|
Valayapathi
''Valaiyapadhi'' ( ta, வளையாபதி, lit=Unbending Man, translit=Vaḷaiyāpati; ), also spelled ''Valayapathi'', is one of the five great Tamil epics, but one that is almost entirely lost. It is a story of a father who has two wives, abandons one who gives birth to their son, and the son grows up and seeks his real father. The dominant emotion of this epic is love, and its predominant object is the inculcation of Jain principles and doctrines. Palm-leaf manuscripts of the epic likely existed until the 19th-century, but presently only uncertain fragments of the epic are known from commentaries and the 14th-century anthology ''Purattirattu''. Based on these fragments, the epic appears to be the story of a merchant with an overseas trading business who married two women. He abandoned one, who later gives birth to his son. He has children with the other wife too. The abandoned son is bullied by overseas kids for not knowing the name of his father. His mother then dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Five Great Epics
The Five Great Epics ( ta, ஐம்பெரும்காப்பியங்கள் ''Aimperumkāppiyaṅkaḷ'') are five Tamil language, Tamil epics according to later Tamil literary tradition. They are ''Silappatikaram, Silappatikāram'', ''Manimekalai'', ''Cīvaka Cintāmaṇi'', ''Valayapathi'' and ''Kundalakesi, Kuṇṭalakēci''. Three of the five great epics of Tamil literature are attributed to Tamil Jains, while two are attributed to Tamil Buddhism, Tamil Buddhists. ''Cīvaka Cintāmaṇi'', ''Silappatikaram, Cilappatikāram'', and ''Valayapathi'' were written by Tamil Jains, while ''Manimekalai'' and ''Kundalakesi, Kuṇṭalakēci'' were authored by Buddhists. The first mention of the ''Aimperumkappiyam'' (lit. Five large epics) occurs in Mayilainathar's commentary of ''Nannūl''. However, Mayilainathar does not mention their titles. The titles are first mentioned in the late-18th-to-early-19th-century work ''Thiruthanikaiula''. Earlier works like the 17th-c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Five Great Epics Of Tamil Literature
The Five Great Epics ( ta, ஐம்பெரும்காப்பியங்கள் ''Aimperumkāppiyaṅkaḷ'') are five Tamil epics according to later Tamil literary tradition. They are '' Silappatikāram'', ''Manimekalai'', ''Cīvaka Cintāmaṇi'', ''Valayapathi'' and '' Kuṇṭalakēci''. Three of the five great epics of Tamil literature are attributed to Tamil Jains, while two are attributed to Tamil Buddhists. ''Cīvaka Cintāmaṇi'', '' Cilappatikāram'', and ''Valayapathi'' were written by Tamil Jains, while ''Manimekalai'' and '' Kuṇṭalakēci'' were authored by Buddhists. The first mention of the ''Aimperumkappiyam'' (lit. Five large epics) occurs in Mayilainathar's commentary of ''Nannūl''. However, Mayilainathar does not mention their titles. The titles are first mentioned in the late-18th-to-early-19th-century work ''Thiruthanikaiula''. Earlier works like the 17th-century poem ''Tamil vidu thoothu'' mention the great epics as ''Panchkavyams''. Among ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
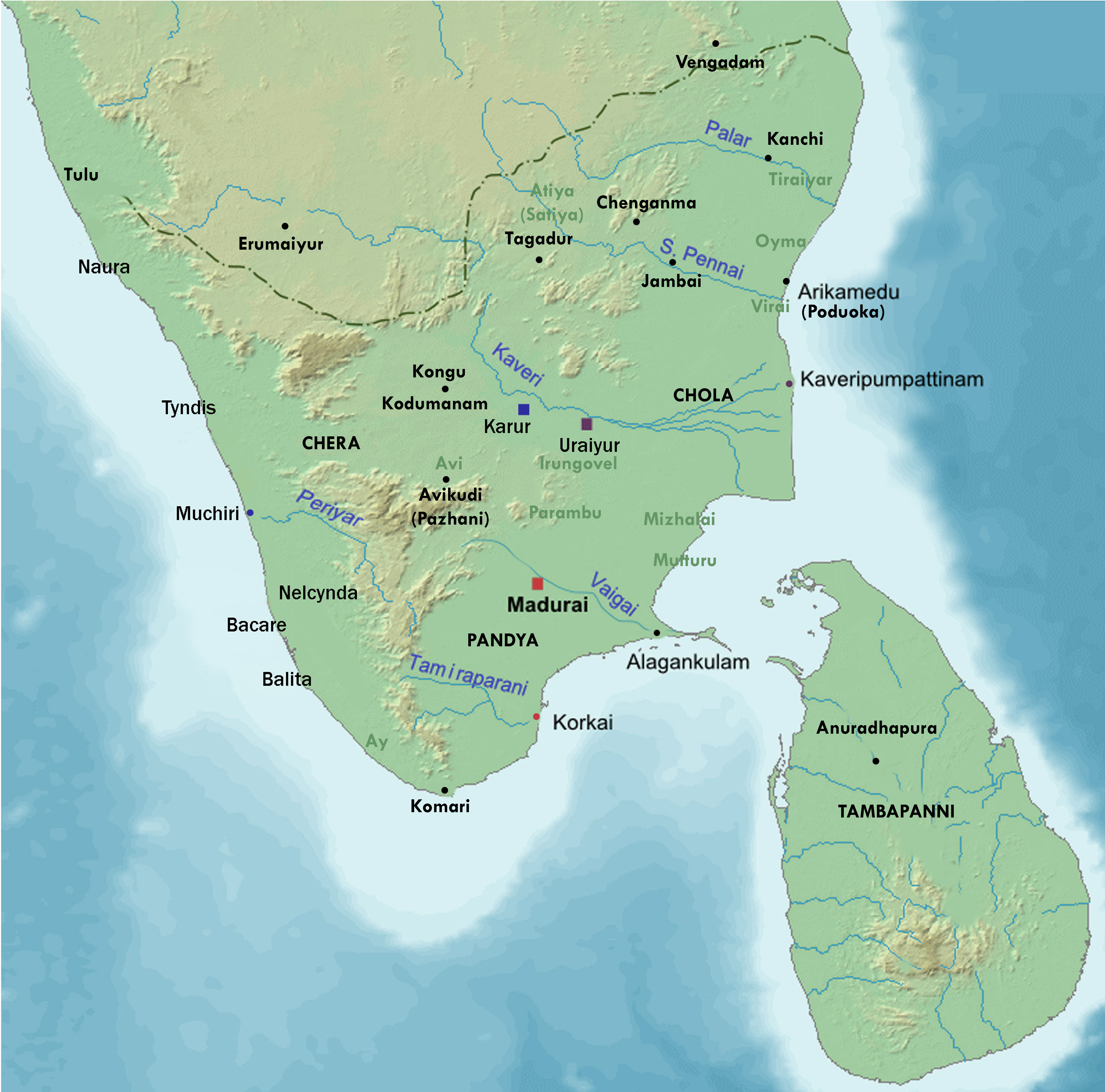
Tamil Literature
Tamil literature has a rich and long literary tradition spanning more than two thousand years. The oldest extant works show signs of maturity indicating an even longer period of evolution. Contributors to the Tamil literature are mainly from Tamil people from South India, including the land now comprising Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Eelam Tamils from Sri Lanka, as well as the Tamil diaspora. The history of Tamil literature follows the history of Tamil Nadu, closely following the social, economical, political and cultural trends of various periods. The early Sangam literature, dated before 300 BCE, contain anthologies of various poets dealing with many aspects of life, including love, war, social values and religion.Akananuru (1, 15, 31, 55, 61, 65, 91, 97, 101, 115, 127, 187, 197, 201, 211, 233, 251, 265, 281, 311, 325, 331, 347, 349, 359, 393, 281, 295), Kurunthogai (11), and Natrinai (14, 75) are dated before 300 BCE. This was followed by the early epics and moral literature, author ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jain Texts
Jain literature (Sanskrit: जैन साहित्य) refers to the literature of the Jain religion. It is a vast and ancient literary tradition, which was initially transmitted orally. The oldest surviving material is contained in the canonical ''Jain Agamas,'' which are written in Ardhamagadhi, a Prakrit ( Middle-Indo Aryan) language. Various commentaries were written on these canonical texts by later Jain monks. Later works were also written in other languages, like Sanskrit and Maharashtri Prakrit. Jain literature is primarily divided between the canons of the ''Digambara'' and ''Śvētāmbara'' orders. These two main sects of Jainism do not always agree on which texts should be considered authoritative. More recent Jain literature has also been written in other languages, like Marathi, Tamil, Rajasthani, Dhundari, Marwari, Hindi, Gujarati, Kannada, Malayalam and more recently in English. Beliefs The Jain tradition believes that their religion is eternal, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kundalakesi
''Kundalakesi'' ( ta, குண்டலகேசி Kuṇṭalakēci, ''lit.'' "woman with curly hair"), also called ''Kuntalakeciviruttam'', is a Tamil Buddhist epic written by Nathakuthanaar, likely sometime in the 10th-century.Aiyangar 2004, p. 360 The epic is a story about love, marriage, getting tired with the married partner, murder and then discovering religion. The ''Kundalakesi'' epic has partially survived into the modern age in fragments, such as in commentaries written centuries later. From these fragments, it appears to be a tragic love story about a Hindu or Jain girl of merchant caste named Kundalakesi who falls in love with Kalan – a Buddhist criminal on a death sentence. The girl's rich merchant father gets the criminal pardoned and freed, the girl marries him. Over time, their love fades and they start irritating each other. During an argument, Kundalakesi reminds him of his criminal past which angers Kalan. A few days later, he invites her to a hike up a hil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tamil Epic Poems
Tamil may refer to: * Tamils, an ethnic group native to India and some other parts of Asia **Sri Lankan Tamils, Tamil people native to Sri Lanka also called ilankai tamils **Tamil Malaysians, Tamil people native to Malaysia * Tamil language, natively spoken by the Tamils * Tamil script, primarily used to write the Tamil language **Tamil (Unicode block), a block of Tamil characters in Unicode * Tamil dialects, referencing geographical variations in speech See also * Tamil cinema, also known as Kollywood, the word being a portmanteau of Kodambakkam and Hollywood. * Tamil cuisine * Tamil culture, is considered to be one of the world's oldest civilizations. * Tamil diaspora * Tamil Eelam, a proposed independent state in the north and east of Sri Lanka * Tamil Nadu, one of the 28 states of India * Tamil nationalism * ''Tamil News'', a daily Tamil-language television news program in Tamil Nadu * Tamilakam, the geographical region inhabited by the ancient Tamil people, covered today's Tam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nannūl
Nannūl ( ta, நன்னூல்) is a work on Tamil grammar written by a Jain ascetic Pavananthi Munivar around 13th century CE. It is the most significant work on Tamil grammar after Tolkāppiyam. The work credits Western Ganga vassal king Seeya Gangan of Kolar with patronising it. About 20 commentaries have been written on Nannūl up to 19th century CE. Nannūl was divided into five sections: written language, spoken language, semantics, poetic language and rhetorical devices. The latter three sections have been lost, so only the parts on written and spoken language are extant today. In Tamil, ''nūl'' means ''book'', and ''Nannūl'' means ''good book''. See also * Karanthai Thirupanamoor and Karanthai are twin villages about 19 km from Kanchipuram. They host historically important Jain temples containing historical inscriptions. There is a population of local Jains in these and nearby villages. Thirupanamoor vil ... Pavananthi munivar References External li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manimegalai
Manimegalai is an Indian television presenter and video jockey who is working in Tamil television industry for almost 12 years. Since 2010, she has regularly been a host for shows on Sun Network before joining Star Vijay in 2019. She gained followers for her boldness in expressing her thoughts and for raising her voice against odds. She is currently participating as comali in Cook with comali (Season 3) along with hosting programs on Vijay TV. Personal life Manimegalai was born in Tiruppur district, Tamil Nadu to businessman Ramaayyappan and Jothimani. She has a younger sibling, Gunamani, who is a Visual Communications graduate. Until class 3, Manimegalai studied in Coimbatore, and then moved to Chennai with her family and continued her schooling at Shanthosh Vidyala Matriculation School. She completed her MBA(dual) in HR & Finance from SRM university (Vadapalani Campus). While at college she started performing as a video jockey on Sun Music. She met assistant choreograp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silappatikaram
''Cilappatikāram'' ( ta, சிலப்பதிகாரம் ml, ചിലപ്പതികാരം,IPA: ʧiləppət̪ikɑːrəm, ''lit.'' "the Tale of an Anklet"), also referred to as ''Silappathikaram'' or ''Silappatikaram'', is the earliest Tamil epic. It is a poem of 5,730 lines in almost entirely ''akaval'' (''aciriyam'') meter. The epic is a tragic love story of an ordinary couple, Kannaki and her husband Kovalan. The ''Silappathikaram'' has more ancient roots in the Tamil bardic tradition, as Kannaki and other characters of the story are mentioned or alluded to in the Sangam literature such as in the ''Naṟṟiṇai'' and later texts such as the ''Kovalam Katai''. It is attributed to a prince-turned-monk Iḷaṅkõ Aṭikaḷ, and was probably composed in the 5th or 6th century CE. The ''Silappatikaram'' is set in a flourishing seaport city of the early Chola kingdom. Kannaki and Kovalan are a newly married couple, in love, and living in bliss. Over time, Kova ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kamil Zvelebil
Kamil Václav Zvelebil (November 17, 1927 – January 17, 2009) was a Czech scholar in Indian literature and linguistics, notably Tamil, Sanskrit, Dravidian linguistics and literature and philology. Life and career Zvelebil studied at the Charles University in Prague from 1946 to 1952 where he majored in Indology, English, literature and philosophy. After obtaining his PhD in 1952 and until 1970 he was a senior research fellow in Tamil and Dravidian linguistics and literature at the Oriental Institute of the Czechoslovak Academy of Sciences. He held the role of associate professor of Tamil and Dravidian at Charles University in Prague until 1968, when he and his family (including his son, the later archaeologist, Marek Zvelebil) were forced to flee after the Warsaw Pact invasion of Czechoslovakia. They fled to the United States at first, but later settled in the Netherlands. During the late 1960s, he made many field trips including those to South India. From 1965 to 1966, he w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tamil Language
Tamil (; ' , ) is a Dravidian language natively spoken by the Tamil people of South Asia. Tamil is an official language of the Indian state of Tamil Nadu, the sovereign nations of Sri Lanka and Singapore, and the Indian territory of Puducherry. Tamil is also spoken by significant minorities in the four other South Indian states of Kerala, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh and Telangana, and the Union Territory of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. It is also spoken by the Tamil diaspora found in many countries, including Malaysia, Myanmar, South Africa, United Kingdom, United States, Canada, Australia and Mauritius. Tamil is also natively spoken by Sri Lankan Moors. One of 22 scheduled languages in the Constitution of India, Tamil was the first to be classified as a classical language of India. Tamil is one of the longest-surviving classical languages of India.. "Tamil is one of the two longest-surviving classical languages in India" (p. 7). A. K. Ramanujan described it as "the on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |