|
Vortex Lift
Vortex lift is that portion of lift due to the action of leading edge vortices. It is generated by wings with highly sweptback, sharp, leading edges (beyond 50 degrees of sweep) or highly-swept wing-root extensions added to a wing of moderate sweep. It is sometimes known as non-linear lift due to its rapid increase with angle of attack. and controlled separation lift, to distinguish it from conventional lift which occurs with attached flow. How it works Vortex lift works by capturing vortices generated from the sharply swept leading edge of the wing. The vortex, formed roughly parallel to the leading edge of the wing, is trapped by the airflow and remains fixed to the upper surface of the wing. As the air flows around the leading edge, it flows over the trapped vortex and is pulled in and down to generate the lift. A straight, or moderate sweep, wing may experience, depending on its airfoil section, a leading-edge stall and loss of lift, as a result of flow separation at the le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
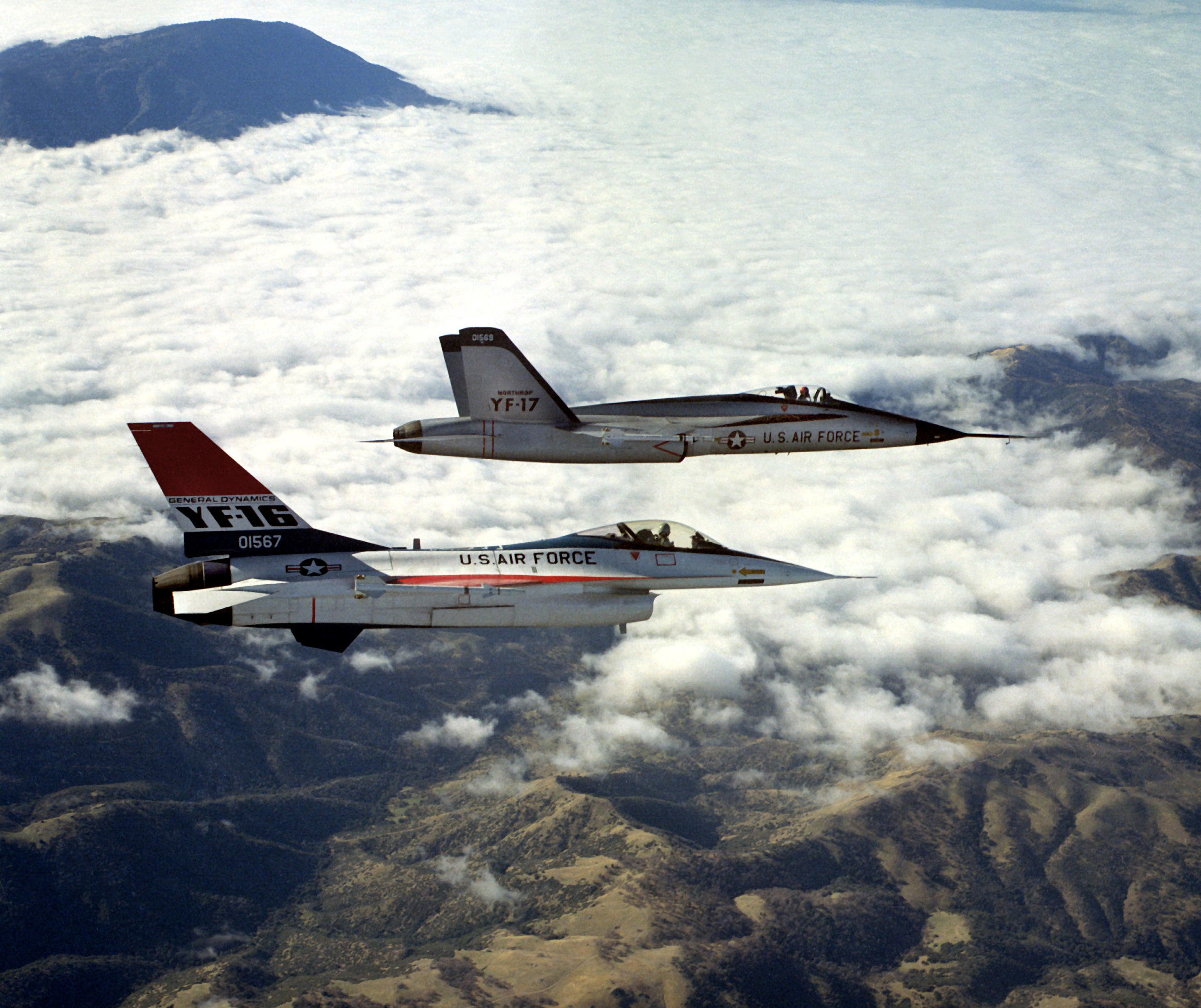
General Dynamics F-16 Fighting Falcon
The General Dynamics F-16 Fighting Falcon is a single-engine multirole fighter aircraft originally developed by General Dynamics for the United States Air Force (USAF). Designed as an air superiority day fighter, it evolved into a successful all-weather multirole aircraft. Over 4,600 aircraft have been built since production was approved in 1976. Although no longer being purchased by the U.S. Air Force, improved versions are being built for export customers. In 1993, General Dynamics sold its aircraft manufacturing business to the Lockheed Corporation, which in turn became part of Lockheed Martin after a 1995 merger with Martin Marietta. The Fighting Falcon's key features include a frameless bubble canopy for good visibility, side-mounted control stick to ease control while maneuvering, an ejection seat reclined 30 degrees from vertical to reduce the effect of g-forces on the pilot, and the first use of a relaxed static stability/ fly-by-wire flight control system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerodynamics
Aerodynamics, from grc, ἀήρ ''aero'' (air) + grc, δυναμική (dynamics), is the study of the motion of air, particularly when affected by a solid object, such as an airplane wing. It involves topics covered in the field of fluid dynamics and its subfield of gas dynamics. The term ''aerodynamics'' is often used synonymously with gas dynamics, the difference being that "gas dynamics" applies to the study of the motion of all gases, and is not limited to air. The formal study of aerodynamics began in the modern sense in the eighteenth century, although observations of fundamental concepts such as aerodynamic drag were recorded much earlier. Most of the early efforts in aerodynamics were directed toward achieving heavier-than-air flight, which was first demonstrated by Otto Lilienthal in 1891. Since then, the use of aerodynamics through mathematical analysis, empirical approximations, wind tunnel experimentation, and computer simulations has formed a rational basis f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kármán Vortex Street
In fluid dynamics, a Kármán vortex street (or a von Kármán vortex street) is a repeating pattern of swirling vortices, caused by a process known as vortex shedding, which is responsible for the unsteady separation of flow of a fluid around blunt bodies. It is named after the engineer and fluid dynamicist Theodore von Kármán, and is responsible for such phenomena as the " singing" of suspended telephone or power lines and the vibration of a car antenna at certain speeds. Mathematical modeling of von Kármán vortex street can be performed using different techniques including but not limited to solving the full Navier-Stokes equations with k-epsilon, SST, k-omega and Reynolds stress, and large eddy simulation (LES) turbulence models, by numerically solving some dynamic equations such as the Ginzburg-Landau equation, or by use of a bicomplex variable. Analysis A vortex street will form only at a certain range of flow velocities, specified by a range of Reynolds numb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leading Edge
The leading edge of an airfoil surface such as a wing is its foremost edge and is therefore the part which first meets the oncoming air.Crane, Dale: ''Dictionary of Aeronautical Terms, third edition'', page 305. Aviation Supplies & Academics, 1997. Characteristics Sweep Seen in plan the leading edge may be straight, curved, kinked or a combination of these. A straight leading edge may be swept or unswept, while curves or kinks always mean that part of the leading edge is swept. On a swept wing the sweep angle may differ from that of the wing, as wing sweep is conventionally measured at the airfoil 25% chord line. However on a delta wing the leading edge sweep defines the wing sweep. Radius and stagnation point A rounded leading edge helps to maintain a smooth airflow at varying angles of incidence to the airflow. Most subsonic airfoils therefore have a rounded leading edge. The degree of rounding is characterised by the profile radius at that point. The airflow divides t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
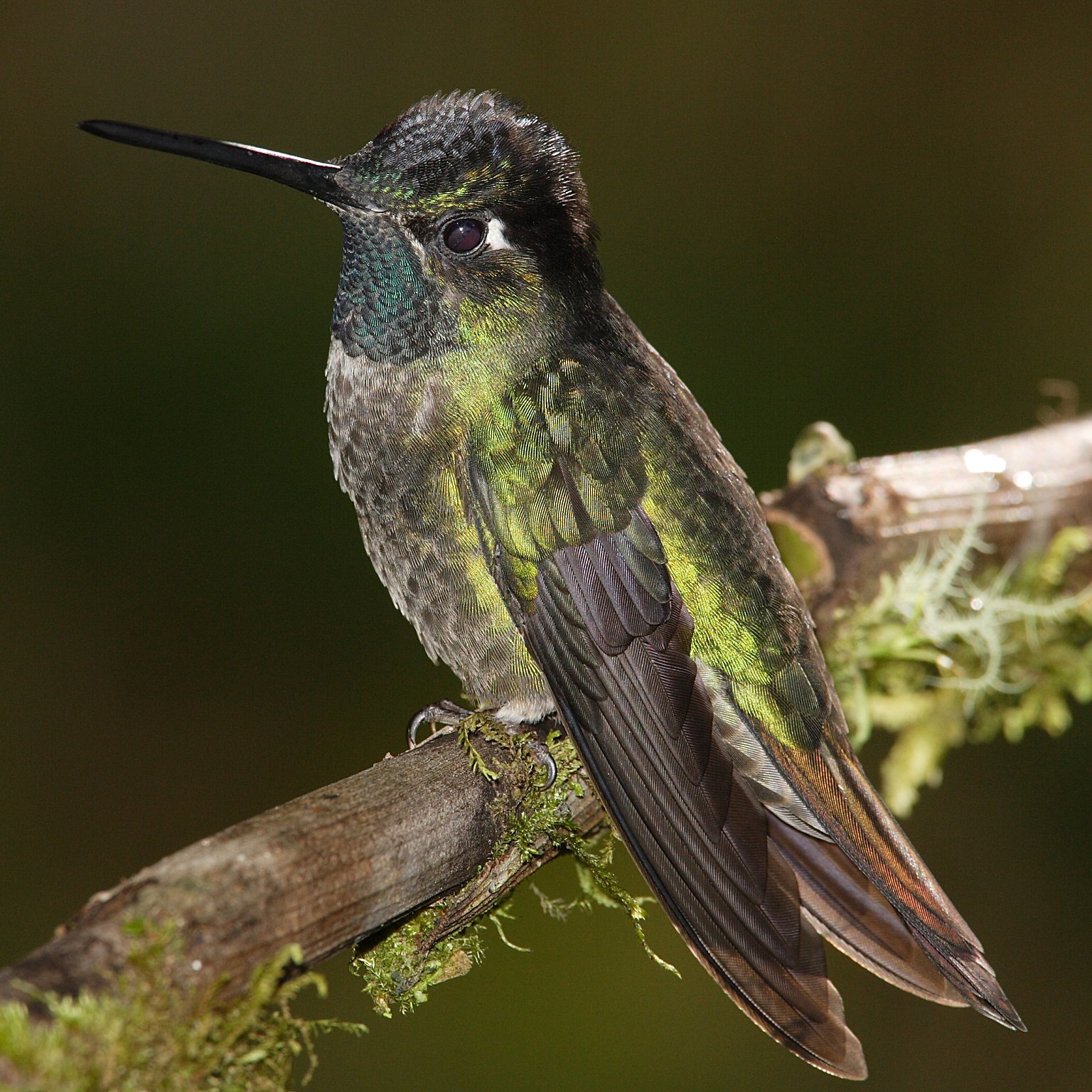
Hummingbird
Hummingbirds are birds native to the Americas and comprise the biological family Trochilidae. With about 361 species and 113 genera, they occur from Alaska to Tierra del Fuego, but the vast majority of the species are found in the tropics around the equator. They are small birds, with most species measuring in length. The smallest extant hummingbird species is the bee hummingbird, which weighs less than . The largest hummingbird species is the giant hummingbird, weighing . They are specialized for feeding on flower nectar, but all species also consume flying insects or spiders. Hummingbirds split from their sister group, the swifts and treeswifts, around 42 million years ago. The common ancestor of extant hummingbirds is estimated to have lived 22 million years ago in South America. They are known as hummingbirds because of the humming sound created by their beating wings, which flap at high frequencies audible to humans. They hover in mid-air at rapid wing-flapping ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
F-106 Delta Dart
The Convair F-106 Delta Dart was the primary all-weather interceptor aircraft of the United States Air Force from the 1960s through to the 1980s. Designed as the so-called "Ultimate Interceptor", it proved to be the last specialist interceptor in U.S. Air Force service to date. It was gradually retired during the 1980s, with the QF-106 drone conversions of the aircraft being used until 1998 under the ''Pacer Six'' program.Winchester 2006, p. 55. Development Antecedents The F-106 was the ultimate development of the USAF's 1954 interceptor program of the early 1950s. The initial winner of this competition had been the F-102 Delta Dagger, but early versions of this aircraft had demonstrated extremely poor performance, limited to subsonic speeds and relatively low altitudes. During the testing program the F-102 underwent numerous changes to improve its performance, notably the application of the area rule to the fuselage shaping and a change of engine, and the dropping of the advanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lippisch DM-1
The Lippisch DM-1 was a single-seat research glider that was designed and built in Germany from 1944. Development During World War II, Dr. Alexander Lippisch proposed a ramjet propelled point defence fighter, the Lippisch P.12/13a. It was a sharply-swept delta flying wing with the engine buried in a thick, blunt-nosed wing. The pilot was accommodated in the forward section of the tail fin, which was as thick as the wings and almost as large. A scale model of the P.12/13a was successfully flown at Spitzerberg, near Vienna.Dan Sharp; ''Luftwaffe: Secret Jets of the Third Reich'', Mortons, 2015, p.119. Lippisch himself lost interest in the design and began work on the P.13b with a different wing, but he was approached by students of Akaflieg Darmstadt and Akaflieg München, who asked for vital war work so that they would not be drafted. By this time in 1944 Lippisch realised that the war was hopeless and was happy to oblige, arranging for them to build a full-scale aerodyna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
McDonnell Douglas F/A-18 Hornet
The McDonnell Douglas F/A-18 Hornet is an all-weather, twin-engine, supersonic, carrier-capable, multirole combat aircraft, designed as both a fighter and attack aircraft (hence the F/A designation). Designed by McDonnell Douglas (now part of Boeing) and Northrop (now part of Northrop Grumman), the F/A-18 was derived from the latter's YF-17 in the 1970s for use by the United States Navy and Marine Corps. The Hornet is also used by the air forces of several other nations, and formerly by the U.S. Navy's Flight Demonstration Squadron, the Blue Angels. The F/A-18 was designed to be a highly versatile aircraft due to its avionics, cockpit displays, and excellent aerodynamic characteristics, with the ability to carry a wide variety of weapons. The aircraft can perform fighter escort, fleet air defense, suppression of enemy air defenses, air interdiction, close air support, and aerial reconnaissance. Its versatility and reliability have proven it to be a valuable carrier as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
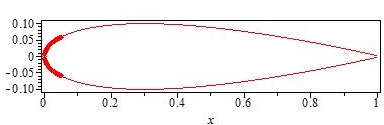
Airplane Vortex Edit
An airplane or aeroplane (informally plane) is a fixed-wing aircraft that is propelled forward by thrust from a jet engine, propeller, or rocket engine. Airplanes come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and wing configurations. The broad spectrum of uses for airplanes includes recreation, transportation of goods and people, military, and research. Worldwide, commercial aviation transports more than four billion passengers annually on airliners and transports more than 200 billion tonne- kilometersMeasured in RTKs—an RTK is one tonne of revenue freight carried one kilometer. of cargo annually, which is less than 1% of the world's cargo movement. Most airplanes are flown by a pilot on board the aircraft, but some are designed to be remotely or computer-controlled such as drones. The Wright brothers invented and flew the first airplane in 1903, recognized as "the first sustained and controlled heavier-than-air powered flight". [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northrop F-5
The Northrop F-5 is a family of supersonic light fighter aircraft initially designed as a privately funded project in the late 1950s by Northrop Corporation. There are two main models, the original F-5A and F-5B Freedom Fighter variants and the extensively updated F-5E and F-5F Tiger II variants. The design team wrapped a small, highly aerodynamic fighter around two compact and high-thrust General Electric J85 engines, focusing on performance and a low cost of maintenance. Smaller and simpler than contemporaries such as the McDonnell Douglas F-4 Phantom II, the F-5 cost less to procure and operate, making it a popular export aircraft. Though primarily designed for a day air superiority role, the aircraft is also a capable ground-attack platform. The F-5A entered service in the early 1960s. During the Cold War, over 800 were produced through 1972 for U.S. allies. Though at the time the United States Air Force (USAF) did not have a need for a light fighter, it did procure app ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |