|
VACTERL
The VACTERL association (also VATER association, and less accurately VACTERL syndrome) refers to a recognized group of birth defects which tend to co-occur (see below). This pattern is a recognized association, as opposed to a syndrome, because there is no known pathogenetic cause to explain the grouped incidence. Each child with this condition can be unique. At present this condition is treated after birth with issues being approached one at a time. Some infants are born with symptoms that cannot be treated and they do not survive. Also, VACTERL association can be linked to other similar conditions such as Klippel Feil and Goldenhar syndrome including crossovers of conditions. No specific genetic or chromosome problem has been identified with VACTERL association. VACTERL can be seen with some chromosomal defects such as Trisomy 18 and is more frequently seen in babies of diabetic mothers. VACTERL association, however, is most likely caused by multiple factors. VACTERL associat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
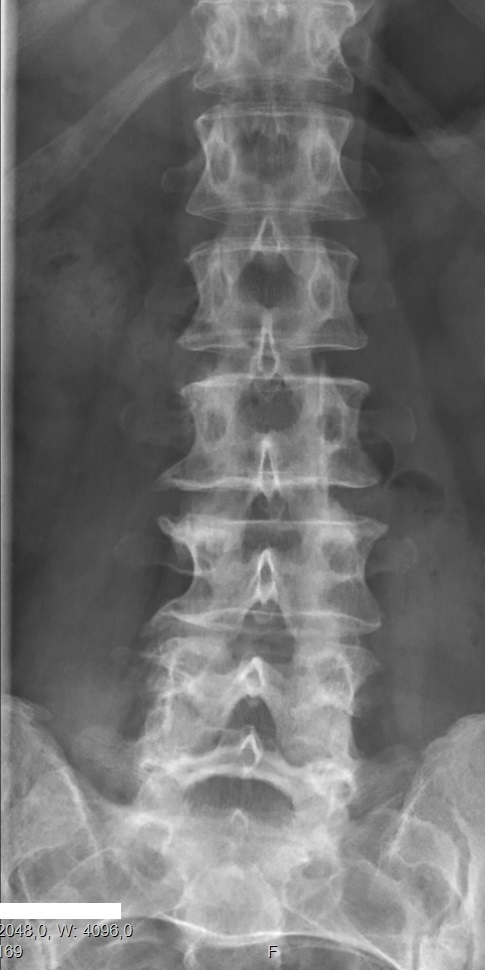
Vertebral Anomalies
Congenital vertebral anomalies are a collection of malformations of the spine. Most, around 85%, are not clinically significant, but they can cause compression of the spinal cord by deforming the vertebral canal or causing instability. This condition occurs in the womb. Congenital vertebral anomalies include alterations of the shape and number of vertebrae. Lumbarization and sacralization ''Lumbarization'' is an anomaly in the spine. It is defined by the nonfusion of the first and second segments of the sacrum. The lumbar spine subsequently appears to have six vertebrae or segments, not five. This sixth lumbar vertebra is known as a transitional vertebra. Conversely the sacrum appears to have only four segments instead of its designated five segments. Lumbosacral transitional vertebrae consist of the process of the last lumbar vertebra fusing with the first sacral segment. While only around 10 percent of adults have a spinal abnormality due to genetics, a sixth lumbar verteb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congenital Heart Disease
A congenital heart defect (CHD), also known as a congenital heart anomaly and congenital heart disease, is a defect in the structure of the heart or great vessels that is present at birth. A congenital heart defect is classed as a cardiovascular disease. Signs and symptoms depend on the specific type of defect. Symptoms can vary from none to life-threatening. When present, symptoms may include rapid breathing, bluish skin (cyanosis), poor weight gain, and feeling tired. CHD does not cause chest pain. Most congenital heart defects are not associated with other diseases. A complication of CHD is heart failure. The cause of a congenital heart defect is often unknown. Risk factors include certain infections during pregnancy such as rubella, use of certain medications or drugs such as alcohol or tobacco, parents being closely related, or poor nutritional status or obesity in the mother. Having a parent with a congenital heart defect is also a risk factor. A number of genetic condition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperforate Anus
An imperforate anus or anorectal malformations (ARMs) are birth defects in which the rectum is malformed. ARMs are a spectrum of different congenital anomalies which vary from fairly minor lesions to complex anomalies. The cause of ARMs is unknown; the genetic basis of these anomalies is very complex because of their anatomical variability. In 8% of patients, genetic factors are clearly associated with ARMs. Anorectal malformation in Currarino syndrome represents the only association for which the gene ''HLXB9'' has been identified. Types There are other forms of anorectal malformations though imperforate anus is most common. Other variants include anterior ectopic anus. This form is more commonly seen in females and presents with constipation. Presentation There are several forms of imperforate anus and anorectal malformations. The new classification is in relation of the type of associated fistula. The classical Wingspread classification was in low and high anomalies: * A lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anorectal Malformations
An imperforate anus or anorectal malformations (ARMs) are birth defects in which the rectum is malformed. ARMs are a spectrum of different congenital anomalies which vary from fairly minor lesions to complex anomalies. The cause of ARMs is unknown; the genetic basis of these anomalies is very complex because of their anatomical variability. In 8% of patients, genetic factors are clearly associated with ARMs. Anorectal malformation in Currarino syndrome represents the only association for which the gene ''HLXB9'' has been identified. Types There are other forms of anorectal malformations though imperforate anus is most common. Other variants include anterior ectopic anus. This form is more commonly seen in females and presents with constipation. Presentation There are several forms of imperforate anus and anorectal malformations. The new classification is in relation of the type of associated fistula. The classical Wingspread classification was in low and high anomalies: * A lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radial Aplasia
Radial aplasia is a congenital defect which affects the formation of the radius bone in the arm. The radius is the lateral bone (thumb side) which connects the humerus of the upper arm to the wrist via articulation with the carpal bones. A child born with this condition has either a short or absent radius bone in one or both of his or her arms. Radial aplasia also results in the thumb being either partly formed or completely absent from the hand, which can result in difficulties performing activities of daily living. Radial aplasia is connected with the condition VACTERL association The VACTERL association (also VATER association, and less accurately VACTERL syndrome) refers to a recognized group of birth defects which tend to co-occur (see below). This pattern is a recognized association, as opposed to a syndrome, because th ..., under the 'L' for limb malformations. Radial aplasia is not inherited. The cause for radial aplasia is unknown, but it widely believed to occur within ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tracheoesophageal Fistula
A tracheoesophageal fistula (TEF, or TOF; see spelling differences) is an abnormal connection (fistula) between the esophagus and the trachea. TEF is a common congenital abnormality, but when occurring late in life is usually the sequela of surgical procedures such as a laryngectomy. Presentation Tracheoesophageal fistula is suggested in a newborn by copious salivation associated with choking, coughing, vomiting, and cyanosis coincident with the onset of feeding. Esophageal atresia and the subsequent inability to swallow typically cause polyhydramnios in utero. Rarely it may present in an adult. Complications Surgical repair can sometimes result in complications, including: * Stricture, due to gastric acid erosion of the shortened esophagus * Leak of contents at the point of anastomosis * Recurrence of fistula * Gastro-esophageal reflux disease * Dysphagia * Asthma-like symptoms, such as persistent coughing/wheezing * Recurrent chest infections * Tracheomalacia Associations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oesophageal Atresia
The esophagus (American English) or oesophagus (British English; both ), non-technically known also as the food pipe or gullet, is an organ in vertebrates through which food passes, aided by peristaltic contractions, from the pharynx to the stomach. The esophagus is a fibromuscular tube, about long in adults, that travels behind the trachea and heart, passes through the diaphragm, and empties into the uppermost region of the stomach. During swallowing, the epiglottis tilts backwards to prevent food from going down the larynx and lungs. The word ''oesophagus'' is from Ancient Greek οἰσοφάγος (oisophágos), from οἴσω (oísō), future form of φέρω (phérō, “I carry”) + ἔφαγον (éphagon, “I ate”). The wall of the esophagus from the lumen outwards consists of mucosa, submucosa (connective tissue), layers of muscle fibers between layers of fibrous tissue, and an outer layer of connective tissue. The mucosa is a stratified squamous epithelium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tracheoesophageal Fistula
A tracheoesophageal fistula (TEF, or TOF; see spelling differences) is an abnormal connection (fistula) between the esophagus and the trachea. TEF is a common congenital abnormality, but when occurring late in life is usually the sequela of surgical procedures such as a laryngectomy. Presentation Tracheoesophageal fistula is suggested in a newborn by copious salivation associated with choking, coughing, vomiting, and cyanosis coincident with the onset of feeding. Esophageal atresia and the subsequent inability to swallow typically cause polyhydramnios in utero. Rarely it may present in an adult. Complications Surgical repair can sometimes result in complications, including: * Stricture, due to gastric acid erosion of the shortened esophagus * Leak of contents at the point of anastomosis * Recurrence of fistula * Gastro-esophageal reflux disease * Dysphagia * Asthma-like symptoms, such as persistent coughing/wheezing * Recurrent chest infections * Tracheomalacia Associations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypoplastic Thumb
Thumb hypoplasia is a spectrum of congenital abnormalities of the thumb varying from small defects to complete absence of the thumb.Riley, S.A. & Burgess, R.C. (2009). Thumb Hypoplasia. ''Journal of Hand Surgery'', vol 34A, 1564–1573 It can be isolated, when only the thumb is affected, and in 60% of the casesAshbaugh, H. & Gellman, H. (2009). Congenital Thumb Deformities and Associated Syndromes. Journal of Craniofacial Surgery, vol 20, number 4, 1039–1044 it is associated with radial dysplasia (or radial club, radius dysplasia, longitudinal radial deficiency). Radial dysplasia is the condition in which the forearm bone and the soft tissues on the thumb side are underdeveloped or absent.Manske, P.R. & Goldfarb, C.A. (2009). Congenital Failure of Formation of the Upper Limb. ''Hand Clinics'', 25, 157–170 In an embryo the upper extremities develop from week four of the gestation. During the fifth to eighth week the thumb will further develop.Hovius, S., Foucher, G. & Raimondi, P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syndrome
A syndrome is a set of medical signs and symptoms which are correlated with each other and often associated with a particular disease or disorder. The word derives from the Greek σύνδρομον, meaning "concurrence". When a syndrome is paired with a definite cause this becomes a disease. In some instances, a syndrome is so closely linked with a pathogenesis or cause that the words ''syndrome'', ''disease'', and ''disorder'' end up being used interchangeably for them. This substitution of terminology often confuses the reality and meaning of medical diagnoses. This is especially true of inherited syndromes. About one third of all phenotypes that are listed in OMIM are described as dysmorphic, which usually refers to the facial gestalt. For example, Down syndrome, Wolf–Hirschhorn syndrome, and Andersen–Tawil syndrome are disorders with known pathogeneses, so each is more than just a set of signs and symptoms, despite the ''syndrome'' nomenclature. In other instances, a synd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesoderm
The mesoderm is the middle layer of the three germ layers that develops during gastrulation in the very early development of the embryo of most animals. The outer layer is the ectoderm, and the inner layer is the endoderm.Langman's Medical Embryology, 11th edition. 2010. The mesoderm forms mesenchyme, mesothelium, non-epithelial blood cells and coelomocytes. Mesothelium lines coeloms. Mesoderm forms the muscles in a process known as myogenesis, septa (cross-wise partitions) and mesenteries (length-wise partitions); and forms part of the gonads (the rest being the gametes). Myogenesis is specifically a function of mesenchyme. The mesoderm differentiates from the rest of the embryo through intercellular signaling, after which the mesoderm is polarized by an organizing center. The position of the organizing center is in turn determined by the regions in which beta-catenin is protected from degradation by GSK-3. Beta-catenin acts as a co-factor that alters the activity of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetralogy Of Fallot
Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF), formerly known as Steno-Fallot tetralogy, is a congenital heart defect characterized by four specific cardiac defects. Classically, the four defects are: *pulmonary stenosis, which is narrowing of the exit from the right ventricle; * a ventricular septal defect, which is a hole allowing blood to flow between the two ventricles; * right ventricular hypertrophy, which is thickening of the right ventricular muscle; and * an overriding aorta, which is where the aorta expands to allow blood from both ventricles to enter. At birth, children may be asymptomatic or present with many severe symptoms. Later in infancy, there are typically episodes of bluish colour to the skin due to a lack of sufficient oxygenation, known as cyanosis. When affected babies cry or have a bowel movement, they may undergo a "tet spell" where they turn cyanotic, have difficulty breathing, become limp, and occasionally lose consciousness. Other symptoms may include a heart murmur, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |