|
VAP Protein Family
VAP proteins are conserved integral membrane proteins of the endoplasmic reticulum found in all eukaryotic cells. VAP stands for VAMP-associated protein, where VAMP stands for vesicle-associated membrane protein. Humans have two VAPs that consist of the essential Major Sperm Protein domain and linker plus transmembrane helix) to attach to the ER: VAPA and VAPB. A third VAP-like protein is Motile sperm domain containing 2 (MOSPD2), which has all the elements of VAP, and like them binds FFAT motifs, but has at its N-terminus a CRAL-TRIO domain that can bind and transfer lipids. VAP includes the whole family of protein homologues in all species. For example, baker's yeast Baker's yeast is the common name for the strains of yeast commonly used in baking bread and other bakery products, serving as a leavening agent which causes the bread to rise (expand and become lighter and softer) by converting the fermentable ... expresses two VAPs: Scs2 and Scs22. References {{Reflist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integral Membrane Protein
An integral, or intrinsic, membrane protein (IMP) is a type of membrane protein that is permanently attached to the biological membrane. All ''transmembrane proteins'' are IMPs, but not all IMPs are transmembrane proteins. IMPs comprise a significant fraction of the proteins encoded in an organism's genome. Proteins that cross the membrane are surrounded by annular lipids, which are defined as lipids that are in direct contact with a membrane protein. Such proteins can only be separated from the membranes by using detergents, nonpolar solvents, or sometimes denaturing agents. Structure Three-dimensional structures of ~160 different integral membrane proteins have been determined at atomic resolution by X-ray crystallography or nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. They are challenging subjects for study owing to the difficulties associated with extraction and crystallization. In addition, structures of many water-soluble protein domains of IMPs are available in the Prote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
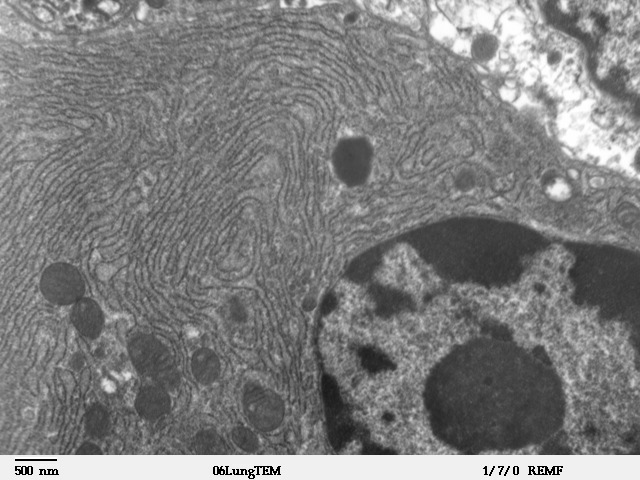
Endoplasmic Reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is, in essence, the transportation system of the eukaryotic cell, and has many other important functions such as protein folding. It is a type of organelle made up of two subunits – rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER), and smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER). The endoplasmic reticulum is found in most eukaryotic cells and forms an interconnected network of flattened, membrane-enclosed sacs known as cisternae (in the RER), and tubular structures in the SER. The membranes of the ER are continuous with the outer nuclear membrane. The endoplasmic reticulum is not found in red blood cells, or spermatozoa. The two types of ER share many of the same proteins and engage in certain common activities such as the synthesis of certain lipids and cholesterol. Different types of cells contain different ratios of the two types of ER depending on the activities of the cell. RER is found mainly toward the nucleus of cell and SER towards the cell membrane or plasma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eukaryotic Cells
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the Three-domain system, three domains of life. Bacteria and Archaea (both prokaryotes) make up the other two domains. The eukaryotes are usually now regarded as having emerged in the Archaea or as a sister of the Asgard (archaea), Asgard archaea. This implies that there are only Two-domain system, two domains of life, Bacteria and Archaea, with eukaryotes incorporated among archaea. Eukaryotes represent a small minority of the number of organisms, but, due to their generally much larger size, their collective global biomass (ecology), biomass is estimated to be about equal to that of prokaryotes. Eukaryotes emerged approximately 2.3–1.8 billion years ago, during the Proterozoic eon, likely as Flagellated cell, flagellated phagotrophs. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vesicle-associated Membrane Protein
Vesicle associated membrane proteins (VAMP) are a family of SNARE proteins with similar structure, and are mostly involved in vesicle fusion. * VAMP1 and VAMP2 proteins known as synaptobrevins are expressed in brain and are constituents of the synaptic vesicles, where they participate in neurotransmitter release. * VAMP3 (known as cellubrevin) is ubiquitously expressed and participates in regulated and constitutive exocytosis as a constituent of secretory granules and secretory vesicles. * VAMP5 and VAMP7 ( SYBL1) participate in constitutive exocytosis. ** VAMP5 is a constituent of secretory vesicles, myotubes and tubulovesicular structures. ** VAMP7 is found both in secretory granules and endosomes. * VAMP8 (known as endobrevin) participates in endocytosis and is found in early endosomes. VAMP8 also participates the regulated exocytosis in pancreatic acinar cells. *VAMP4 Vesicle-associated membrane protein 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''VAMP4'' gene. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homo Sapiens
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, and language. Humans are highly social and tend to live in complex social structures composed of many cooperating and competing groups, from families and kinship networks to political states. Social interactions between humans have established a wide variety of values, social norms, and rituals, which bolster human society. Its intelligence and its desire to understand and influence the environment and to explain and manipulate phenomena have motivated humanity's development of science, philosophy, mythology, religion, and other fields of study. Although some scientists equate the term ''humans'' with all members of the genus ''Homo'', in common usage, it generally refers to ''Homo sapiens'', the only extant member. Anatomically mod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VAPA
VAMP-Associated Protein A ( or Vesicle-Associated Membrane Protein-Associated Protein A) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''VAPA'' gene. Together with VAPB and VAPC it forms the VAP protein family. They are integral endoplasmic reticulum membrane proteins of the type II and are ubiquitous among eukaryotes. VAPA is ubiquitously expressed in human tissues and is thought to be involved in membrane trafficking by interaction with SNAREs, in regulation of lipid transport and metabolism, and in the Unfolded Protein Response ( UPR). Protein structure The protein is divided in three different domains. First, an N-terminal beta-sheet with an immunoglobulin-like fold that shares homology with the Nematode major sperm protein ( MSP). Secondly, a central coiled-coil domain. Then finally a C-terminal transmembrane domain (TMD) which is usually present in proteins of the t-SNARE superfamily and has been found in other proteins associated with vesicular transport. VAPA can form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VAPB
Vesicle-associated membrane protein-associated protein B/C is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''VAPB'' gene. The VAPB gene is found on the 20th human chromosome. Together with VAPA, it forms the VAP protein family. Function The protein encoded by this gene is a type IV membrane protein found in plasma and intracellular vesicle membranes. The encoded protein is found as a homodimer and as a heterodimer with VAPA. This protein also can interact with VAMP1 and VAMP2 and may be involved in vesicle trafficking. Like VAPA, VAPB binds to proteins that contain a FFAT motif. Considerable interest in VAPB has arisen because mutations in this protein are associated with rare, familial forms of motor neuron disease (also called amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and Lou Gehrig's disease Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as motor neuron disease (MND) or Lou Gehrig's disease, is a neurodegenerative disease that results in the progressive loss of motor neur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motile Sperm Domain Containing 2
Motile sperm domain containing 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MOSPD2 gene. It is an endoplasmic reticulum–resident protein involved in membrane contact site formation. Its domain homologous to Major Sperm Protein (MSP domain) is very similar to VAPA/VAPB Vesicle-associated membrane protein-associated protein B/C is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''VAPB'' gene. The VAPB gene is found on the 20th human chromosome. Together with VAPA, it forms the VAP protein family. Function The ..., so it has been described as the third human member of the VAP protein family. References Further reading * External links PDBe-KB provides an overview of all the structure information available in the PDB for Mouse Motile sperm domain-containing protein 2 {{gene-X-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FFAT Motif
A FFAT motif (FFAT being an acronym for two phenylalanines (FF) in an acidic tract) is a protein sequence motif of six defined amino acids plus neighbouring residues that binds to proteins in the VAP protein family. Initial definition The classic FFAT motif was defined on the basis of finding the sequence EFFDAxE in 16 different eukaryotic cytoplasmic proteins (where E = glutamate, F = phenylalanine, D = aspartate, A = alanine, x = any amino acid, according to the single letter amino acid code (see Table of standard amino acid abbreviations and properties in amino acids). In all cases, the core sequence is surrounded by regions that are rich in acids D and E (hence negatively charged), and also in residues that can acquire negative charge by phosphorylation (S and T – serine and threonine). This is the Acidic Tract of the name FFAT, and it is mainly found amino-terminal to the core motif, but also extends to the carboxy-terminal side to some extent. Also, this immediate regio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CRAL-TRIO Domain
CRAL-TRIO domain is a protein structural domain that binds small lipophilic molecules. This domain is named after cellular retinaldehyde-binding protein (CRALBP) and TRIO guanine exchange factor. CRALB protein carries 11-cis-retinol or 11-cis-retinaldehyde. It modulates interaction of retinoids with visual cycle enzymes. TRIO is involved in coordinating actin remodeling, which is necessary for cell migration and growth. Other members of the family are alpha-tocopherol transfer protein and phosphatidylinositol-transfer protein (Sec14). They transport their substrates ( alpha-tocopherol and phosphatidylinositol or phosphatidylcholine, respectively) between different intracellular membranes. Family also include a guanine nucleotide exchange factor that may function as an effector of RAC1 small G-protein. The N-terminal domain of yeast ECM25 protein has been identified as containing a lipid binding CRAL-TRIO domain. Structure The Sec14 protein was the first CRAL-TRIO domain fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Homologue
A protein superfamily is the largest grouping (clade) of proteins for which common ancestry can be inferred (see homology). Usually this common ancestry is inferred from structural alignment and mechanistic similarity, even if no sequence similarity is evident. Sequence homology can then be deduced even if not apparent (due to low sequence similarity). Superfamilies typically contain several protein families which show sequence similarity within each family. The term ''protein clan'' is commonly used for protease and glycosyl hydrolases superfamilies based on the MEROPS and CAZy classification systems. Identification Superfamilies of proteins are identified using a number of methods. Closely related members can be identified by different methods to those needed to group the most evolutionarily divergent members. Sequence similarity Historically, the similarity of different amino acid sequences has been the most common method of inferring homology. Sequence similarity is conside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saccharomyces Cerevisiae
''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' () (brewer's yeast or baker's yeast) is a species of yeast (single-celled fungus microorganisms). The species has been instrumental in winemaking, baking, and brewing since ancient times. It is believed to have been originally isolated from the skin of grapes. It is one of the most intensively studied eukaryotic model organisms in molecular biology, molecular and cell biology, much like ''Escherichia coli'' as the model bacteria, bacterium. It is the microorganism behind the most common type of fermentation (biochemistry), fermentation. ''S. cerevisiae'' cells are round to ovoid, 5–10 micrometre, μm in diameter. It reproduces by budding. Many proteins important in human biology were first discovered by studying their Homology (biology), homologs in yeast; these proteins include cell cycle proteins, signaling proteins, and protein-processing enzymes. ''S. cerevisiae'' is currently the only yeast cell known to have Berkeley body, Berkeley bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |