|
Viral Disease Testing
Viral disease testing is the use of a variety of testing techniques for a variety of purposes, including diagnosing conditions, assessing immunity and understanding disease prevalence. The primary approaches include DNA/RNA tests, serological tests and antigen tests. History COVID-19 In March 2020, Abbott received emergency use authorization (EUA) for its isothermal nucleic acid test for COVID-19. It produces test results in 5 minutes using its ID NOW portable testing system. It also received EUA for its m2000-based laboratory nucleic acid test for COVID-19. In April 2020, Abbott received EUA for its ARCHITECT IgG laboratory antibody test for COVID-19. Also in April, Abbott's ID NOW test was reported to have sensitivity of 85.2%. A later study found sensitivity of only 52%, inducing the FDA to issue an alert. A different study found sensitivity of 91%. The UK spent $20 million for antibody tests that proved flawed. In May 2020, a rapid antigen test from Quidel Corporation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serology
Serology is the scientific study of Serum (blood), serum and other body fluids. In practice, the term usually refers to the medical diagnosis, diagnostic identification of Antibody, antibodies in the serum. Such antibodies are typically formed in response to an infection (against a given microorganism), against other foreign proteins (in response, for example, to a Acute hemolytic transfusion reaction, mismatched blood transfusion), or to one's own proteins (in instances of autoimmune disease). In either case, the procedure is simple. Serological tests Serological tests are diagnostic methods that are used to identify antibodies and antigens in a patient's sample. Serological tests may be performed to diagnose infections and autoimmune illnesses, to check if a person has immunity (medical), immunity to certain diseases, and in many other situations, such as determining an individual's blood type. Serological tests may also be used in forensic serology to investigate crime scene evid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Influenza
Influenza, commonly known as "the flu", is an infectious disease caused by influenza viruses. Symptoms range from mild to severe and often include fever, runny nose, sore throat, muscle pain, headache, coughing, and fatigue. These symptoms begin from one to four days after exposure to the virus (typically two days) and last for about 2–8 days. Diarrhea and vomiting can occur, particularly in children. Influenza may progress to pneumonia, which can be caused by the virus or by a subsequent bacterial infection. Other complications of infection include acute respiratory distress syndrome, meningitis, encephalitis, and worsening of pre-existing health problems such as asthma and cardiovascular disease. There are four types of influenza virus, termed influenza viruses A, B, C, and D. Aquatic birds are the primary source of Influenza A virus (IAV), which is also widespread in various mammals, including humans and pigs. Influenza B virus (IBV) and Influenza C virus (ICV) pri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viral Diseases
Viral means "relating to viruses" (small infectious agents). Viral may also refer to: Viral behavior, or virality Memetic behavior likened that of a virus, for example: * Viral marketing, the use of existing social networks to spread a marketing message * Viral phenomenon, relating to contagion theory or the "virality" of network culture, such as a meme * Viral video, a video that quickly attains a high popularity Titled works * ''Viral'' (2016 American film), a 2016 American science fiction horror drama * ''Viral'' (2016 Hindi film), an Indian Bollywood film based on social media * ''Viral'' (web series), a 2014 Brazilian comedy web series * '' V/H/S: Viral'', an American anthology horror film * '' Viral: The Search for the Origin of COVID-19'', a book by Alina Chand and Matt Ridley See also * ''Virals'', a novel series by Kathy Reichs * Virulence Virulence is a pathogen's or microorganism's ability to cause damage to a host. In most, especially in animal system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle East Respiratory Syndrome
Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS) is a viral respiratory infection caused by ''Middle East respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus'' (MERS-CoV). Symptoms may range from none, to mild, to severe. Typical symptoms include fever, cough, diarrhea, and shortness of breath. The disease is typically more severe in those with other health problems. The first case was identified in June 2012 by Egyptian physician Ali Mohamed Zaki at the Dr. Soliman Fakeeh Hospital in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia, and most cases have occurred in the Arabian Peninsula. Over 2,500 cases have been reported as of January 2021, including 45 cases in the year 2020. About 35% of those who are diagnosed with the disease die from it. Larger outbreaks have occurred in South Korea in 2015 and in Saudi Arabia in 2018. MERS-CoV is a coronavirus believed to be originally from bats. However, humans are typically infected from camels, either during direct contact or indirectly. Spread between humans typically r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
H1N1
In virology, influenza A virus subtype H1N1 (A/H1N1) is a subtype of influenza A virus. Major outbreaks of H1N1 strains in humans include the Spanish flu, the 1977 Russian flu pandemic and the 2009 swine flu pandemic. It is an orthomyxovirus that contains the glycoproteins hemagglutinin and neuraminidase. For this reason, they are described as H1N1, H1N2 etc., depending on the type of H or N antigens they express with metabolic synergy. Hemagglutinin causes red blood cells to clump together and binds the virus to the infected cell. Neuraminidase is a type of glycoside hydrolase enzyme which helps to move the virus particles through the infected cell and assist in budding from the host cells. Some strains of H1N1 are endemic in humans and cause a small fraction of all influenza-like illness and a small fraction of all seasonal influenza, for instance in 2004–2005. Other strains of H1N1 are endemic in pigs (swine influenza) and in birds (avian influenza). Its size is in d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SARS
Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) is a viral respiratory disease of zoonotic origin caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV or SARS-CoV-1), the first identified strain of the SARS coronavirus species, ''severe acute respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus'' (SARSr-CoV). The first known cases occurred in November 2002, and the syndrome caused the 2002–2004 SARS outbreak. In the 2010s, Chinese scientists traced the virus through the intermediary of Asian palm civets to cave-dwelling horseshoe bats in Xiyang Yi Ethnic Township, Yunnan.The locality was referred to be "a cave in Kunming" in earlier sources because the Xiyang Yi Ethnic Township is administratively part of Kunming, though 70 km apart. Xiyang was identified on * For an earlier interview of the researchers about the locality of the caves, see: SARS was a relatively rare disease; at the end of the epidemic in June 2003, the incidence was 8,469 cases with a case fatality rate (CFR ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helicobacter Pylori
''Helicobacter pylori'', previously known as ''Campylobacter pylori'', is a gram-negative, microaerophilic, spiral (helical) bacterium usually found in the stomach. Its helical shape (from which the genus name, helicobacter, derives) is thought to have evolved in order to penetrate the mucoid lining of the stomach and thereby establish infection. The bacterium was first identified in 1982 by the Australian doctors Barry Marshall and Robin Warren. ''H. pylori'' has been associated with cancer of the mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue in the stomach, esophagus, colon, rectum, or tissues around the eye (termed extranodal marginal zone B-cell lymphoma of the cited organ), and of lymphoid tissue in the stomach (termed diffuse large B-cell lymphoma). ''H. pylori'' infection usually has no symptoms but sometimes causes gastritis (stomach inflammation) or ulcers of the stomach or first part of the small intestine. The infection is also associated with the development of cer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
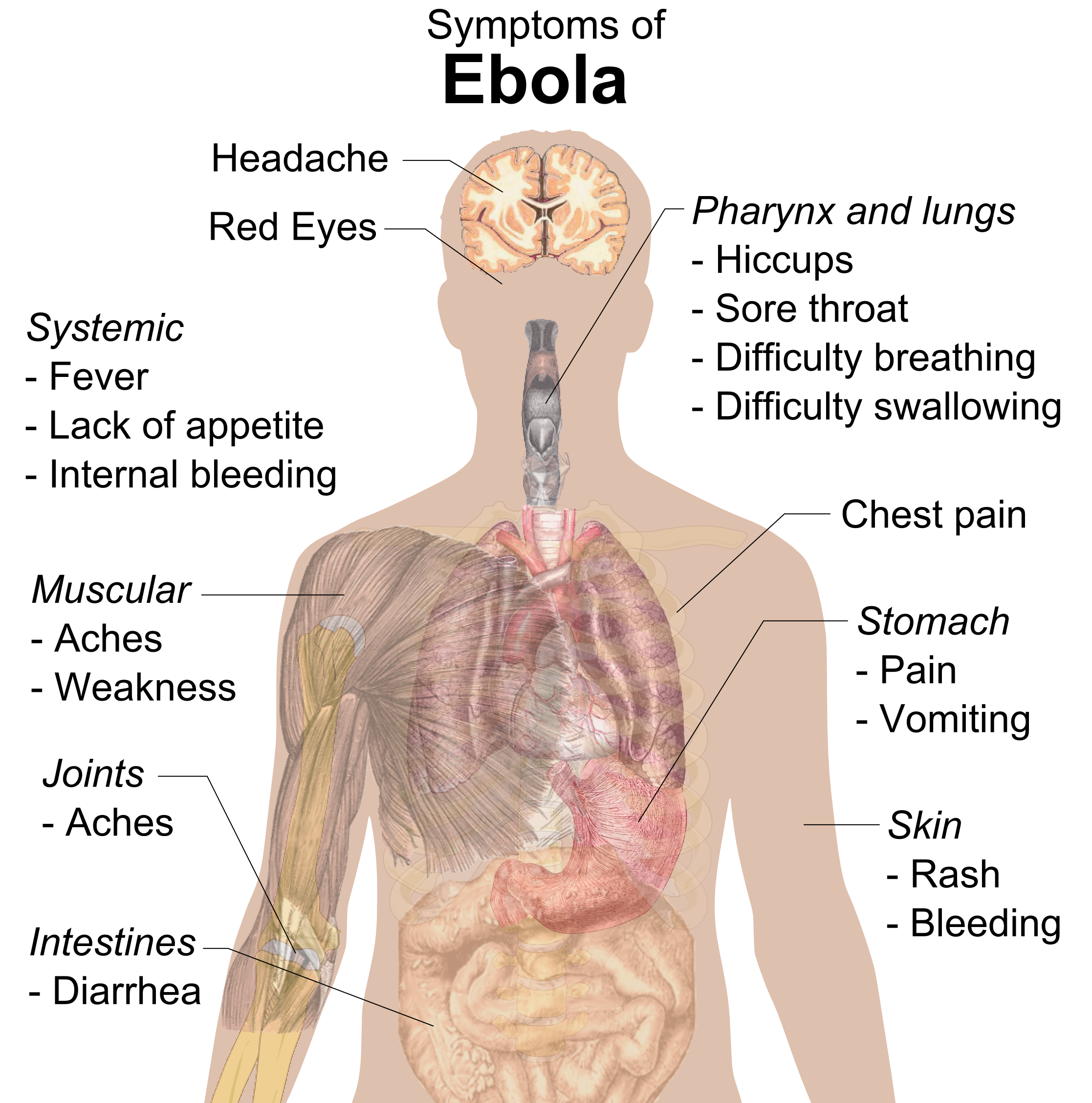
Ebola
Ebola, also known as Ebola virus disease (EVD) and Ebola hemorrhagic fever (EHF), is a viral hemorrhagic fever in humans and other primates, caused by ebolaviruses. Symptoms typically start anywhere between two days and three weeks after becoming infected with the virus. The first symptoms are usually fever, sore throat, muscle pain, and headaches. These are usually followed by vomiting, diarrhoea, rash and decreased liver and kidney function, at which point, some people begin to bleed both internally and externally. The disease kills between 25% and 90% of those infected – about 50% on average. Death is often due to shock from fluid loss, and typically occurs between six and 16 days after the first symptoms appear. Early treatment of symptoms increases the survival rate considerably compared to late start. The virus spreads through direct contact with body fluids, such as blood from infected humans or other animals, or from contact with items that have recently been conta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giardia
''Giardia'' ( or ) is a genus of anaerobic flagellated protozoan parasites of the phylum Metamonada that colonise and reproduce in the small intestines of several vertebrates, causing the disease giardiasis. Their life cycle alternates between a swimming trophozoite and an infective, resistant cyst. ''Giardia'' were first described by the Dutch microscopist Antonie van Leeuwenhoek in 1681. The genus is named after French zoologist Alfred Mathieu Giard. Characteristics Like other diplomonads, ''Giardia'' have two nuclei, each with four associated flagella, and were thought to lack both mitochondria and Golgi apparatuses. However, they are now known to possess a complex endomembrane system as well as mitochondrial remnants, called mitosomes, through mitochondrial reduction. The mitosomes are not used in ATP synthesis the way mitochondria are, but are involved in the maturation of iron-sulfur proteins. The synapomorphies of genus ''Giardia'' include cells with duplicate org ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streptococcus
''Streptococcus'' is a genus of gram-positive ' (plural ) or spherical bacteria that belongs to the family Streptococcaceae, within the order Lactobacillales (lactic acid bacteria), in the phylum Bacillota. Cell division in streptococci occurs along a single axis, so as they grow, they tend to form pairs or chains that may appear bent or twisted. This differs from staphylococci, which divide along multiple axes, thereby generating irregular, grape-like clusters of cells. Most streptococci are oxidase-negative and catalase-negative, and many are facultative anaerobes (capable of growth both aerobically and anaerobically). The term was coined in 1877 by Viennese surgeon Albert Theodor Billroth (1829–1894), by combining the prefix "strepto-" (from ), together with the suffix "-coccus" (from Modern , from .) In 1984, many bacteria formerly grouped in the genus ''Streptococcus'' were separated out into the genera ''Enterococcus'' and ''Lactococcus''. Currently, over 50 species ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abbott Laboratories
Abbott Laboratories is an American multinational medical devices and health care company with headquarters in Abbott Park, Illinois, United States. The company was founded by Chicago physician Wallace Calvin Abbott in 1888 to formulate known drugs; today, it sells medical devices, diagnostics, branded generic medicines and nutritional products. It split off its research-based pharmaceuticals business into AbbVie in 2013. The firm has also been present in India for over 100 years through its subsidiary Abbott India Limited, and it is currently India's largest healthcare products company. Among its well-known products across the medical devices, diagnostics, and nutrition product divisions are Pedialyte, Similac, BinaxNOW, Ensure, Glucerna, ZonePerfect, FreeStyle Libre, i-STAT and MitraClip. History Foundation and early history In 1888 at the age of 30, Wallace Abbott (1857–1921), an 1885 graduate of the University of Michigan, founded the Abbott Alkaloidal Company in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)
.jpg)