltic Sea, and the world's northernmost city of more than 1 million residents. As Russia's Imperial capital, and a historically strategic port, it is governed as a federal city. The city was founded by Tsar Peter the Great on 27 May 1703 on the site of a captured Swedish fortress, and was named after apostle Saint Peter. In Russia, Saint Petersburg is historically and culturally associated with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Physics
Nuclear physics is the field of physics that studies atomic nuclei and their constituents and interactions, in addition to the study of other forms of nuclear matter. Nuclear physics should not be confused with atomic physics, which studies the atom as a whole, including its electrons. Discoveries in nuclear physics have led to applications in many fields. This includes nuclear power, nuclear weapons, nuclear medicine and magnetic resonance imaging, industrial and agricultural isotopes, ion implantation in materials engineering, and radiocarbon dating in geology and archaeology. Such applications are studied in the field of nuclear engineering. Particle physics evolved out of nuclear physics and the two fields are typically taught in close association. Nuclear astrophysics, the application of nuclear physics to astrophysics, is crucial in explaining the inner workings of stars and the origin of the chemical elements. History The history of nuclear physics as a discipl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
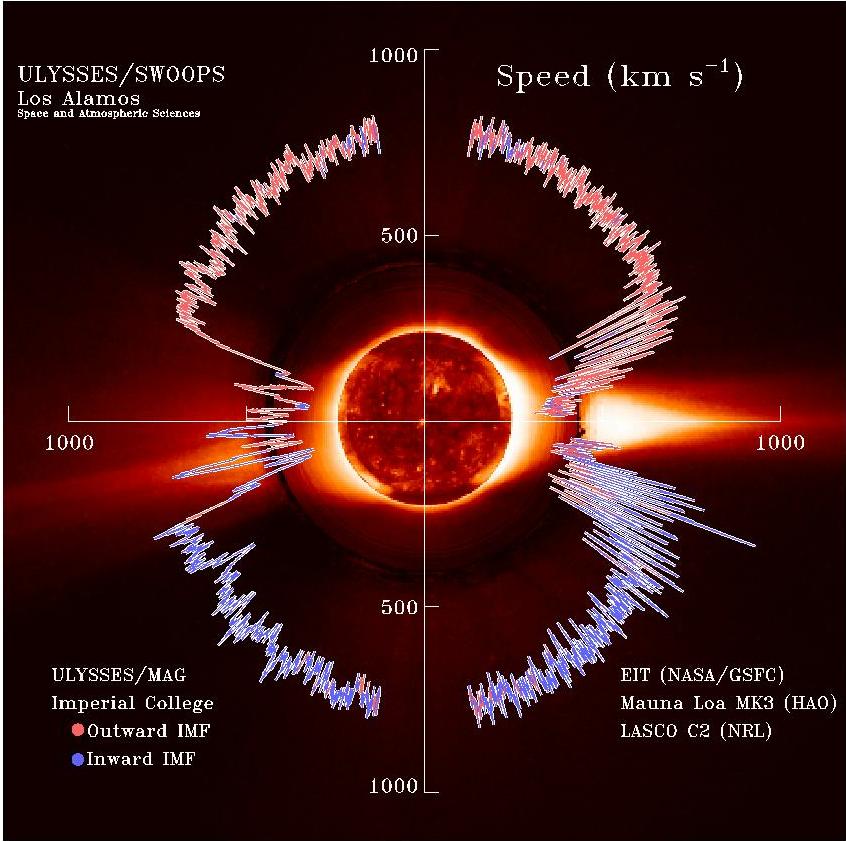
Solar Wind
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles released from the upper atmosphere of the Sun, called the corona. This plasma mostly consists of electrons, protons and alpha particles with kinetic energy between . The composition of the solar wind plasma also includes a mixture of materials found in the solar plasma: trace amounts of heavy ions and atomic nuclei such as C, N, O, Ne, Mg, Si, S, and Fe. There are also rarer traces of some other nuclei and isotopes such as P, Ti, Cr, 54Fe and 56Fe, and 58Ni, 60Ni, and 62Ni. Superposed with the solar-wind plasma is the interplanetary magnetic field. The solar wind varies in density, temperature and speed over time and over solar latitude and longitude. Its particles can escape the Sun's gravity because of their high energy resulting from the high temperature of the corona, which in turn is a result of the coronal magnetic field. The boundary separating the corona from the solar wind is called the Alfvén surface. At a distance of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interplanetary Magnetic Field
The interplanetary magnetic field (IMF), now more commonly referred to as the heliospheric magnetic field (HMF), is the component of the solar magnetic field that is dragged out from the solar corona by the solar wind flow to fill the Solar System. Coronal and solar wind plasma The coronal and solar wind plasmas are highly electrically conductive, meaning the magnetic field lines and the plasma flows are effectively "frozen" together and the magnetic field cannot diffuse through the plasma on time scales of interest. In the solar corona, the magnetic pressure greatly exceeds the plasma pressure and thus the plasma is primarily structured and confined by the magnetic field. However, with increasing altitude through the corona, the solar wind accelerates as it extracts energy from the magnetic field through the Lorentz force interaction, resulting in the flow momentum exceeding the restraining magnetic tension force and the coronal magnetic field is dragged out by the solar wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Geosphere-Biosphere Programme
The International Geosphere-Biosphere Programme (IGBP) was a research programme that ran from 1987 to 2015 dedicated to studying the phenomenon of global change. Its primary focus was coordinating "international research on global-scale and regional-scale interactions between Earth's biological, chemical and physical processes and their interactions with human systems." The International Council of Scientific Unions, a coordinating body of national science organizations, launched IGBP. It looked at the total Earth system, the changes that are occurring, and the manner in which changes are influenced by human actions. IGBP aimed to describe and understand how the physical, chemical and biological processes regulate the Earth system. It also sought to increase knowledge of how humans are influencing global processes, such as the carbon cycle, nitrogen cycle, sulfur cycle, water cycle and phosphorus cycle. "It delivers scientific knowledge to help human societies develop in harmony ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Trobe University
La Trobe University is a public research university based in Melbourne, Victoria, Australia. Its main campus is located in the suburb of Bundoora. The university was established in 1964, becoming the third university in the state of Victoria and the twelfth university in Australia. La Trobe is one of the Australian verdant universities and also part of the Innovative Research Universities group. La Trobe's original and principal campus is located in the Melbourne metropolitan area, within the northern Melbourne suburb of Bundoora. It is the largest metropolitan campus in the country, occupying over . It has two other major campuses located in the regional Victorian city of Bendigo and the twin border cities of Albury-Wodonga. There are two smaller regional campuses in Mildura and Shepparton and a city campus in Melbourne's CBD on Collins Street and in Sydney on Elizabeth Street. La Trobe offers undergraduate and postgraduate courses across its two colleges of Arts, Social ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Astronomical Society
(Whatever shines should be observed) , predecessor = , successor = , formation = , founder = , extinction = , merger = , merged = , type = NGO, learned society , status = Registered charity , purpose = To promote the sciences of astronomy & geophysics , professional_title = Fellow of the Royal Astronomical Society (FRAS) , headquarters = Burlington House , location = Piccadilly, London , coords = , region_served = , services = , membership = , language = , general = , leader_title = Patron , leader_name = King Charles III , leader_title2 = President , leader_name2 = Mike Edmunds , leader_title3 = Executive Director , leader_name3 = Philip Diamond , leader_title4 = , leader_name4 = , key_peop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academy Of Sciences Leopoldina
The German National Academy of Sciences Leopoldina (german: Deutsche Akademie der Naturforscher Leopoldina – Nationale Akademie der Wissenschaften), short Leopoldina, is the national academy of Germany, and is located in Halle (Saale). Founded on January 1, 1652, based on academic models in Italy, it was originally named the ''Academia Naturae Curiosorum'' until 1687 when Emperor Leopold I raised it to an academy and named it after himself. It was since known under the German name ''Deutsche Akademie der Naturforscher Leopoldina'' until 2007, when it was declared to be Germany's National Academy of Sciences. History ' The Leopoldina was founded in the imperial city of Schweinfurt on 1 January 1652 under the Latin name sometimes translated into English as "Academy of the Curious as to Nature." It was founded by four local physicians- Johann Laurentius Bausch, the first president of the society, Johann Michael Fehr, Georg Balthasar Metzger, and Georg Balthasar Wohlfarth; and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finnish Academy Of Science And Letters
The Finnish Academy of Science and Letters (Finnish ''Suomalainen Tiedeakatemia''; Latin ''Academia Scientiarum Fennica'') is a Finnish learned society. It was founded in 1908 and is thus the second oldest academy in Finland. The oldest is the Finnish Society of Sciences and Letters, which was founded in 1838. Members The academy has a total of 328 seats for Finnish members. When a member of the academy turns 65 years, his seat is free for selection of a new member, but he remains a full member until death. The seats are divided into two sections Section of Science * Mathematics and Computer Science 28 members * Physics and Astronomy 26 members * Geosciences 24 members * Chemistry 21 members * Biology 22 members * Agriculture and Forestry 22 members * Medicine 46 members 189 seats Section of the Humanities * Theology and Religion 11 members * Philosophy and Aesthetics 12 members * Psychology and Pedagogy 14 members * History and Archaeology 17 members * Finno-Ugric Studi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Committee On Space Research
The Committee on Space Research (COSPAR) was established on October 3, 1958 by the International Council for Scientific Unions (ICSU). Among COSPAR's objectives are the promotion of scientific research in space on an international level, with emphasis on the free exchange of results, information, and opinions, and providing a forum, open to all scientists, for the discussion of problems that may affect space research. These objectives are achieved through the organization of symposia, publication, and other means. COSPAR has created a number of research programmes on different topics, a few in cooperation with other scientific Unions. The long-term project COSPAR international reference atmosphere started in 1960; since then it has produced several editions of the high-atmosphere code CIRA. The code "IRI" of the URSI-COSPAR working group on the International Reference Ionosphere was first edited in 1978 and is yearly updated. General Assembly Every second year, COSPAR c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Association Of Geomagnetism And Aeronomy
The International Association of Geomagnetism and Aeronomy (IAGA) is an international scientific association that focuses on the study of terrestrial and planetary magnetism and space physics. IAGA is one of the eight associations of the International Union of Geodesy and Geophysics. It is a non-governmental body funded through the subscriptions paid to IUGG by its member countries. IAGA have been responsible for developing and maintaining the International Geomagnetic Reference Field, a reference for the magnetic field of the Earth that was adopted in 1968 and is updated every five years. The most recent version is IGRF-12. History IAGA has a long history and can trace its origins to the Commission for Terrestrial Magnetism and Atmospheric Electricity, part of the World Meteorological Organization originated from the International Meteorological Organization (IMO), which was founded in 1873. At the First IUGG General Assembly (Rome, 1922), the Section de Magnétisme et Electri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Borok
Borok (russian: Борок) is the name of several rural localities in Russia. Altai Krai As of 2010, one rural locality in Altai Krai bears this name: * Borok, Altai Krai, a settlement in Borkovsky Selsoviet of Pospelikhinsky District Arkhangelsk Oblast As of 2010, six rural localities in Arkhangelsk Oblast bear this name: * Borok, Kholmogorsky District, Arkhangelsk Oblast, a village in Khavrogorsky Selsoviet of Kholmogorsky District * Borok, Kotlassky District, Arkhangelsk Oblast, a village in Pacheozersky Selsoviet of Kotlassky District * Borok, Krasnoborsky District, Arkhangelsk Oblast, a village in Berezonavolotsky Selsoviet of Krasnoborsky District * Borok, Lensky District, Arkhangelsk Oblast, a village in Safronovsky Selsoviet of Lensky District * Borok, Verkhnetoyemsky District, Arkhangelsk Oblast, a village in Fedkovsky Selsoviet of Verkhnetoyemsky District * Borok, Vilegodsky District, Arkhangelsk Oblast, a village in Selyansky Selsoviet of Vilegodsky District Ir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |