 |
Volcanic Field
A volcanic field is an area of Earth's crust that is prone to localized volcanic activity. The type and number of volcanoes required to be called a "field" is not well-defined. Volcanic fields usually consist of clusters of up to 100 volcanoes such as cinder cones. Lava flows may also occur. They may occur as a monogenetic volcanic field or a polygenetic volcanic field. Description Alexander von Humboldt observed in 1823 that geologically young volcanoes are not distributed uniformly across the Earth's surface, but tend to be clustered into specific regions. Young volcanoes are rarely found within cratons, but are characteristic of subduction zones, rift zones, or in ocean basins. Intraplate volcanoes are clustered along hotspot traces. Within regions of volcanic activity, volcanic fields are clusters of volcanoes that share a common magma source. Scoria cones are particularly prone to cluster into volcanic fields, which are typically in diameter and consist of several t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Durango
Durango (), officially named Estado Libre y Soberano de Durango ( en, Free and Sovereign State of Durango; Tepehuán: ''Korian''; Nahuatl: ''Tepēhuahcān''), is one of the 31 states which make up the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico, situated in the northwest of the country. With a population of 1,832,650, the 8th lowest of Mexico's states, Durango has Mexico's second-lowest population density, after Baja California Sur. The capital city, Victoria de Durango, is named after the first President of Mexico, Guadalupe Victoria. Geography General information With , Durango accounts for about 6.3% of the entire territory of Mexico. It is the fourth largest state lying at the extreme northwest of the Central Mexican Plateau, where it meets the Sierra Madre Occidental—the highest peaks in the state. The state has an average elevation of 1,775 meters above sea level, with a mean elevation of 1,750 m in the Valleys region and 2,450 m in the Sierra region. The city of Durango is o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Durango Volcanic Field
Durango volcanic field is a volcanic field in north-central Mexico (Durango), east of the Sierra Madre Occidental. The field covers a surface area of . The volcanic field is located in the Tepehuano terrane. Volcanism in the area was accompanied by tectonic extension. There are around hundred cones in the field. Some volcanic rocks have been affected by faulting; buried faults are also found. The San Luis-Tepehuanes fault system is associated with the field. The whole field is covered by lavas, which are about thick and reach a total volume of . Magma ascent has been controlled by northwest-trending faults. Volcanism in the wider territory was related to the subduction of the Farallon plate until 29 mya. Later tectonic changes caused a start of more alkaline volcanism. The volcanoes have erupted basanite. The main components of the rocks at La Breña-El Jagüey are clinopyroxene, ilmenite, olivine, plagioclase and titanomagnetite, with rocks sporting variable textures. The par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Baja California
Baja California (; 'Lower California'), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Baja California ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Baja California), is a state in Mexico. It is the northernmost and westernmost of the 32 federal entities of Mexico. Before becoming a state in 1952, the area was known as the North Territory of Baja California (). It has an area of (3.57% of the land mass of Mexico) and comprises the northern half of the Baja California Peninsula, north of the 28th parallel, plus oceanic Guadalupe Island. The mainland portion of the state is bordered on the west by the Pacific Ocean; on the east by Sonora, the U.S. state of Arizona, and the Gulf of California; on the north by the U.S. state of California; and on the south by Baja California Sur. The state has an estimated population of 3,769,020 as of 2020, significantly higher than the sparsely populated Baja California Sur to the south, and similar to San Diego County, California, to its north. Over 75% of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
San Quintín Volcanic Field
The San Quintín Volcanic Field is a collection of ten or eleven volcanic cinder cones situated along the Pacific coast of the Baja California peninsula in Mexico. The field formed by repeated eruptions beginning in the Pleistocene and ending about 3000 years ago.Gorsline, D. S. and R. A. Stewart, Benthic marine exploration of Bahía de San Quintín, Baja California, 1960-61. Marine and Quaternary geology. ''Pac. Nat., 3'', 282-319, 1962.Woodford, A. O.The San Quintín volcanic field, lower California ''American Journal of Science'' 15:337-345, 1928. It is one of several known Quaternary period volcanic fields in Baja. The lava shields appear to have first grown as subaqueous volcanoes that emerged as islands.Luhr, J. F., Aranda-Gómez, J. J., and Housh, T. B. San Quintín Volcanic Field, Baja California Norte, México: Geology, petrology, and geochemistry. ''Journal of Geophysical Research'' 100:10353–10380, 1995. Currently located in a shallow bay, the cones are found in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Yukon Territory
Yukon (; ; formerly called Yukon Territory and also referred to as the Yukon) is the smallest and westernmost of Canada's three territories. It also is the second-least populated province or territory in Canada, with a population of 43,964 as of March 2022. Whitehorse, the territorial capital, is the largest settlement in any of the three territories. Yukon was split from the North-West Territories in 1898 as the Yukon Territory. The federal government's ''Yukon Act'', which received royal assent on March 27, 2002, established Yukon as the territory's official name, though ''Yukon Territory'' is also still popular in usage and Canada Post continues to use the territory's internationally approved postal abbreviation of ''YT''. In 2021, territorial government policy was changed so that “''The'' Yukon” would be recommended for use in official territorial government materials. Though officially bilingual (English and French), the Yukon government also recognizes First Na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
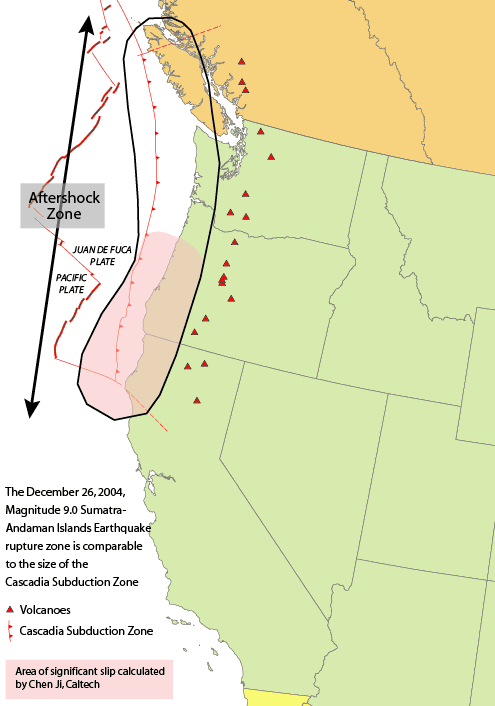
Wrangell Volcanic Field
The Wrangell Volcanic Field is a volcanic field stretching from eastern Alaska in the United States to the southwestern Yukon Territory in Canada. The field includes the four highest volcanoes in the United States, Mount Bona, Mount Blackburn, Mount Sanford, and Mount Churchill, all of which exceed 15,000 ft (4,600 m) in elevation. It formed as a result of subduction of the Pacific Plate beneath the North American Plate at the easternmost end of the Aleutian Trench. The bulk of the Wrangell Volcanic Field lies within the Wrangell Mountains of Alaska, but the field also extends eastwards into the neighboring Saint Elias Mountains and the Yukon Territory. The east-west length of the field is over 200 mile (320 km), while the width reaches up to 80 miles (130 km) in the central Wrangell Mountains. The field includes numerous shield volcanoes, stratovolcanoes, caldera complexes, cinder cones, and extensive lava flows, which have erupted throughout the past 26 milli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Wells Gray-Clearwater Volcanic Field
The Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field, also called the Clearwater Cone Group, is a potentially active monogenetic volcanic field in east-central British Columbia, Canada, located approximately north of Kamloops. It is situated in the Cariboo Mountains of the Columbia Mountains and on the Quesnel and Shuswap Highlands. As a monogenetic volcanic field, it is a place with numerous small basaltic volcanoes and extensive lava flows. Most of the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field is encompassed within a large wilderness park called Wells Gray Provincial Park. This park was established in 1939 to protect Helmcken Falls and the unique features of the Clearwater River drainage basin, including this volcanic field. Five roads enter the park and provide views of some of the field's volcanic features. Short hikes lead to several other volcanic features, but some areas are accessible only by aircraft. Geology Pleistocene epoch Based on radiocarbon and potassium-argon dating, v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Mount Cayley Volcanic Field
The Mount Cayley volcanic field (MCVF) is a remote volcanic zone on the South Coast of British Columbia, Canada, stretching from the Pemberton Icefield to the Squamish River. It forms a segment of the Garibaldi Volcanic Belt, the Canadian portion of the Cascade Volcanic Arc, which extends from Northern California to southwestern British Columbia. Most of the MCVF volcanoes were formed during periods of volcanism under sheets of glacial ice throughout the last glacial period. These subglacial eruptions formed steep, flat-topped volcanoes and subglacial lava domes, most of which have been entirely exposed by deglaciation. However, at least two volcanoes predate the last glacial period and both are highly eroded. The field gets its name from Mount Cayley, a volcanic peak located at the southern end of the Powder Mountain Icefield. This icefield covers much of the central portion of the volcanic field and is one of the several glacial fields in the Pacific Ranges of the Coast Mou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Garibaldi Lake Volcanic Field
The Garibaldi Lake volcanic field is a volcanic field, located in British Columbia, Canada. It was formed by a group of nine small andesitic stratovolcanoes and basaltic andesite vents in the scenic Garibaldi Lake area immediately north of Mount Garibaldi was formed during the late Pleistocene and early Holocene. The oldest stratovolcano, The Black Tusk, formed between about 1.3 and 1.1 million years ago ( Ma). Following glacial dissection, renewed volcanism produced the lava dome and flow forming its summit. Other Pleistocene vents are located along and to the west of the Cheakamus River. Cinder Cone, to the east of The Black Tusk, produced a 9-km-long lava flow during the late Pleistocene or early Holocene. Mount Price, west of Garibaldi Lake, 5 km south of The Black Tusk, was formed in three stages of activity, dating back 1.1 million years, the latest of which produced two large lava flows from Clinker Peak during the early Holocene that ponded against the retreating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |