|
VMF(N)-534
Marine Night Fighter Squadron 534 (VMF(N)-534) was a United States Marine Corps night fighter squadron that was commissioned during World War II. It was the fourth night fighter squadron commissioned in the service and participated in limited combat operations throughout 1944 and 1945 during Marine Corps operations over Kwajalein Atoll and the Mariana Islands. The squadron was decommissioned on May 31, 1947, as part of the post-war draw down of the service. Since then, no other Marine Corps squadron has carried the lineage and honors of VMF(N)-534. History Commissioning, training and, deployment VMF(N)-534 was commissioned on October 1, 1943, at Marine Corps Air Station Cherry Point, North Carolina on the authority of Marine Corps Dispatch 292038, dated September 23, 1943. The squadron received its first F6F-3N night fighter on December 1, 1943, and commenced training in eastern North Carolina until departing for the west coast on April 1, 1944. Squadron member arrived at Marin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Warning Squadron 2
Air Warning Squadron 2 (AWS-2) was a United States Marine Corps aviation command and control squadron during World War II. The squadron was tasked to provide aerial surveillance and early warning during amphibious assaults. They took part in the Battle of Guam in 1944 and would eventually move to Peleliu in 1945 assuming responsibility for air defense in that sector until the end of the war. The squadron departed Peleliu for the United States in January 1946 and was quickly decommissioned upon its arrival in California. To date, no other Marine Corps squadron has carried the lineage and honors of AWS-2 to include Marine Air Control Squadron 2 (MACS-2). Mission (Primary) – Operation in the Pacific Ocean Area. To furnish early warning information on approaching air and sea attack and to furnish fighter direction against this attack. (Secondary) – Participation in the local defense when released to the operational control of the Hawaiian Sea Frontier and/or the Seventh A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Interdiction
Air interdiction (AI), also known as deep air support (DAS), is the use of preventive tactical bombing and strafing by combat aircraft against enemy targets that are not an immediate threat, to delay, disrupt or hinder later enemy engagement of friendly forces. It is a core capability of virtually all military air forces, and has been conducted in conflicts since World War I. A distinction is often made between tactical and strategic air interdiction, depending on the objectives of the operation. Typical objectives in tactical interdiction are meant to affect events rapidly and locally, for example through direct destruction of forces or supplies en route to the active battle area. By contrast, strategic objectives are often broader and more long-term, with fewer direct attacks on enemy fighting capabilities, instead focusing on infrastructure, logistics and other supportive assets. The term deep air support relates to close air support and denotes the difference between their re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luganville Airfield
Luganville Airfield or Bomber Field #3 is a former World War II airfield on the island of Espiritu Santo in the New Hebrides Islands at the Espiritu Santo Naval Base. History World War II The Seabees of the 40th Naval Construction Battalion arrived on Santo on 3 February 1943 and were tasked with building a third bomber field in dense jungle to the west of Luganville. By July the Battalion had completed a by coral runway, with of taxiways and 75 hardstands. Additional facilities constructed included a tank farm of six 1,000-barrel steel tanks, two truck-loading stations, two repair areas, fifteen by arch-rib warehouses, one by hangar, eighteen quonset huts for living quarters, six mess halls, and all necessary utilities. of two-lane access and supply roads, were cut through dense jungle. VP-44 operating PBY-5s operated from Luganville from 11 March 1944 until 15 June 1944 when it moved to Nissan Island Nissan Island (also Green Island or Sir Charles Hardy Island) is t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine Corps Air Station Eagle Mountain Lake
Marine Corps Air Station Eagle Mountain Lake (MCAS Eagle Mountain Lake) was a United States Marine Corps air station that was located northwest of Fort Worth, Texas during World War II. Commissioned on December 1, 1942, the air station was originally supposed to be the home of the Marine Corps glider program. When the program was cancelled in 1943 the station became home to the newly created Marine Night Fighting Squadrons. After the war the air station went into caretaker status in December 1946 and became an Outlying Landing Field of Naval Air Station Dallas. After the war, it was used by various branches of the military before being sold to a private owner in the 1970s. Today, the airfield is a private airport run by the Kenneth Copeland Ministry as Kenneth Copeland Airport. History World War II In 1942, of former ranch land were purchased on the eastern shore of Eagle Mountain Lake so the Marine Corps could set up glider operations. Construction of the base began on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine Aircraft Group 53
Marine Aircraft Group 53 (MAG-53) was a United States Marine Corps night fighter training group that was commissioned during World War II. It was the first night-fighter group in the Marine Corps. During the course of the war the group trained eight night fighting squadrons and sent seven of them into combat. The group was decommissioned after the war during the post-war drawdown of forces. History Marine Night Fighting Group 53 (MAG(N)-53) was formed on April 1, 1943 at Marine Corps Air Station Cherry Point, North Carolina. It was the first night fighter group in the Marine Corps and was responsible for the training of all VMF(N) squadrons. The group trained in Vero Beach, Florida in the spring and summer of 1944 and moved to Marine Corps Air Station Eagle Mountain Lake, Texas in November 1944. MAG(N)-53 was re-designated Marine Night Fighter Group 53 (MNFG 53) in April 1945. The group remained in Texas until the end of the war. The group moved back to MCAS Cherry Po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enewetak Atoll
Enewetak Atoll (; also spelled Eniwetok Atoll or sometimes Eniewetok; mh, Ānewetak, , or , ; known to the Japanese as Brown Atoll or Brown Island; ja, ブラウン環礁) is a large coral atoll of 40 islands in the Pacific Ocean and with its 664 people (as of 2011) forms a legislative district of the Ralik Chain of the Marshall Islands. With a land area total less than , it is no higher than and surrounds a deep central lagoon, in circumference. It is the second-westernmost atoll of the Ralik Chain and is west from Bikini Atoll. It was held by the Japanese from 1914 until its capture by the United States in February 1944, during World War II, then became Naval Base Eniwetok. Nuclear testing by the US totaling the equivalent of over 30 megatons of TNT took place during the Cold War; in 1977–1980, a concrete dome (the Runit Dome) was built on Runit Island to deposit radioactive soil and debris. The Runit Dome is deteriorating and could be breached by a typhoon, though ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saipan
Saipan ( ch, Sa’ipan, cal, Seipél, formerly in es, Saipán, and in ja, 彩帆島, Saipan-tō) is the largest island of the Northern Mariana Islands, a Commonwealth (U.S. insular area), commonwealth of the United States in the western Pacific Ocean. According to 2020 estimates by the United States Census Bureau, the population of Saipan was 43,385, a decline of 10% from its 2010 count of 48,220. The legislative and executive branches of Commonwealth government are located in the village of Capitol Hill, Saipan, Capitol Hill on the island while the judicial branch is headquartered in the village of Susupe. Since the entire island is organized as a single municipality, most publications designate Saipan as the Commonwealth's capital. As of 2015, Saipan's mayor is David M. Apatang and the governor of the Northern Mariana Islands is Ralph Torres. History Prehistory Traces of human settlements on Saipan have been found by archaeologists ranging over 4,000 years, includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kobler Field
Kobler Field is a former a World War II airfield on Saipan in the Mariana Islands, part of Naval Advance Base Saipan. It was closed in 1977 and redeveloped as a residential housing area. History World War II Kobler Field was constructed between August and October 1944 near Aslito on the southern end of Saipan as a base for Twentieth Air Force B-29 Superfortresses carrying out the strategic bombing campaign against the Japanese Home Islands. The facility had a runway, repair and maintenance facilities, and hardstanding for 120 aircraft. The airfield was named after Lt. Wayne F. Kobler, a 19th Fighter Squadron pilot who was killed on 27 June 1944 while flying his P-47 on a low-level attack mission on Tinian. As Isely Field, North Field, and West Field on Tinian became operational, Kobler Field was increasingly used by the Twentieth Air Force as an auxiliary field for storage and basing of miscellaneous aircraft. A LORAN navigation station was established at the end of K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nakajima C6N
The Nakajima C6N ''Saiun'' (彩雲, "Iridescent Cloud") was a carrier-based reconnaissance aircraft used by the Imperial Japanese Navy Air Service in World War II. Advanced for its time, it was the fastest carrier-based aircraft put into service by Japan during the war. The Allied reporting name was ''Myrt''. Development and design The C6N originated from a 1942 Imperial Japanese Navy specification for a carrier-based reconnaissance plane with a top speed of 350 knots (650 km/h) at 6,000 m and range of 2,500 nautical miles (4,960 km).Francillon 1970, p. 434. Nakajima's initial proposal, designated N-50, was for a craft with two engines housed in tandem in the fuselage, driving two propellers mounted on the wings. With the development of the class Nakajima Homare engine, the dual powerplant configuration was abandoned and Nakajima decided on a more conventional single-engine layout. Unfortunately the new Homare's power output was less than expected, and the design had to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
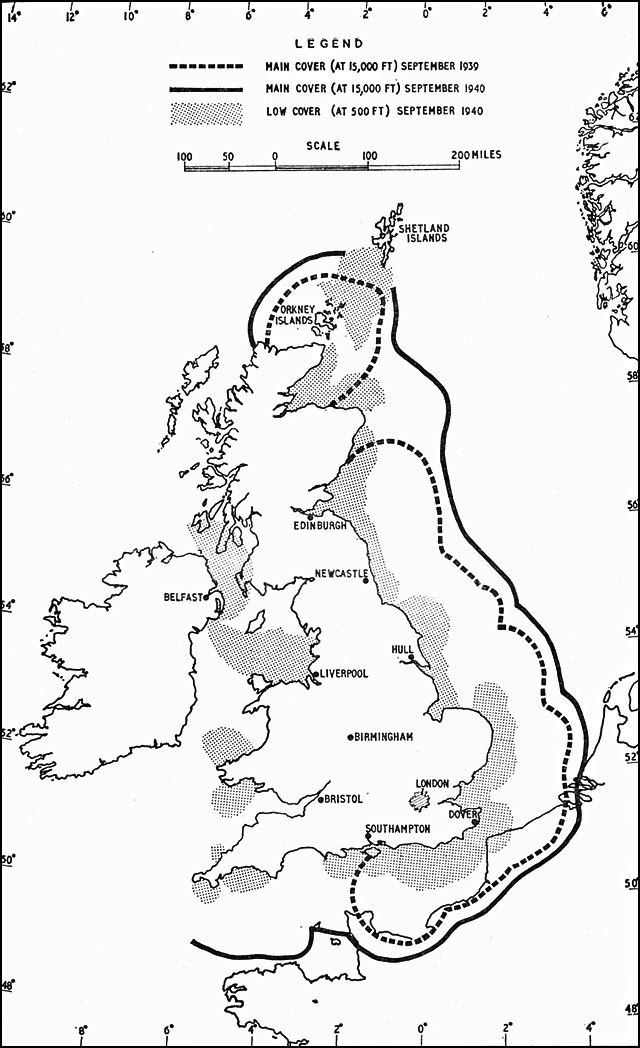
Ground-controlled Interception
Ground-controlled interception (GCI) is an air defence tactic whereby one or more radar stations or other observational stations are linked to a command communications centre which guides interceptor aircraft to an airborne target. This tactic was pioneered during World War I by the London Air Defence Area organization, which became the Royal Air Force's Dowding system in World War II, the first national-scale system. The ''Luftwaffe'' introduced similar systems during the war, but most other combatants did not suffer the same threat of air attack and did not develop complex systems like these until the Cold War era. Today the term GCI refers to the style of battle direction, but during WWII it also referred to the radars themselves. Specifically, the term was used to describe a new generation of radars that spun on their vertical axis in order to provide a complete 360 degree view of the sky around the station. Previous systems, notably Chain Home (CH), could only be directed along ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rota (island)
Rota (Chamorro: Luta), also known as the "Friendly Island", is the southernmost island of the United States Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands (CNMI) and the second southernmost of the Marianas Archipelago. In early Spanish records it is called "Zarpana"; the name Rota may have come from the Spaniards possibly naming the island after the municipality of Rota, Spain. It lies approximately north-northeast of the United States territory of Guam. Sinapalo village is the largest and most populated, followed by Songsong village (Songsong). Rota also functions as one of the four municipalities of the CNMI. History In 1521, the first European to see Rota was the lookout on Ferdinand Magellan's ship ''Victoria'', Lope Navarro. However, Magellan's armada of three ships did not stop until they reached Guam, so the first European to arrive in Rota (in 1524), was the Spanish navigator Juan Sebastián Elcano, who annexed it together with the rest of the Mariana Islands on behalf o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Combat Air Patrol
Combat air patrol (CAP) is a type of flying mission for fighter aircraft. A combat air patrol is an aircraft patrol provided over an objective area, over the force protected, over the critical area of a combat zone, or over an air defense area, for the purpose of intercepting and destroying hostile aircraft before they reach their target. Combat air patrols apply to both overland and overwater operations, protecting other aircraft, fixed and mobile sites on land, or ships at sea. Known by the acronym CAP, it typically entails fighters flying a tactical pattern around or screening a defended target, while looking for incoming attackers. Effective CAP patterns may include aircraft positioned at both high and low altitudes, in order to shorten response times when an attack is detected. Modern CAPs are either GCI or AWACS-controlled to provide maximum early warning for defensive reaction. The first CAPs were characteristic of aircraft carrier operations, where CAPs were flown to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |