|
Voromonas Pontica
''Voromonas'' is a genus of predatory Alveolata, alveolates. The genus and species were described by Mylnikov in 2000. It was originally described as ''Colpodella pontica'' but was later renamed by Thomas Cavalier-Smith, Cavalier-Smith and Chao in 2004. Taxonomy There is one species known in this genus. A DNA based analysis suggests that this species may be related to the ''Colpodella''. Feeding At the anterior end of the protozoan, this organism manifests a rostrum which contains a microtubular structure (the pseudoconoid) The pseudoconoid forms an open cone and which is located adjacent to microtubules, microtubular bands, micronemes and rhoptries. The pseudoconoid begins near the kinetosomes of the flagella and passes along the flagellate pocket into the rostrum. While feeding on prey organisms the rostrum is inserted into the body of the prey and the cytoplasm is sucked out. Known prey organisms include bodonids, chrysomonads, percolomonads. Known non prey organisms i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eukaryota
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacteria and Archaea (both prokaryotes) make up the other two domains. The eukaryotes are usually now regarded as having emerged in the Archaea or as a sister of the Asgard archaea. This implies that there are only two domains of life, Bacteria and Archaea, with eukaryotes incorporated among archaea. Eukaryotes represent a small minority of the number of organisms, but, due to their generally much larger size, their collective global biomass is estimated to be about equal to that of prokaryotes. Eukaryotes emerged approximately 2.3–1.8 billion years ago, during the Proterozoic eon, likely as Flagellated cell, flagellated phagotrophs. Their name comes from the Greek language, Greek wikt:εὖ, εὖ (''eu'', "well" or "good") and wikt:� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhoptries
A rhoptry is a specialized secretory organelle. They are club-shaped organelles connected by thin necks to the extreme apical pole of the parasite. These organelles, like micronemes, are characteristic of the motile stages of Apicomplexa protozoa Protozoa (singular: protozoan or protozoon; alternative plural: protozoans) are a group of single-celled eukaryotes, either free-living or parasitic, that feed on organic matter such as other microorganisms or organic tissues and debris. Histo ...ns. They can vary in number and shape and contain numerous enzymes that are released during the penetration process. The proteins they contain are important in the interaction between the host and the parasite, including the formation of the parasitophorous vacuole. References Organelles {{Cell-biology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euglenoid
Euglenids (euglenoids, or euglenophytes, formally Euglenida/Euglenoida, ICZN, or Euglenophyceae, ICBN) are one of the best-known groups of flagellates, which are excavate eukaryotes of the phylum Euglenophyta and their cell structure is typical of that group. They are commonly found in freshwater, especially when it is rich in organic materials, with a few marine and endosymbiotic members. Many euglenids feed by phagocytosis, or strictly by diffusion. A monophyletic group consisting of the mixotrophic Rapaza viridis (1 species) and the two groups Eutreptiales (24 species) and Euglenales (983 species) have chloroplasts and produce their own food through photosynthesis. This group is known to contain the carbohydrate paramylon. Euglenids split from other Euglenozoa more than a billion years ago. The plastids in all extant photosynthetic species is the result from secondary endosymbiosis between a phagotrophic eukaryovorous euglenid and a Pyramimonas-related green alga. Structure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryptomonad
The cryptomonads (or cryptophytes) are a group of algae, most of which have plastids. They are common in freshwater, and also occur in marine and brackish habitats. Each cell is around 10–50 μm in size and flattened in shape, with an anterior groove or pocket. At the edge of the pocket there are typically two slightly unequal flagella. Some may exhibit mixotrophy. Characteristics Cryptomonads are distinguished by the presence of characteristic extrusomes called ejectosomes, which consist of two connected spiral ribbons held under tension. If the cells are irritated either by mechanical, chemical or light stress, they discharge, propelling the cell in a zig-zag course away from the disturbance. Large ejectosomes, visible under the light microscope, are associated with the pocket; smaller ones occur underneath the periplast, the cryptophyte-specific cell surrounding. Except for the class '' Goniomonadea'', which lacks plastids entirely, and ''Cryptomonas paramecium'' ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
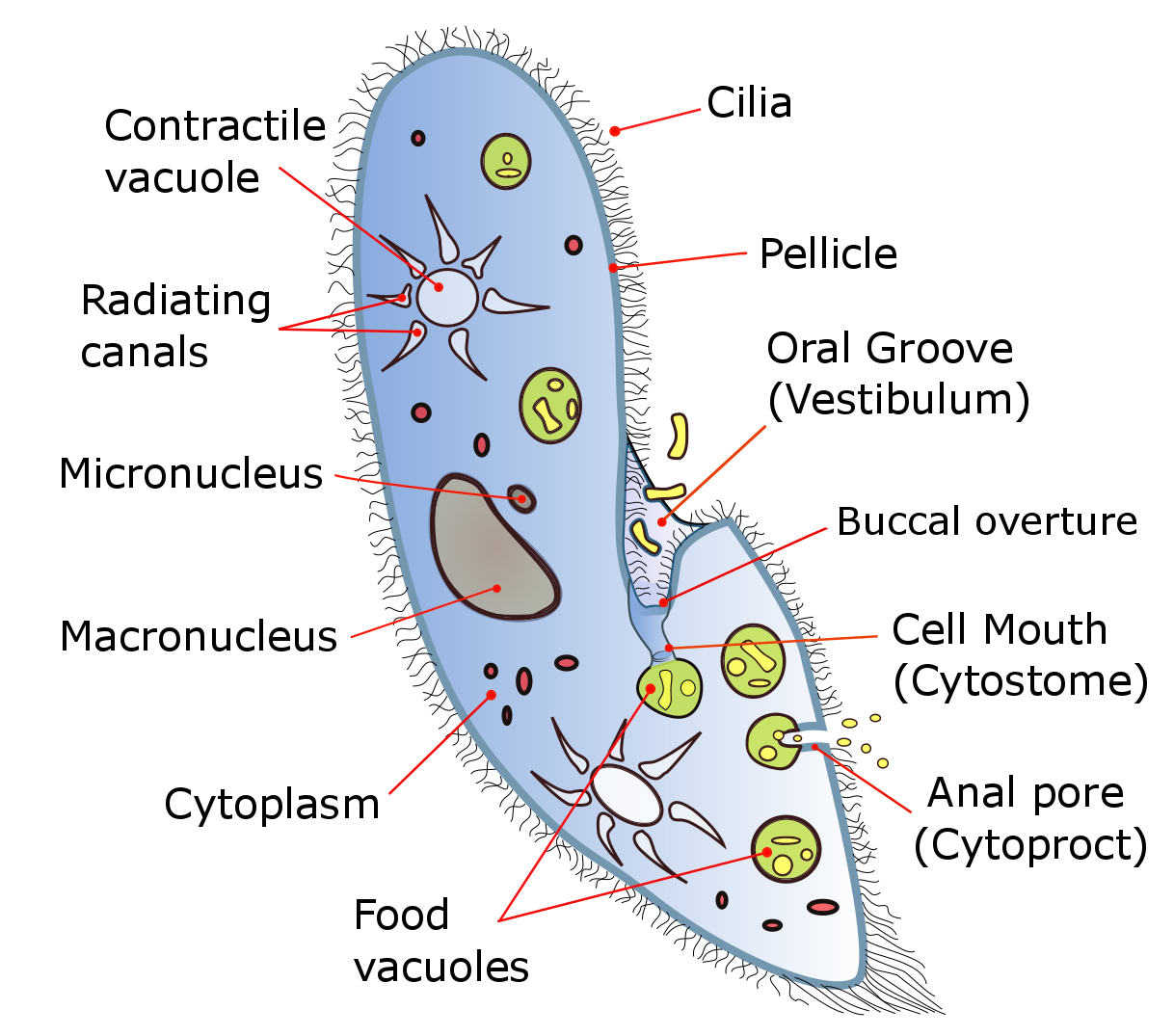
Ciliate
The ciliates are a group of alveolates characterized by the presence of hair-like organelles called cilia, which are identical in structure to eukaryotic flagella, but are in general shorter and present in much larger numbers, with a different undulating pattern than flagella. Cilia occur in all members of the group (although the peculiar Suctoria only have them for part of their life cycle) and are variously used in swimming, crawling, attachment, feeding, and sensation. Ciliates are an important group of protists, common almost anywhere there is water—in lakes, ponds, oceans, rivers, and soils. About 4,500 unique free-living species have been described, and the potential number of extant species is estimated at 27,000–40,000. Included in this number are many ectosymbiotic and endosymbiotic species, as well as some obligate and opportunistic parasites. Ciliate species range in size from as little as 10 µm in some colpodeans to as much as 4 mm in length in s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amoeba
An amoeba (; less commonly spelled ameba or amœba; plural ''am(o)ebas'' or ''am(o)ebae'' ), often called an amoeboid, is a type of cell or unicellular organism with the ability to alter its shape, primarily by extending and retracting pseudopods. Amoebae do not form a single taxonomic group; instead, they are found in every major lineage of eukaryotic organisms. Amoeboid cells occur not only among the protozoa, but also in fungi, algae, and animals. Microbiologists often use the terms "amoeboid" and "amoeba" interchangeably for any organism that exhibits amoeboid movement. In older classification systems, most amoebae were placed in the class or subphylum Sarcodina, a grouping of single-celled organisms that possess pseudopods or move by protoplasmic flow. However, molecular phylogenetic studies have shown that Sarcodina is not a monophyletic group whose members share common descent. Consequently, amoeboid organisms are no longer classified together in one group.Jan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chrysomonad
The Chrysophyceae, usually called chrysophytes, chrysomonads, golden-brown algae or golden algae are a large group of algae, found mostly in freshwater. Golden algae is also commonly used to refer to a single species, ''Prymnesium parvum'', which causes fish kills. The Chrysophyceae should not be confused with the Chrysophyta, which is a more ambiguous taxon. Although "chrysophytes" is the anglicization of "Chrysophyta", it generally refers to the Chrysophyceae. Members Originally they were taken to include all such forms of the diatoms and multicellular brown algae, but since then they have been divided into several different groups (e.g., Haptophyceae, Synurophyceae) based on pigmentation and cell structure. Some heterotrophic flagellates as the bicosoecids and choanoflagellates were sometimes seen as related to golden algae too. They are now usually restricted to a core group of closely related forms, distinguished primarily by the structure of the flagella in motile cells, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bodonid
Bodonida is an order of kinetoplastid flagellate excavates. It contains the genera ''Bodo Bodo may refer to: Ethnicity * Boro people, an ethno-linguistic group mainly from Northwest Assam, India * Bodo-Kachari people, an umbrella group from Nepal, India and Bangladesh that includes the Bodo people Culture and language * Boro cu ...'' and '' Rhynchomonas'', relatives to the parasitic trypanosomes. This order also contains the colonial genus '' Cephalothamnium''. Taxonomy Bodonida contains the following suborders and families: * Eubodonina * Neobodonina ** Bodonidae Bütschli, 1887 ** Neobodonidae ** Rhynchomonadidae * Parabodonina ** Cryptobiidae Vickerman ** Parabodonidae Cavalier-Smith References Kinetoplastids Excavata orders {{Excavata-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flagella
A flagellum (; ) is a hairlike appendage that protrudes from certain plant and animal sperm cells, and from a wide range of microorganisms to provide motility. Many protists with flagella are termed as flagellates. A microorganism may have from one to many flagella. A gram-negative bacterium ''Helicobacter pylori'' for example uses its multiple flagella to propel itself through the mucus lining to reach the stomach epithelium, where it may cause a gastric ulcer to develop. In some bacteria the flagellum can also function as a sensory organelle, being sensitive to wetness outside the cell. Across the three domains of Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukaryota the flagellum has a different structure, protein composition, and mechanism of propulsion but shares the same function of providing motility. The Latin word means "whip" to describe its lash-like swimming motion. The flagellum in archaea is called the archaellum to note its difference from the bacterial flagellum. Eukary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinetosome
A basal body (synonymous with basal granule, kinetosome, and in older cytological literature with blepharoplast) is a protein structure found at the base of a eukaryotic undulipodium ( cilium or flagellum). The basal body was named by Theodor Wilhelm Engelmann in 1880 It is formed from a centriole and several additional protein structures, and is, essentially, a modified centriole. The basal body serves as a nucleation site for the growth of the axoneme microtubules. Centrioles, from which basal bodies are derived, act as anchoring sites for proteins that in turn anchor microtubules, and are known as the microtubule organizing center (MTOC). These microtubules provide structure and facilitate movement of vesicles and organelles within many eukaryotic cells. Assembly, structure Cilia and basal bodies form during quiescence or the G1 phase of the cell cycle. Before the cell enters G1 phase, i.e. before the formation of the cilium, the mother centriole serves as a compo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microneme
Micronemes are secretory organelles, possessed by parasitic apicomplexans. Micronemes are located on the apical third of the protozoan body. They are surrounded by a typical unit membrane. On electron microscopy they have an electron-dense matrix due to the high protein content. They are specialized secretory organelles important for host-cell invasion and gliding motility. These organelles secrete several proteins such as the '' Plasmodium falciparum'' apical membrane antigen-1, or PfAMA1, and Erythrocyte family antigen, or EBA, family proteins. These proteins specialize in binding to erythrocyte surface receptors and facilitating erythrocyte entry. Only by this initial chemical exchange can the parasite enter into the erythrocyte via actin-myosin motor complex. It has been posited that this organelle works cooperatively with its counterpart organelle, the rhoptry, which also is a secretory organelle. It is possible that, while the microneme initiates erythrocyte-binding, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |