|
Volcano Rabbit
The volcano rabbit (''Romerolagus diazi''), also known as teporingo or zacatuche, is a small rabbit that resides in the mountains of Mexico.Hoth, J., A. Velázquez F. Romero, L. León, M. Aranda and D. Bell, 1987. The Volcano Rabbit- a Shrinking Distribution and a Threatened Habitat. Oryx. IUCN. 21 (2): 85-91 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/232022237_The_volcano_rabbit_-_A_shrinking_distribution_and_a_threatened_habitat It is the world's second-smallest rabbit, second only to the pygmy rabbit. It has small rounded ears, short legs, and short, thick fur and weighs approximately 390–600 g (0.86–1.3 lb). It has a life span of 7 to 9 years. The volcano rabbit lives in groups of 2 to 5 animals in burrows (underground nests) and runways among grass tussocks. The burrows can be as long as 5 m and as deep as 40 cm. There are usually 2 to 3 young per litter, born in the burrows. In semi-captivity, however, they do not make burrows and the young are born in nests made ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chapultepec Zoo
Chapultepec Zoo (Spanish: ''Zoológico de Chapultepec'') is a zoo located in Chapultepec Park; it is one of four zoos near Mexico City, and the best known Mexican zoo. It was founded July 6, 1923 by Mexican biologist Alfonso Luis Herrera using donations from private citizens and governmental funds from the Ministry of Agriculture and Development, and also with funds from the Society of Biological Studies. The zoo houses almost 2000 animals from more than 200 species. The zoo is known for its success in breeding programs of threatened species, including: giant pandas (first institution outside of China to successively breed the species in captivity), California condors (first institution outside of the United States to successively breed the species) and Mexican wolves (first litter of cubs born to released wolves). History The zoo opened in 1924. The biologist Alfonso L. Herrera, founder of Chapultepec Zoo, wanted to recreate the famous zoo and aviary of Moctezuma II. He wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
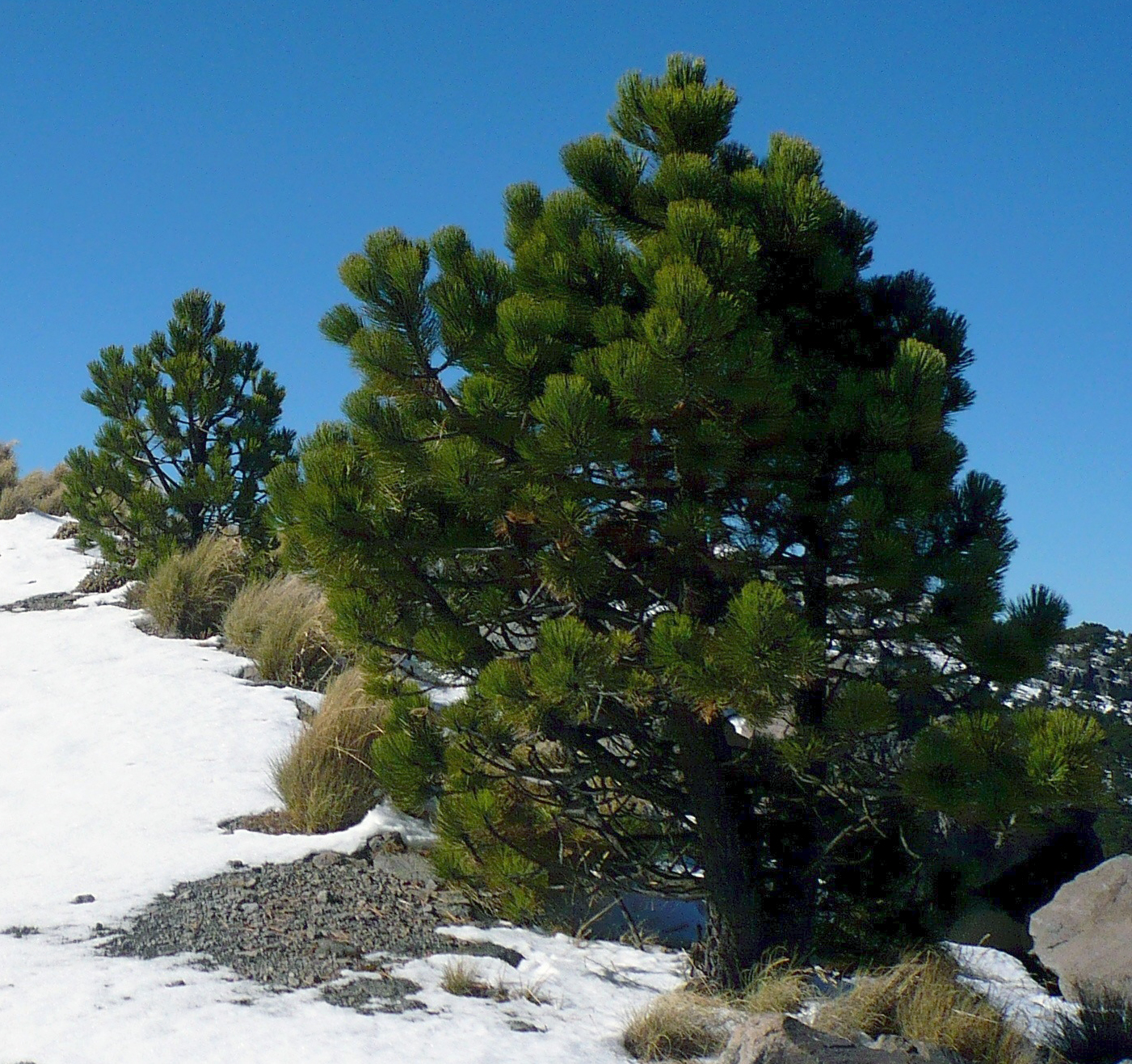
Pinus Hartwegii
''Pinus hartwegii'' ( syn. ''P. rudis'', ''P. donnell-smithii''), Hartweg's pine or pino de las alturas, is a pine native to the mountains of Mexico and Central America east to Honduras. It is named after Karl Theodor Hartweg, who described it in 1838. Distribution ''Pinus hartwegii'' is a very high elevation species, growing at elevations of . It forms the alpine tree line on most of Mexico's higher mountains. It grows on both the Sierra Madre Occidental and Sierra Madre Oriental (mountain ranges) (29° North latitude) from Chihuahua State and Nuevo León (26°) to the highest peaks in the mountain ranges on the El Salvador—Honduras border (15° North latitude). In the Sierra Madre Occidental this pine grows with very dry winters and a very heavy rainy season in summer, with constant frosts from October to March. This pine does not acquire the dwarfed and contorted shape shared by many species at high elevation. Even at the alpine tree line, this tree is not damaged by the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammals Described In 1893
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or hair, and three middle ear bones. These characteristics distinguish them from reptiles (including birds) from which they diverged in the Carboniferous, over 300 million years ago. Around 6,400 extant species of mammals have been described divided into 29 orders. The largest orders, in terms of number of species, are the rodents, bats, and Eulipotyphla (hedgehogs, moles, shrews, and others). The next three are the Primates (including humans, apes, monkeys, and others), the Artiodactyla ( cetaceans and even-toed ungulates), and the Carnivora (cats, dogs, seals, and others). In terms of cladistics, which reflects evolutionary history, mammals are the only living members of the Synapsida (synapsids); this clade, together w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemic Mammals Of Mexico
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. For example, the Cape sugarbird is found exclusively in southwestern South Africa and is therefore said to be ''endemic'' to that particular part of the world. An endemic species can be also be referred to as an ''endemism'' or in scientific literature as an ''endemite''. For example '' Cytisus aeolicus'' is an endemite of the Italian flora. '' Adzharia renschi'' was once believed to be an endemite of the Caucasus, but it was later discovered to be a non-indigenous species from South America belonging to a different genus. The extreme opposite of an endemic species is one with a cosmopolitan distribution, having a global or widespread range. A rare alternative term for a species that is endemic is "precinctive", which applies to s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EDGE Species
Evolutionarily Distinct and Globally Endangered (EDGE) species are animal species which have a high 'EDGE score', a metric combining endangered conservation status with the genetic distinctiveness of the particular taxon. Distinctive species have few closely related species, and EDGE species are often the only surviving member of their genus or even higher taxonomic rank. The extinction of such species would therefore represent a disproportionate loss of unique evolutionary history and biodiversity. Some EDGE species, such as elephants and pandas, are well-known and already receive considerable conservation attention, but many others, such as the vaquita (the world's rarest cetacean) the bumblebee bat (arguably the world's smallest mammal) and the egg-laying long-beaked echidnas, are highly threatened yet remain poorly understood, and are frequently overlooked by existing conservation frameworks. The Zoological Society of London launched the EDGE of Existence Programme in 2007 to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leporidae
Leporidae is the family of rabbits and hares, containing over 60 species of extant mammals in all. The Latin word ''Leporidae'' means "those that resemble ''lepus''" (hare). Together with the pikas, the Leporidae constitute the mammalian order Lagomorpha. Leporidae differ from pikas in that they have short, furry tails and elongated ears and hind legs. The common name "rabbit" usually applies to all genera in the family except ''Lepus'', while members of ''Lepus'' (almost half the species) usually are called hares. Like most common names, however, the distinction does not match current taxonomy completely; jackrabbits are members of ''Lepus'', and members of the genera ''Pronolagus'' and ''Caprolagus'' sometimes are called hares. Various countries across all continents except Antarctica and Australia have indigenous species of Leporidae. Furthermore, rabbits, most significantly the European rabbit, ''Oryctolagus cuniculus'', also have been introduced to most of Oceania and to m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CITES
CITES (shorter name for the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora, also known as the Washington Convention) is a multilateral treaty to protect endangered plants and animals from the threats of international trade. It was drafted as a result of a resolution adopted in 1963 at a meeting of members of the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). The convention was opened for signature in 1973 and CITES entered into force on 1 July 1975. Its aim is to ensure that international trade (import/export) in specimens of animals and plants included under CITES, does not threaten the survival of the species in the wild. This is achieved via a system of permits and certificates. CITES affords varying degrees of protection to more than 38,000 species. , Secretary-General of CITES is Ivonne Higuero. Background CITES is one of the largest and oldest conservation and sustainable use agreements in existence. There are three working langu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Locus (genetics)
In genetics, a locus (plural loci) is a specific, fixed position on a chromosome where a particular gene or genetic marker is located. Each chromosome carries many genes, with each gene occupying a different position or locus; in humans, the total number of protein-coding genes in a complete haploid set of 23 chromosomes is estimated at 19,000–20,000. Genes may possess multiple variants known as alleles, and an allele may also be said to reside at a particular locus. Diploid and polyploid cells whose chromosomes have the same allele at a given locus are called homozygous with respect to that locus, while those that have different alleles at a given locus are called heterozygous. The ordered list of loci known for a particular genome is called a gene map. Gene mapping is the process of determining the specific locus or loci responsible for producing a particular phenotype or biological trait. Association mapping, also known as "linkage disequilibrium mapping", is a method of ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sylvilagus
Cottontail rabbits are the leporid species in the genus ''Sylvilagus'', found in the Americas. Most ''Sylvilagus'' species have stub tails with white undersides that show when they retreat, giving them their characteristic name. However, this feature is not present in all cottontails nor is it unique to the genus. The genus is widely distributed across North America, Central America and northern and central South America, though most species are confined to some particular regions. Most species live in nests called forms, and all have altricial young. An adult female averages three litters per year, which can occur in any season; occurrence, and litter size depend on several factors including time of the year, weather, and location. The average litter size is four but can range from as few as two to as many as eight, most of whom do not go on to survive to adulthood. Cottontail rabbits show a greater resistance to myxomatosis than European rabbits. Evolution Cottontails ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Habitat Destruction
Habitat destruction (also termed habitat loss and habitat reduction) is the process by which a natural habitat becomes incapable of supporting its native species. The organisms that previously inhabited the site are displaced or dead, thereby reducing biodiversity and species abundance. Habitat destruction is the leading cause of biodiversity loss. Fragmentation and loss of habitat have become one of the most important topics of research in ecology as they are major threats to the survival of endangered species. Activities such as harvesting natural resources, industrial production and urbanization are human contributions to habitat destruction. Pressure from agriculture is the principal human cause. Some others include mining, logging, trawling, and urban sprawl. Habitat destruction is currently considered the primary cause of species extinction worldwide. Environmental factors can contribute to habitat destruction more indirectly. Geological processes, climate change, introdu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zacatón
Zacatón is a cenote (a thermal water-filled sinkhole) belonging to the Zacatón system - a group of unusual karst features located in Aldama Municipality near the Sierra de Tamaulipas in the northeastern state of Tamaulipas, Mexico. It is the deepest known water-filled sinkhole in the world with a total depth of . The deep Pozzo del Merro is deeper (actual depth unknown), but Using an autonomous robot, the underwater portion of Zacatón has been measured to be deep (a difference between the rim of cliff and surface of water adds to the total depth). Zacatón is the only sinkhole of the five located in Rancho La Azufrosa to have any noticeable water flow. The name Zacatón comes from the free-floating islands of zacate grass which move around on the surface with the wind. Scrapings from the rock walls beneath the surface yielded at least three new phyla of bacteria. Diving El Zacatón's depth has made it an important dive site: * Dr. Ann Kristovich set the women's wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overgrazing
Overgrazing occurs when plants are exposed to intensive grazing for extended periods of time, or without sufficient recovery periods. It can be caused by either livestock in poorly managed agricultural applications, game reserves, or nature reserves. It can also be caused by immobile, travel restricted populations of native or non-native wild animals. Overgrazing reduces the usefulness, productivity, and biodiversity of the land and is one cause of desertification and erosion. Overgrazing is also seen as a cause of the spread of invasive species of non-native plants and of weeds. Degrading land, emissions from animal agriculture and reducing the biomass in a ecosystem contribute directly to climate change. Overgrazing can be reversed or prevented by removing grazers in order to give plants time to recover between grazing events. Successful planned grazing strategies have been support in the American bison of the Great Plains, or migratory Wildebeests of the African savann ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)