|
Vranjina Island
Vranjina ( cnr, Врањина) is a settlement, island, and a hill in Lake Skadar, in the Montenegrin municipality of Podgorica. Until the first half of the 18th century, Vranjina like other islands of Skadar lake, was one of the hills in the Zeta–Skadar lowlands. Island Created by a delta of the Morača River, the island is in the northern part of the lake. It has an area of 4.6 km2 and its highest point is at 296 meters, making it the highest island in Montenegro. The island is connected to the mainland by a bridge, towards Podgorica, and a causeway, across the lake towards Bar. Vranjina Monastery is a well-known feature of the island. According to the legend, the island had different name before the monastery has been built. When Ilarion Šišojević, the first metropolitan bishop of the Zetan Orthodox Metropolitanate, started the construction of the monastery he decided that the island will be named against the first bird he would notice. It was a crow ( sr, В� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Žabljak Crnojevića
Žabljak Crnojevića ( sr-cyrl, Жабљак Црнојевића, ), commonly referred to as Žabljak, is an abandoned medieval fortified town (fortress) in Montenegro. The fortress is located on the confluence of the Morača river in Lake Skadar. History It is believed that this fortress was founded in the 10th century during the reign of the Vojislavljević dynasty in then-known Dioclea, whereas the first known written testimony of the fortress originate from mid-14th century. The fortress served as the capital of Zeta under the Crnojević dynasty from 1466 till 1478, being the seat of Stefan and Ivan Crnojević. However, Ivan Crnojević was forced to move the capital in 1478 when the Ottomans seized the town during the siege of Shkodra, holding it until the decision of the Berlin Congress in 1878 when it fell under Montenegrin administration once again after 400 years of Turkish rule. The town has tall walls with towers, as well as one gate. Within the walls can be found: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zetan Orthodox Metropolitanate
The Metropolitanate of Montenegro and the Littoral of the Serbian Orthodox Church ( sr, Митрополија црногорско-приморска Српске православне цркве, Mitropolija crnogorsko-primorska Srpske pravoslavne crkve) is the largest eparchy (diocese) of the Serbian Orthodox Church in modern Montenegro. Founded in 1219 by Saint Sava, as the ''Eparchy of Zeta'', it continued to exist, without interruption, up to the present time, and remained one of the most prominent dioceses of the Serbian Orthodox Church. The current Metropolitan bishop is Joanikije. His official title is "Metropolitan of Montenegro and the Littoral" ( sr, Mитрополит црногорско-приморски, Arhiepiskop cetinjski i mitropolit crnogorsko-primorski). History Eparchy of Zeta (1219–1346) The Eparchy of Zeta was founded in 1219 by Sava of the Nemanjić dynasty, the first Archbishop of the autocephalous Serbian Orthodox Church. After receiving the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islands Of Montenegro
An island (or isle) is an isolated piece of habitat that is surrounded by a dramatically different habitat, such as water. Very small islands such as emergent land features on atolls can be called islets, skerries, cays or keys. An island in a river or a lake island may be called an eyot or ait, and a small island off the coast may be called a holm. Sedimentary islands in the Ganges delta are called chars. A grouping of geographically or geologically related islands, such as the Philippines, is referred to as an archipelago. There are two main types of islands in the sea: continental and oceanic. There are also artificial islands, which are man-made. Etymology The word ''island'' derives from Middle English ''iland'', from Old English ''igland'' (from ''ig'' or ''ieg'', similarly meaning 'island' when used independently, and -land carrying its contemporary meaning; cf. Dutch ''eiland'' ("island"), German ''Eiland'' ("small island")). However, the spelling of the word ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
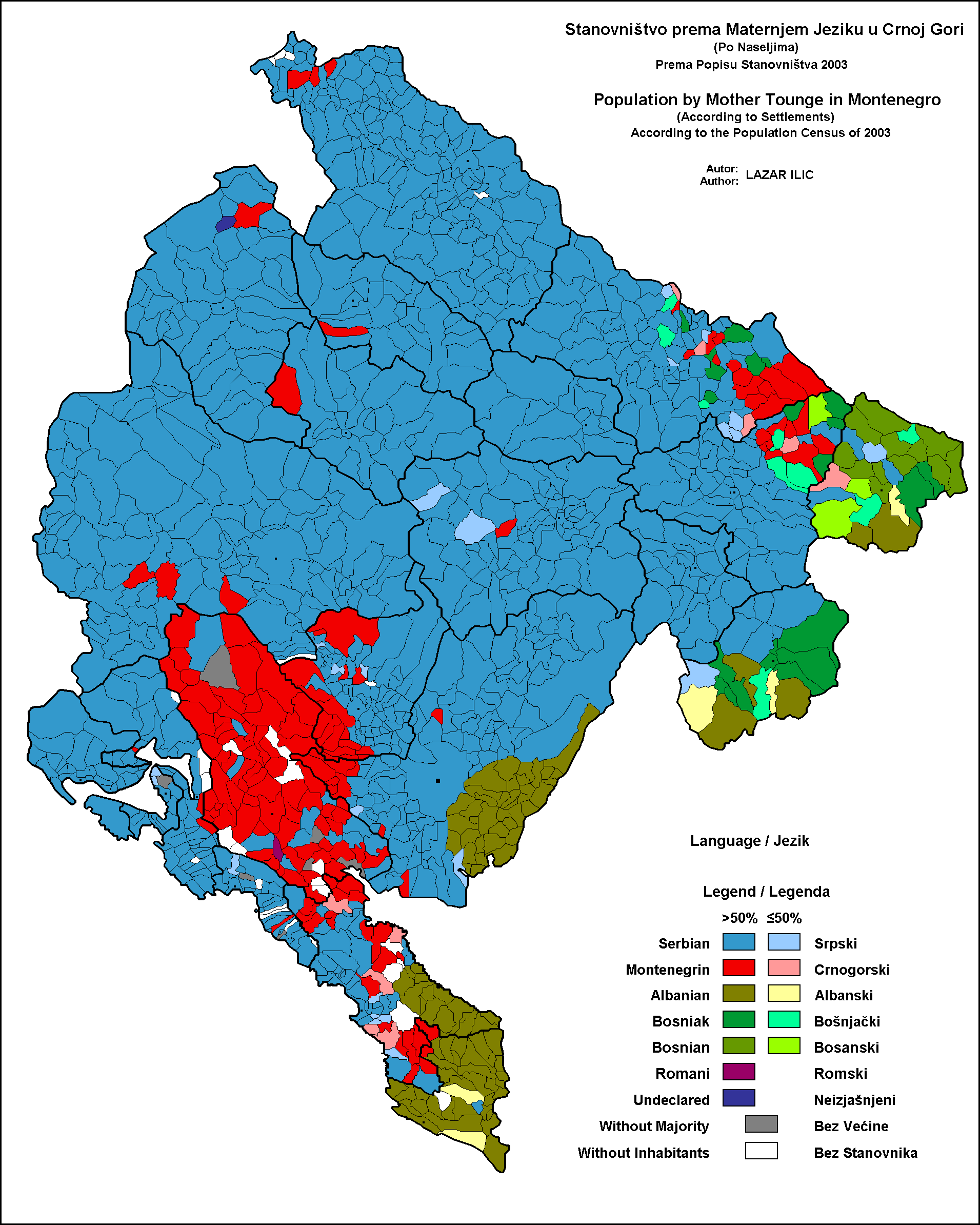
Serbian Language
Serbian (, ) is the standardized variety of the Serbo-Croatian language mainly used by Serbs. It is the official and national language of Serbia, one of the three official languages of Bosnia and Herzegovina and co-official in Montenegro and Kosovo. It is a recognized minority language in Croatia, North Macedonia, Romania, Hungary, Slovakia, and the Czech Republic. Standard Serbian is based on the most widespread dialect of Serbo-Croatian, Shtokavian (more specifically on the dialects of Šumadija-Vojvodina and Eastern Herzegovina), which is also the basis of standard Croatian, Bosnian, and Montenegrin varieties and therefore the Declaration on the Common Language of Croats, Bosniaks, Serbs, and Montenegrins was issued in 2017. The other dialect spoken by Serbs is Torlakian in southeastern Serbia, which is transitional to Macedonian and Bulgarian. Serbian is practically the only European standard language whose speakers are fully functionally digraphic, using both Cyril ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montenegrin Language
Montenegrin ( ; cnr, label=none, / ) is a normative variety of the Serbo-Croatian language mainly used by Montenegrins and is the official language of Montenegro. Montenegrin is based on the most widespread dialect of Serbo-Croatian, Shtokavian, more specifically on Eastern Herzegovinian, which is also the basis of Standard Croatian, Serbian, and Bosnian. Montenegro's language has historically and traditionally been called either Serbian or Montenegrin. The idea of a standardized Montenegrin standard language separate from Serbian appeared in the 1990s during the breakup of Yugoslavia, through proponents of Montenegrin independence from the State Union of Serbia and Montenegro. Montenegrin became the official language of Montenegro with the ratification of a new constitution on 22 October 2007. Language standardization In January 2008, the government of Montenegro formed the Board (Council) for Standardization of the Montenegrin Language, which aims to standardize the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serbs Of Montenegro
Serbs of Montenegro ( sr, / ) or Montenegrin Serbs ( sr, / ),, meaning "Montenegrin Serbs", and meaning "Serbs Montenegrins". Specifically, Their regional autonym is simply , literal meaning "Montenegrins",Charles Seignobos, Political History of Europe, since 1814, ed. S. M. Macvane, H. Holt and Company, New York, 1900, pp. 663–664; excerpt from chapter XXI The Christian Nations of The Balkans, subchapter Servia and Montenegro, passages Montenegro the same as the ethnic group of ''Montenegrins''). In the early modern times, before the Kingdom of Montenegro, people iving within present-day borderswere divided by the identities of (; Brda), (; Old Herzegovina), (; Boka Kotorska) and (; Old Montenegro). , meaning "Serbs in Montenegro". compose native and the second largest ethnic group in Montenegro (28.7% of country's population), after the ethnic Montenegrins. Additional 0.64% of the population is made up of ''Serbs-Montenegrins'' () and ''Montenegrins-Serbs'' (). Hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montenegrins
Montenegrins ( cnr, Црногорци, Crnogorci, or ; lit. "Black Mountain People") are a South Slavic ethnic group that share a common Montenegrin culture, history, and language, identified with the country of Montenegro. Genetics According to one triple analysis – autosomal, mitochondrial and paternal — of available data from large-scale studies on Balto-Slavs and their proximal populations, the whole genome SNP data situates Montenegrins with Serbs in between two Balkan clusters. According to a 2020 autosomal marker analysis, Montenegrins are situated in-between Serbians and Kosovo Albanians. Y-DNA genetic study done in 2010 on 404 male individuals from Montenegro gave the following results: haplogroup I2a (29.7%), E-V13 (26.9%), R1b (9.4%), R1a (7.6%), I1 (6.1%), J2a1 (4.7%), J2b (4.4%), G2a (2.4%), Q (1.9%), I2b (1.7%), N (1.4%), H (1.4%), L (1.2%), and J1 (0.49%). A 2022 study on 267 samples from northeastern Montenegro found that the "most common hap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistical Office Of Montenegro
Statistical Office of Montenegro ( cnr, Uprava za statistiku Crne Gore) or MONSTAT is the statistics agency of Montenegro. It provides information service and indicators for monitoring the economic and social development of Montenegro, and regularly publishes publications compiling figures about the country. References External links * Montenegro ) , image_map = Europe-Montenegro.svg , map_caption = , image_map2 = , capital = Podgorica , coordinates = , largest_city = capital , official_languages = M ... Demographics of Montenegro Government of Montenegro {{org-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albanians
The Albanians (; sq, Shqiptarët ) are an ethnic group and nation native to the Balkan Peninsula who share a common Albanian ancestry, culture, history and language. They primarily live in Albania, Kosovo, North Macedonia, Montenegro, Serbia as well as in Croatia, Greece, Italy and Turkey. They also constitute a large diaspora with several communities established across Europe, the Americas and Oceania. Albanians have Paleo-Balkanic origins. Exclusively attributing these origins to the Illyrians, Thracians or other Paleo-Balkan people is still a matter of debate among historians and ethnologists. The first certain reference to Albanians as an ethnic group comes from 11th century chronicler Michael Attaleiates who describes them as living in the theme of Dyrrhachium. The Shkumbin River roughly demarcates the Albanian language between Gheg and Tosk dialects. Christianity in Albania was under the jurisdiction of the Bishop of Rome until the 8th century AD. Then, dioceses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) // CITED: p. 36 (PDF p. 38/338) also known as the Turkish Empire, was an empire that controlled much of Southeast Europe, Western Asia, and Northern Africa between the 14th and early 20th centuries. It was founded at the end of the 13th century in northwestern Anatolia in the town of Söğüt (modern-day Bilecik Province) by the Turkoman tribal leader Osman I. After 1354, the Ottomans crossed into Europe and, with the conquest of the Balkans, the Ottoman beylik was transformed into a transcontinental empire. The Ottomans ended the Byzantine Empire with the conquest of Constantinople in 1453 by Mehmed the Conqueror. Under the reign of Suleiman the Magnificent, the Ottoman Empire marked the peak of its power and prosperity, as well a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oso Kuka
Osman Bejtullah Agë Kuka, also known as Oso Kuka (c. 1812/1820–1862), was an Albanian border guard in the Ottoman-Montenegrin border. Surrounded by Montenegrin soldiers in a tower on the island of Vranjina, he blew it up killing himself and many of the Montenegrin soldiers. In the following decades, he became a rallying figure of the Albanian independence movement and a much-celebrated character of important works in Albanian literature. Background Two Decades earlier, several battles had been fought over the possession of the island, primarily between Ottoman forces, joined by Albanians, and Montenegrins. Between 1835-1844, various rebellions among Albanian highlanders against the Porte led to the enforcement of local Albanian interests. On October 16, 1843, Ottoman forces numbering 12000, led by the Governor of Shkodër, seized the island. The Ottomans arrived at the lake with 50-60 Cannons and opened fire against the Montenegrin troops in the tower. The Ottomans blew u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plantaže
Plantaže ( cnr, Плантаже, ; MNSEPLAP is a Montenegrin wine and grape brandy producer. Overview ''AD Plantaže'', a joint stock company presently incorporated into Holding company "Agrokombinat 13 jul", is the biggest Montenegrin viticultural and winemaking company, and one of the biggest companies in Montenegro overall. The company is based in the Montenegrin capital of Podgorica. It was founded in 1963, and deals with the production of wine and table grapes, peach, production and distribution of wine and grape brandies, fish farming, catering and retail trade. The most important segment of the company is related to the production of grapes and wine, and it owns one of the largest vineyards in Europe with over surface, covered with more than 11 million grapevines. The vineyards are situated in the ''Ćemovsko polje'', a flat and sunny area located south of Podgorica. AD Plantaže is one of the largest producers of grapes and wine in the region, with an annual product ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |