|
Värmland Savonian Dialect
Värmland Finnish dialect ( fi, Vermlannin savolaismurteet) is an extinct Savonian dialect spoken in Värmland by the Forest Finns. However some speakers also lived in Norway. In Savonian dialects The Savonian dialects (also called Savo Finnish)( fi, Savolaismurteet) are forms of the Finnish language spoken in Savonia and other parts of Eastern Finland. Finnish dialects are grouped broadly into Eastern and Western varieties; Savonian diale ..., a vowel is inserted in the middle of a word ''talavi'' 'winter' (written Finnish "talvi"), however this feature is completely lacking from Värmland Finnish, which suggests it was a later development in Savonian. History Savo Finnish speakers came to Sweden during the 1600s (mainly from Rautalampi). During the 1800s, there were thousands of Finnish speakers in Värmland. Unlike Savonian, the Värmland dialect did not have consonant gemination or the schwa, because they were later developments in the Savonian dialects spoken in Fin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Värmland
Värmland () also known as Wermeland, is a ''landskap'' (historical province) in west-central Sweden. It borders Västergötland, Dalsland, Dalarna, Västmanland, and Närke, and is bounded by Norway in the west. Latin name versions are ''Varmelandia'', ''Vermelandia'', ''Wermelandia'', ''Værmalandia'', ''Værmolandia'', ''Virmolandia'' and ''Vermillandia''. Some of the Latinised forms show the origin of the name to come from the large local lake by the name of (from older ''*Virmil''); others from the river name ''*Værma'', the main outlet of that lake. The province was originally part of Götaland, and became part of Svealand in 1815. Geography The largest lake is Vänern. Most streams of importance lead to Vänern. However, the province is rich in small lakes, ponds and streams. The scenery, with mountains and lakes, is usually regarded as picturesque and has inspired painters and writers. Western Värmland There are several mountain plateaus in the western p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finnic Languages
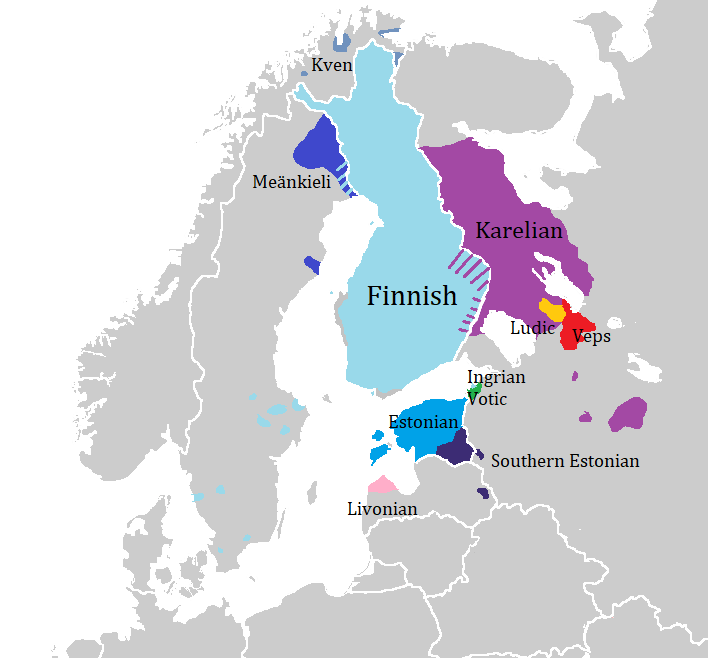
The Finnic (''Fennic'') or more precisely Balto-Finnic (Balto-Fennic, Baltic Finnic, Baltic Fennic) languages constitute a branch of the Uralic language family spoken around the Baltic Sea by the Baltic Finnic peoples. There are around 7 million speakers, who live mainly in Finland and Estonia. Traditionally, eight Finnic languages have been recognized. The major modern representatives of the family are Finnish and Estonian, the official languages of their respective nation states.Finnic Peoples at Encyclopædia Britannica The other Finnic languages in the Baltic Sea region are Ingrian and |
Finnish Language
Finnish (endonym: or ) is a Uralic language of the Finnic branch, spoken by the majority of the population in Finland and by ethnic Finns outside of Finland. Finnish is one of the two official languages of Finland (the other being Swedish). In Sweden, both Finnish and Meänkieli (which has significant mutual intelligibility with Finnish) are official minority languages. The Kven language, which like Meänkieli is mutually intelligible with Finnish, is spoken in the Norwegian county Troms og Finnmark by a minority group of Finnish descent. Finnish is typologically agglutinative and uses almost exclusively suffixal affixation. Nouns, adjectives, pronouns, numerals and verbs are inflected depending on their role in the sentence. Sentences are normally formed with subject–verb–object word order, although the extensive use of inflection allows them to be ordered differently. Word order variations are often reserved for differences in information structure. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Finnish Dialects
Eastern Finnish dialects are chiefly vested in the Savonians (the Savo Finnish, Savonian dialects) and the Karelians (Finns), Karelians (the South Karelian dialects, southeast Finnish dialects). One of the Finnish language spoken group, the North Karelian, represents the East Finnish dialects, however this distinction is not established in any case. Other dialects, such as the North Finnish dialects, are considered as East or West Finnish dialects. Kalevala, one of the earliest and most significant works of Finnish literature, was written in East Finnish and East Finnish features were used extensively in the Finnish language standardization. There is less influence from Scandinavian and Finland-Swedish culture and language. The language is distinguished by vowel-diphthong shifts with respect to the standard language, and the use of palatalization (sound change), palatalization. Epenthetic vowels are added after /l/, /h/ and sometimes /n/ in stressed syllable coda preceding a conso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Savonian Dialects
The Savonian dialects (also called Savo Finnish)( fi, Savolaismurteet) are forms of the Finnish language spoken in Savonia and other parts of Eastern Finland. Finnish dialects are grouped broadly into Eastern and Western varieties; Savonian dialects are of the Eastern variety. Savonian dialects are the most widely distributed Finnish dialect group (setting aside the higher-level east/west split mentioned above). They are spoken in the Savonia region (in both North and South Savo), but also in North Karelia, parts of Päijät-Häme, Central Finland, Kainuu, Koillismaa district of Northern Ostrobothnia, the lake section between Southern and Central Ostrobothnia as far north as Evijärvi and in the municipalities of Pudasjärvi and the Southern part of Ranua in Lapland. Also the language spoken by forest settlers in Värmland and Norwegian Hedmark of Central Scandinavia belonged to the old Savonian dialects. The geographical area the Savonian dialects cover makes up one-third ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forest Finns
Forest Finns ( fi, Metsäsuomalaiset, Norwegian bokmål: ''Skogfinner'', Norwegian nynorsk: ''Skogfinnar'', sv, Skogsfinnar) were Finnish migrants from Savonia and Northern Tavastia in Finland who settled in forest areas of Sweden proper and Norway during the late 16th and early-to-mid-17th centuries, and traditionally pursued slash-and-burn agriculture, a method used for turning forests into farmlands. By the late 18th century, the Forest Finns had become largely assimilated into the Swedish and Norwegian cultures, and their language, a variety of Savonian Finnish (Värmland Savonian dialect), is today extinct, although it survived among a tiny minority until the 20th century. Etymology The use of the term "Forest Finns" is first reported in sanctions issued by the Dano-Norwegian king in 1648, although they (at least locally in Norway) more commonly were known as ('' Savonian Finns''), (''Rye Finns'') from their major crop, or notably (''Slash-and-burn Finns''). The peop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the archipelago of Svalbard also form part of Norway. Bouvet Island, located in the Subantarctic, is a dependency of Norway; it also lays claims to the Antarctic territories of Peter I Island and Queen Maud Land. The capital and largest city in Norway is Oslo. Norway has a total area of and had a population of 5,425,270 in January 2022. The country shares a long eastern border with Sweden at a length of . It is bordered by Finland and Russia to the northeast and the Skagerrak strait to the south, on the other side of which are Denmark and the United Kingdom. Norway has an extensive coastline, facing the North Atlantic Ocean and the Barents Sea. The maritime influence dominates Norway's climate, with mild lowland temperatures on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
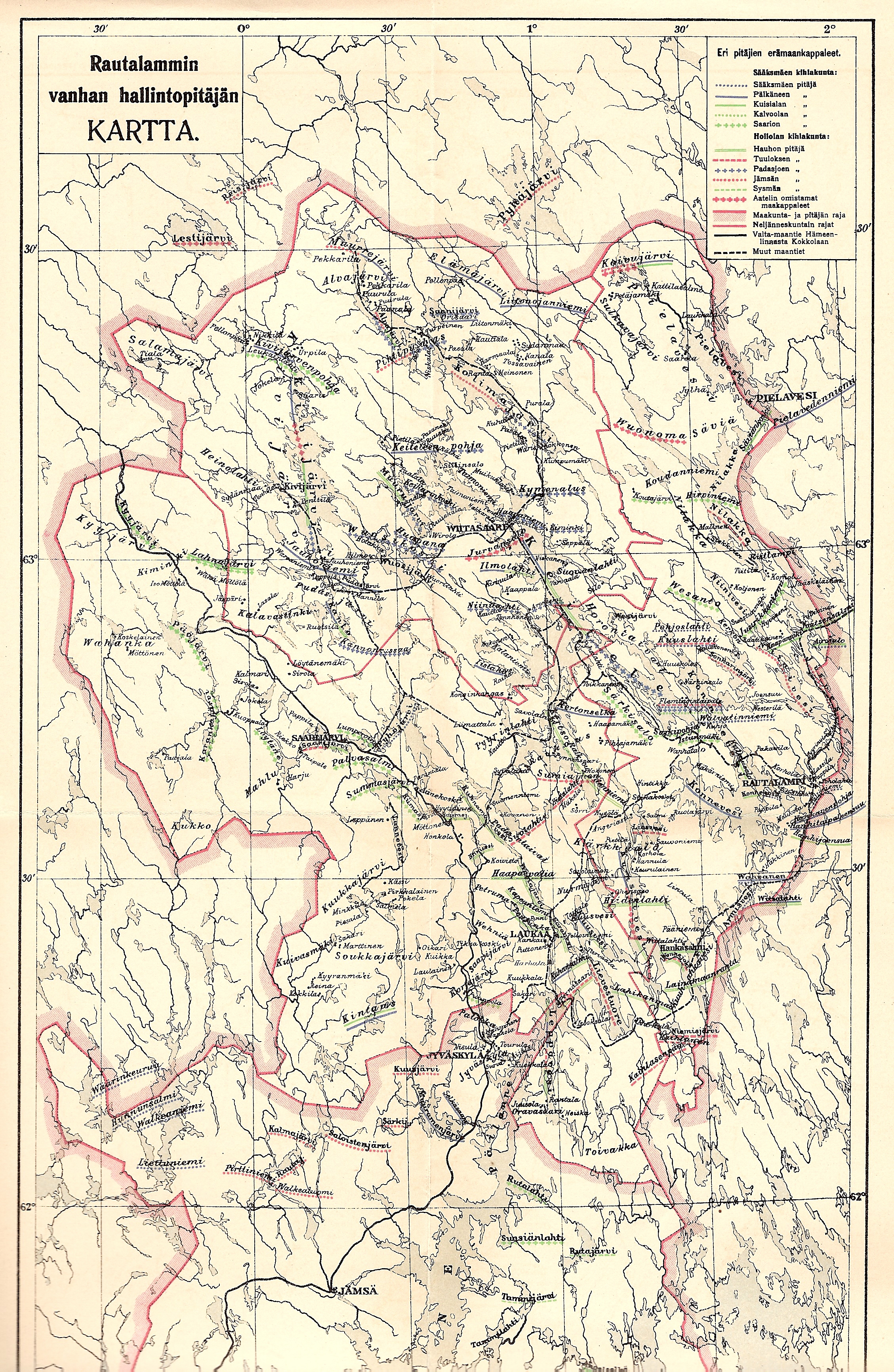
Rautalampi
Rautalampi is a municipality of Finland. It is located in the Northern Savonia region. The municipality has a population of () and covers an area of of which is water. The population density is . The municipality is unilingually Finnish. Neighbouring municipalities are Hankasalmi, Konnevesi, Pieksämäki Pieksämäki () is a town and municipality of Finland. It is located in the Southern Savonia region, about north of Mikkeli, east of Jyväskylä and south of Kuopio. The town has a population of () and covers an area of of which is water. The ..., Suonenjoki, Tervo and Vesanto. The distance from Rautalampi to Kuopio is about 70 kilometers. Name The name of the municipality means "iron pond", which is also why the coat of arms of the municipality features the symbol of iron. History The village was first mentioned in 1549, when it was a part of the parish (''pitäjä'') of Sysmä. The parish (''pitäjä'') of Rautalampi was established in 1561. It was a large pari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |