|
Vitrella Brassicaformis
''Vitrella brassicaformis'' (CCMP3155) is a unicellular alga belonging to the eukaryotic supergroup Alveolata. ''V. brassicaformis'' and its closest known relative, '' Chromera velia,'' are the only two currently described members of the phylum Chromerida, which in turn constitutes part of the taxonomically unranked group Colpodellida. Chromerida is phylogenetically closely related to the phylum Apicomplexa, which includes ''Plasmodium'', the agent of malaria. Notably, both ''V. brassicaformis'' and ''C. velia'' are photosynthetic, each containing a complex secondary plastid. This characteristic defined the discovery of these so-called ' chromerids,' as their photosynthetic capacity positioned them to shed light upon the evolution of Apicomplexa's non-photosynthetic parasitism. Both genera lack chlorophyll ''b'' or '' c''; these absences link the two taxonomically, as algae bearing only chlorophyll ''a'' are rare amid the biodiversity of life. Despite their similarities, ''V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
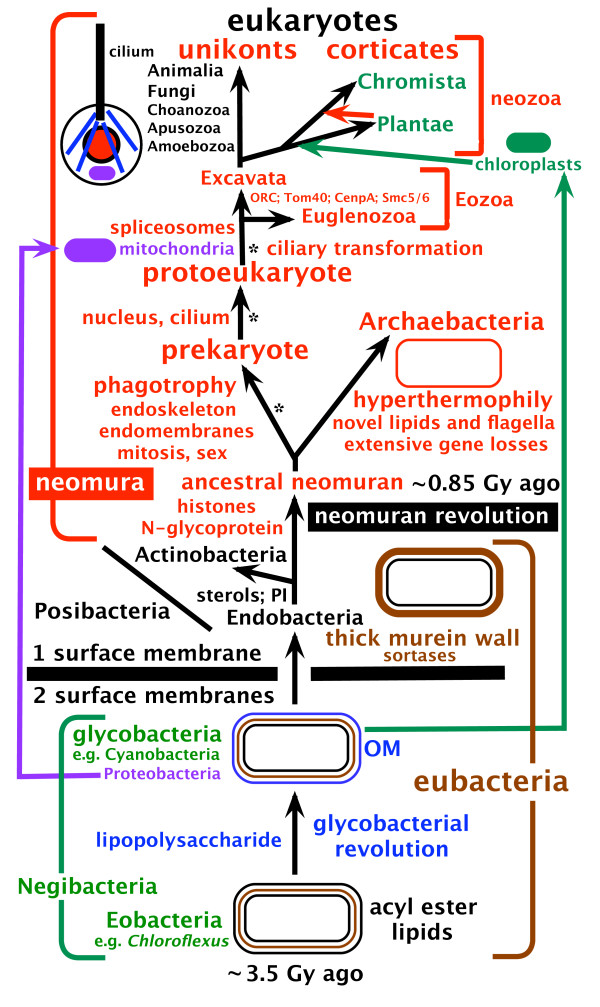
Eukaryota
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the Three-domain system, three domains of life. Bacteria and Archaea (both prokaryotes) make up the other two domains. The eukaryotes are usually now regarded as having emerged in the Archaea or as a sister of the Asgard (archaea), Asgard archaea. This implies that there are only Two-domain system, two domains of life, Bacteria and Archaea, with eukaryotes incorporated among archaea. Eukaryotes represent a small minority of the number of organisms, but, due to their generally much larger size, their collective global biomass (ecology), biomass is estimated to be about equal to that of prokaryotes. Eukaryotes emerged approximately 2.3–1.8 billion years ago, during the Proterozoic eon, likely as Flagellated cell, flagellated phagotrophs. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlorophyll B
} Chlorophyll ''b'' is a form of chlorophyll. Chlorophyll ''b'' helps in photosynthesis by absorbing light energy. It is more soluble than chlorophyll ''a'' in polar solvents because of its carbonyl group. Its color is green, and it primarily absorbs blue light. In land plants, the light-harvesting antennae around photosystem II contain the majority of chlorophyll ''b''. Hence, in shade-adapted chloroplasts, which have an increased ratio of photosystem II to photosystem I, there is a higher ratio of chlorophyll ''b'' to chlorophyll ''a''. This is adaptive, as increasing chlorophyll ''b'' increases the range of wavelengths absorbed by the shade chloroplasts. Biosynthesis The Chlorophyll ''b'' biosynthetic pathway utilizes a variety of enzymes. In most plants, chlorophyll is derived from glutamate and is synthesised along a branched pathway that is shared with heme and siroheme. The initial steps incorporate glutamic acid into 5-aminolevulinic acid (ALA); two molecules of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colpodellid
Colpodellida is an order of alveolate eukaryotes, which includes small predatory species such as ''Colpodella pugnax ''Colpodella'' is a genus of alveolates comprising 5 species, and two further possible species: They share all the synapomorphies of apicomplexans, but are free-living, rather than parasitic. Many members of this genus were previously assigned t ...''. They are active predatory flagellates that consume small protists. However they do not fully ingest the prey, rather they absorb or suck the contents from the prey partially or fully. This method of sucking the contents from the prey is termed as mizocytosis.Mylnikov, A.P. Ultrastructure and phylogeny of colpodellids (Colpodellida, Alveolata). Biol Bull Russ Acad Sci 36, 582–590 (2009). https://link.springer.com/article/10.1134/S1062359009060065 References Apicomplexa orders {{Apicomplexa-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myzozoa
Myzozoa is a grouping of specific phyla within Alveolata, that either feed through myzocytosis, or were ancestrally capable of feeding through myzocytosis. Many protozoan orders are included within Myzozoa. It is sometimes described as a phylum, containing the major subphyla Dinozoa and Apicomplexa, plus minor subphyla. The term Myzozoa superseded the previous term "Miozoa", by the same authority, and gave a slightly altered meaning. Phyla Within Myzozoa, there are around four phyla: *Apicomplexa – parasitic protozoa that lack axonemal locomotive structures except in gametes *Dinoflagellates – mostly marine flagellates many of which have chloroplasts * Chromerida – a marine phylum of photosynthetic protozoa *Perkinsozoa The term/group Myzozoa was not considered in a resolution of protist groups by Adl et al. 2012. Strict taxonomy only considers common traits possessed by all organisms of the group. Some organisms within each of the component groups of Myzozoa have l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Cavalier-Smith
Thomas (Tom) Cavalier-Smith, FRS, FRSC, NERC Professorial Fellow (21 October 1942 – 19 March 2021), was a professor of evolutionary biology in the Department of Zoology, at the University of Oxford. His research has led to discovery of a number of unicellular organisms (protists) and advocated for a variety of major taxonomic groups, such as the Chromista, Chromalveolata, Opisthokonta, Rhizaria, and Excavata. He was known for his systems of classification of all organisms. Life and career Cavalier-Smith was born on 21 October 1942 in London. His parents were Mary Maude (née Bratt) and Alan Hailes Spencer Cavalier Smith. He was educated at Norwich School, Gonville and Caius College, Cambridge (MA) and King's College London (PhD). He was under the supervision of Sir John Randall for his PhD thesis between 1964 and 1967; his thesis was entitled "''Organelle Development in'' Chlamydomonas reinhardii". From 1967 to 1969, Cavalier-Smith was a guest investigato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pocillopora Damicornis
''Pocillopora damicornis'', commonly known as the cauliflower coral or lace coral, is a species of stony coral in the family Pocilloporidae. It is native to tropical and subtropical parts of the Indian and Pacific Oceans. Description ''P. damicornis'' is a colonial coral and can grow into clumps up to high. It is distinguishable from other members of the genus by the verrucae (wart-like growths) on its surface being more irregularly arranged. It is more branched than the otherwise similar '' P. verrucosa''. Its form varies according to its habitat and is more open and branched in calm positions and more compact on the upper parts of reefs where water movement is greater. Its colour varies and may be greenish, pink, yellowish-brown or pale brown. Distribution and habitat Cauliflower coral is native to the tropical and subtropical parts of the Indian and Pacific Oceans. Its wide range extends from East Africa and the Red Sea to Japan, Indonesia, Australia, Hawaii, Easter Island, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterotroph
A heterotroph (; ) is an organism that cannot produce its own food, instead taking nutrition from other sources of organic carbon, mainly plant or animal matter. In the food chain, heterotrophs are primary, secondary and tertiary consumers, but not producers. Living organisms that are heterotrophic include all animals and fungi, some bacteria and protists, and many parasitic plants. The term heterotroph arose in microbiology in 1946 as part of a classification of microorganisms based on their type of nutrition. The term is now used in many fields, such as ecology in describing the food chain. Heterotrophs may be subdivided according to their energy source. If the heterotroph uses chemical energy, it is a chemoheterotroph (e.g., humans and mushrooms). If it uses light for energy, then it is a photoheterotroph (e.g., green non-sulfur bacteria). Heterotrophs represent one of the two mechanisms of nutrition (trophic levels), the other being autotrophs (''auto'' = self, ''troph'' = ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phototroph
Phototrophs () are organisms that carry out photon capture to produce complex organic compounds (e.g. carbohydrates) and acquire energy. They use the energy from light to carry out various cellular metabolic processes. It is a common misconception that phototrophs are obligatorily photosynthetic. Many, but not all, phototrophs often photosynthesize: they anabolically convert carbon dioxide into organic material to be utilized structurally, functionally, or as a source for later catabolic processes (e.g. in the form of starches, sugars and fats). All phototrophs either use electron transport chains or direct proton pumping to establish an electrochemical gradient which is utilized by ATP synthase, to provide the molecular energy currency for the cell. Phototrophs can be either autotrophs or heterotrophs. If their electron and hydrogen donors are inorganic compounds (e.g. , as in some purple sulfur bacteria, or , as in some green sulfur bacteria) they can be also called lithot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinoflagellate
The dinoflagellates (Greek δῖνος ''dinos'' "whirling" and Latin ''flagellum'' "whip, scourge") are a monophyletic group of single-celled eukaryotes constituting the phylum Dinoflagellata and are usually considered algae. Dinoflagellates are mostly marine plankton, but they also are common in freshwater habitats. Their populations vary with sea surface temperature, salinity, and depth. Many dinoflagellates are photosynthetic, but a large fraction of these are in fact mixotrophic, combining photosynthesis with ingestion of prey (phagotrophy and myzocytosis). In terms of number of species, dinoflagellates are one of the largest groups of marine eukaryotes, although substantially smaller than diatoms. Some species are endosymbionts of marine animals and play an important part in the biology of coral reefs. Other dinoflagellates are unpigmented predators on other protozoa, and a few forms are parasitic (for example, ''Oodinium'' and ''Pfiesteria''). Some dinoflagellates pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Barrier Reef
The Great Barrier Reef is the world's largest coral reef system composed of over 2,900 individual reefs and 900 islands stretching for over over an area of approximately . The reef is located in the Coral Sea, off the coast of Queensland, Australia, separated from the coast by a channel 100 miles wide in places and over 200 feet deep. The Great Barrier Reef can be seen from outer space and is the world's biggest single structure made by living organisms. This reef structure is composed of and built by billions of tiny organisms, known as coral polyps. It supports a wide diversity of life and was selected as a World Heritage Site in 1981. CNN labelled it one of the seven natural wonders of the world in 1997. Australian World Heritage places included it in its list in 2007. The Queensland National Trust named it a state icon of Queensland in 2006. A large part of the reef is protected by the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park, which helps to limit the impact of human use, such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |