|
Vilna Troupe
The Vilna Troupe ( yi, Vilner trupe ווילנער טרופע; lt, Vilniaus trupė; pl, Trupa Wileńska; ro, Trupa din Vilna), also known as Fareyn Fun Yiddishe Dramatishe Artistn (Federation of Yiddish Dramatic Actors) and later ''Dramă şi Comedie'', was an international and mostly Yiddish-speaking theatrical company, one of the most famous in the history of Yiddish theater. It was formed in and named after the city of Vilnius (Vilna) in the Russian Empire, later capital city of Lithuania. Distinctly Modernist, and strongly influenced by Russian literature and by the ideas of Konstantin Stanislavski, their travels in Western Europe and later to Romania played a significant role in the dissemination of a disciplined approach to acting that continues to be influential down to the present day. Early years Founded in 1915 or 1916 during World War I, the troupe began with the deserted Vilna State Theatre as their base, toured Kovno, Białystok and Grodno, and soon moved to Warsaw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yiddish
Yiddish (, or , ''yidish'' or ''idish'', , ; , ''Yidish-Taytsh'', ) is a West Germanic language historically spoken by Ashkenazi Jews. It originated during the 9th century in Central Europe, providing the nascent Ashkenazi community with a vernacular based on High German fused with many elements taken from Hebrew (notably Mishnaic) and to some extent Aramaic. Most varieties of Yiddish include elements of Slavic languages and the vocabulary contains traces of Romance languages.Aram Yardumian"A Tale of Two Hypotheses: Genetics and the Ethnogenesis of Ashkenazi Jewry".University of Pennsylvania. 2013. Yiddish is primarily written in the Hebrew alphabet. Prior to World War II, its worldwide peak was 11 million, with the number of speakers in the United States and Canada then totaling 150,000. Eighty-five percent of the approximately six million Jews who were murdered in the Holocaust were Yiddish speakers,Solomon Birnbaum, ''Grammatik der jiddischen Sprache'' (4., erg. Aufl., Hambu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sholem Aleichem
) , birth_date = , birth_place = Pereiaslav, Russian Empire , death_date = , death_place = New York City, U.S. , occupation = Writer , nationality = , period = , genre = Novels, short stories, plays , subject = , movement = Yiddish revival , signature = File:Sholem Aleichem Signature.svg , website = Solomon Naumovich Rabinovich (Соломон Наумович Рабинович), better known under his pen name Sholem Aleichem (Yiddish and he, שלום עליכם, also spelled in Soviet Yiddish, ; Russian and uk, Шо́лом-Але́йхем) (May 13, 1916), was a Yiddish author and playwright who lived in the Russian Empire and in the United States. The 1964 musical ''Fiddler on the Roof'', based on Aleichem's stories about Tevye the Dairyman, was the first commercially successful English-language stage production about Jewish life in Eastern Europe. The Hebrew phras ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the List of United States cities by population density, most densely populated major city in the United States, and is more than twice as populous as second-place Los Angeles. New York City lies at the southern tip of New York (state), New York State, and constitutes the geographical and demographic center of both the Northeast megalopolis and the New York metropolitan area, the largest metropolitan area in the world by urban area, urban landmass. With over 20.1 million people in its metropolitan statistical area and 23.5 million in its combined statistical area as of 2020, New York is one of the world's most populous Megacity, megacities, and over 58 million people live within of the city. New York City is a global city, global Culture of New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Herman (Yiddish Theater)
David Herman (born February 20, 1967) is an American actor and comedian. He was an original cast member on '' MADtv'' from 1995 to 1997, and played Michael Bolton in ''Office Space''. He has done voice-over work in hundreds of episodes of ''Bob's Burgers'', '' Brickleberry'', ''Futurama'', '' King of the Hill'', ''OK K.O.! Let's Be Heroes'', '' Disenchantment'', and '' Father of the Pride''. Early life Herman was born in New York City and raised in Washington Heights, Manhattan. He graduated from the Fiorello H. LaGuardia High School of Music & Art and Performing Arts in 1985, then attended the acting program at SUNY Purchase. Career ''MADtv'' Herman was part of the cast of John Leguizamo's short-lived series ''House of Buggin''' in 1994. When Fox cancelled ''House of Buggin and decided to replace it with a sketch comedy show, Herman was signed on as one of nine original cast members of '' MADtv'' when the series began in 1995. Unlike most of the other featured players ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moscow Art Theater
The Moscow Art Theatre (or MAT; russian: Московский Художественный академический театр (МХАТ), ''Moskovskiy Hudojestvenny Akademicheskiy Teatr'' (МHАТ)) was a theatre company in Moscow. It was founded in 1898 by the seminal Russian theatre practitioner Konstantin Stanislavski, together with the playwright and director Vladimir Nemirovich-Danchenko. It was conceived as a venue for naturalistic theatre, in contrast to the melodramas that were Russia's dominant form of theatre at the time. The theatre, the first to regularly put on shows implementing Stanislavski's system, proved hugely influential in the acting world and in the development of modern American theatre and drama. It was officially renamed the Gorky Moscow Art Theatre in 1932. In 1987, the theatre split into two troupes, the Chekhov Moscow Art Theatre and the Gorky Moscow Art Theatre. Beginnings At the end of the 19th-century, Stanislavski and Nemirovich-Danchenko b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanislavski's System
Stanislavski's system is a systematic approach to training actors that the Russian theatre practitioner Konstantin Stanislavski developed in the first half of the twentieth century. His system cultivates what he calls the "art of experiencing" (with which he contrasts the "art of representation").Benedetti (1999a, 201), Carnicke (2000, 17), and Stanislavski (1938, 16—36 "art of representation" corresponds to Mikhail Shchepkin's "actor of reason" and his "art of experiencing" corresponds to Shchepkin's "actor of feeling"; see Benedetti (1999a, 202). It mobilises the actor's conscious thought and will in order to activate other, less-controllable psychological processes—such as emotional experience and subconscious behaviour—sympathetically and indirectly. In rehearsal, the actor searches for inner motives to justify action and the definition of what the character seeks to achieve at any given moment (a "task"). Later, Stanislavski further elaborated the system with a more p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Language
Russian (russian: русский язык, russkij jazyk, link=no, ) is an East Slavic languages, East Slavic language mainly spoken in Russia. It is the First language, native language of the Russians, and belongs to the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. It is one of four living East Slavic languages, and is also a part of the larger Balto-Slavic languages. Besides Russia itself, Russian is an official language in Belarus, Kazakhstan, and Kyrgyzstan, and is used widely as a lingua franca throughout Ukraine, the Caucasus, Central Asia, and to some extent in the Baltic states. It was the De facto#National languages, ''de facto'' language of the former Soviet Union,1977 Soviet Constitution, Constitution and Fundamental Law of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics, 1977: Section II, Chapter 6, Article 36 and continues to be used in public life with varying proficiency in all of the post-Soviet states. Russian has over 258 million total speakers worldwide. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Dybbuk
''The Dybbuk'', or ''Between Two Worlds'' (russian: Меж двух миров �ибук}, trans. ''Mezh dvukh mirov ibuk'; yi, צווישן צוויי וועלטן - דער דִבּוּק, ''Tsvishn Tsvey Veltn – der Dibuk'') is a play by S. Ansky, authored between 1913 and 1916. It was originally written in Russian and later translated into Yiddish by Ansky himself. ''The Dybbuk'' had its world premiere in that language, performed by the Vilna Troupe at Warsaw in 1920. A Hebrew version was prepared by Hayim Nahman Bialik and staged in Moscow at Habima Theater in 1922. The play, which depicts the possession of a young woman by the malicious spirit – known as ''dybbuk'' in Jewish folklore – of her dead beloved, became a canonical work of both Hebrew and Yiddish theatre, being further translated and performed around the world. Characters * Leah, daughter of Sender, a maiden who had come of age and yet her father constantly rejects her suitors * Khanan, a poor Yeshiva stu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
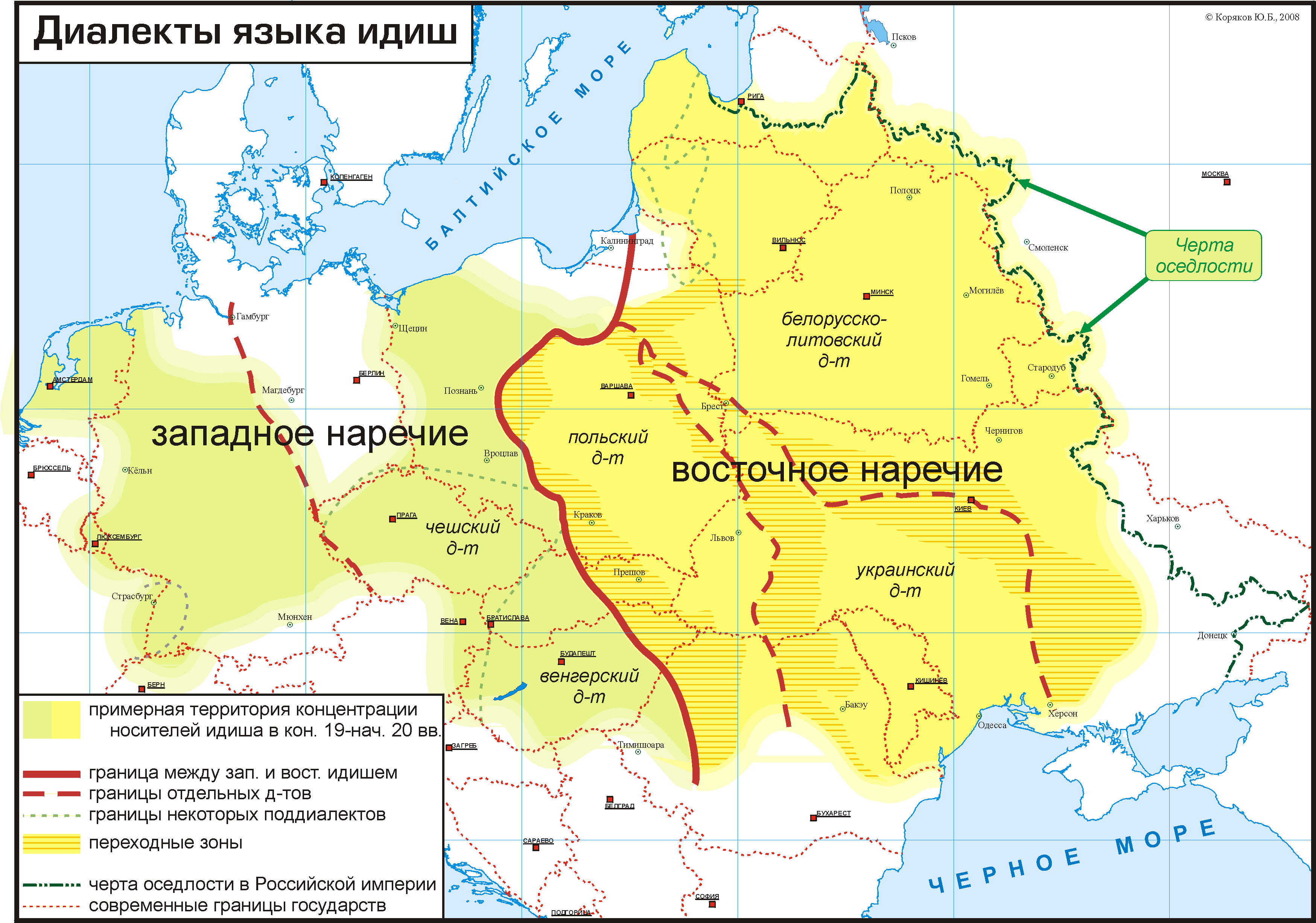
Yiddish Dialects
Yiddish dialects are variants of the Yiddish language and are divided according to the region in Europe where each developed its distinctiveness. Linguistically, Yiddish is divided in distinct Eastern and Western dialects. While the Western dialects mostly died out in the 19th-century due to Jewish language assimilation into mainstream culture, the Eastern dialects were very vital until most of Eastern European Jewry was wiped out by the Shoah. The Northeastern dialects of Eastern Yiddish were dominant in 20th-century Yiddish culture and academia, but in the 21st-century, since Yiddish is largely dying out everywhere due to language assimilation, the Southern dialects of Yiddish that are preserved by many Hasidic communities, have become the most commonly spoken form of Yiddish. Varieties Yiddish dialects are generally grouped into either Western Yiddish and Eastern Yiddish. Western Yiddish developed from the 9th century in Western-Central Europe, in the region which was called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uriel Acosta
Uriel da Costa (; also Acosta or d'Acosta; c. 1585 – April 1640) was a Portuguese philosopher and skeptic who was born Christian, but returned to Judaism and ended up questioning the Catholic and rabbinic institutions of his time. Life Many details about his life appear in his short autobiography, but over the past two centuries documents uncovered in Portugal, Amsterdam, Hamburg and more have changed and added much in the picture. Costa was born in Porto with the name Gabriel da Costa Fiuza. His ancestors were ''Cristãos-novos'', or New Christians, converted from Judaism to Catholicism by state edict at 1497. His father was a well-off international merchant and tax-farmer. Studying canon law in the University of Coimbra intermittently between 1600 and 1608, he began to read the Bible and contemplate it seriously. Costa also occupied an ecclesiastical office. In his autobiography Costa pictured his family as devout Catholics. However they had been subjects to several investi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karl Gutzkow
Karl Ferdinand Gutzkow ( in Berlin – in Sachsenhausen) was a German writer notable in the Young Germany movement of the mid-19th century. Life Gutzkow was born of an extremely poor family, not proletarian, but of the lowest and most menial branch of state employees. His father held a clerkship in the war office in Berlin, and was pietistic and puritanical in his outlook and demands. Jacob Wittmer Hartmann speculates that Gutzkow's later agnosticism was probably a reaction against the excessive religiosity of his early surroundings. After completing his basic studies, beginning in 1829 Gutzkow studied theology and philosophy at the University of Berlin, where his teachers included Hegel and Schleiermacher.Sagarra, Eda (2000).Karl Gutzkow, 1811-1878" ''Encyclopedia of German Literature''. Chicago: Fitzroy Dearborn. p. 391-392. While still a student, he began his literary career by the publication in 1831 of a periodical entitled ''Forum der Journalliteratur''. This brought h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henrik Ibsen
Henrik Johan Ibsen (; ; 20 March 1828 – 23 May 1906) was a Norwegian playwright and theatre director. As one of the founders of modernism in theatre, Ibsen is often referred to as "the father of realism" and one of the most influential playwrights of his time. His major works include ''Brand'', '' Peer Gynt'', '' An Enemy of the People'', ''Emperor and Galilean'', ''A Doll's House'', ''Hedda Gabler'', '' Ghosts'', ''The Wild Duck'', ''When We Dead Awaken'', ''Rosmersholm'', and ''The Master Builder''. Ibsen is the most frequently performed dramatist in the world after Shakespeare, and ''A Doll's House'' was the world's most performed play in 2006. Ibsen's early poetic and cinematic play ''Peer Gynt'' has strong surreal elements. After ''Peer Gynt'' Ibsen abandoned verse and wrote in realistic prose. Several of his later dramas were considered scandalous to many of his era, when European theatre was expected to model strict morals of family life and propriety. Ibsen's later wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |