|
Verticordia Stenopetala
''Verticordia stenopetala'' is a flowering plant in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae and is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It is a low shrub with small leaves and heads of pink to magenta-coloured flowers in late spring and early summer. Description ''Verticordia stenopetala'' is a highly branched shrub which usually grows to a height and wide. The leaves are linear, slightly wider towards the tip, long and semi-circular in cross-section. The flowers are arranged in round or corymb-like groups, each flower on a stalk long. The floral cup is about long, smooth and hairy. The sepals are more or less spreading, long, pink to magenta-coloured with 6 to 8 feathery lobes. The petals are a similar colour to the sepals, about long, egg-shaped with a few short teeth near the tip and are slightly hairy on the outside. The style is long, curved and hairy near the tip. Flowering time is from October to January. Taxonomy and naming ''Verticordia stenopetala'' was first fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ludwig Diels
Dr. Friedrich Ludwig Emil Diels (24 September 1874 – 30 November 1945) was a German botanist. Diels was born in Hamburg, the son of the classical scholar Hermann Alexander Diels. From 1900 to 1902 he traveled together with Ernst Georg Pritzel through South Africa, Java, Australia and New Zealand. Shortly before the First World War he travelled New Guinea and in the 1930s in Ecuador. Especially his collections of plants from Australia and Ecuador, which contained numerous holotypes, enriched the knowledge of the concerning floras. His monography on the Droseraceae from 1906 is still a standard. The majority of his collections were stored at the botanical garden in Berlin-Dahlem, whose vicedirector he had been since 1913, becoming its director in 1921 until 1945. His collections were destroyed there during an air raid in 1943. He died in Berlin on 30 November 1945. Honours Several genus of plants have been named after him including; ''Dielsantha'' (from ''Campanulaceae' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verticordia Helichrysantha
''Verticordia helichrysantha'', commonly known as coast featherflower or Barrens featherflower, is a flowering plant in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae and is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It is a small, woody, open-branched shrub with crowded, linear leaves and small yellow flowers from May to September. Description ''Verticordia helichrysantha'' is an openly branched, more or less sprawling shrub which grows to high and wide. The leaves are clustered, crowded, pale greyish-green, long, linear to club-shaped, semi-circular in cross-section with a rounded end. The flowers are arranged singly or in small groups in the upper leaf axils, each flower on a stalk, long. The floral cup is long, smooth and hairy. The sepals are pale yellow, long, covered with short, soft hairs and have 4 or 5 feathery lobes. The petals are the same colour as the sepals, about long, erect and egg-shaped, covered with short, soft hairs on their outer surface and have irregular teeth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Declared Rare And Priority Flora List
The Declared Rare and Priority Flora List is the system by which Western Australia's conservation flora are given a priority. Developed by the Government of Western Australia's Department of Environment and Conservation, it was used extensively within the department, including the Western Australian Herbarium. The herbarium's journal, ''Nuytsia'', which has published over a quarter of the state's conservation taxa, requires a conservation status to be included in all publications of new Western Australian taxa that appear to be rare or endangered. The system defines six levels of priority taxa: ;X: Threatened (Declared Rare Flora) – Presumed Extinct Taxa: These are taxa that are thought to be extinct, either because they have not been collected for over 50 years despite thorough searching, or because all known wild populations have been destroyed. They have been declared as such in accordance with the Wildlife Conservation Act 1950, and are therefore afforded legislative protecti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBRA
The Interim Biogeographic Regionalisation for Australia (IBRA) is a biogeographic regionalisation of Australia developed by the Australian government's Department of Sustainability, Environment, Water, Population, and Communities. It was developed for use as a planning tool, for example for the establishment of a national reserve system. The first version of IBRA was developed in 1993–94 and published in 1995. Within the broadest scale, Australia is a major part of the Australasia biogeographic realm, as developed by the World Wide Fund for Nature. Based on this system, the world is also split into 14 terrestrial habitats, of which eight are shared by Australia. The Australian land mass is divided into 89 bioregions and 419 subregions. Each region is a land area made up of a group of interacting ecosystems that are repeated in similar form across the landscape. IBRA is updated periodically based on new data, mapping improvements, and review of the existing scheme. The most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mallee (biogeographic Region)
Mallee, also known as Roe Botanical District, is a biogeographic region in southern Western Australia. Located between the Esperance Plains, Avon Wheatbelt and Coolgardie bioregions, it has a low, gently undulating topography, a semi-arid mediterranean climate, and extensive ''Eucalyptus'' mallee vegetation. It has an area of . About half of the region has been cleared for intensive agriculture. Recognised as a region under the Interim Biogeographic Regionalisation for Australia (IBRA), it was first defined by John Stanley Beard in 1980. Geography and geology The Mallee region has a complex shape with tortuous boundaries, but may be roughly approximated as the triangular area south of a line from Bruce Rock to Eyre, but not within 40 kilometres (25 mi) of the south coast, except at its eastern limits. It has an area of about 79000 square kilometres (31000 mi²), making it about a quarter of the South West Botanic Province, 3% of the state, and 1% of Australia. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
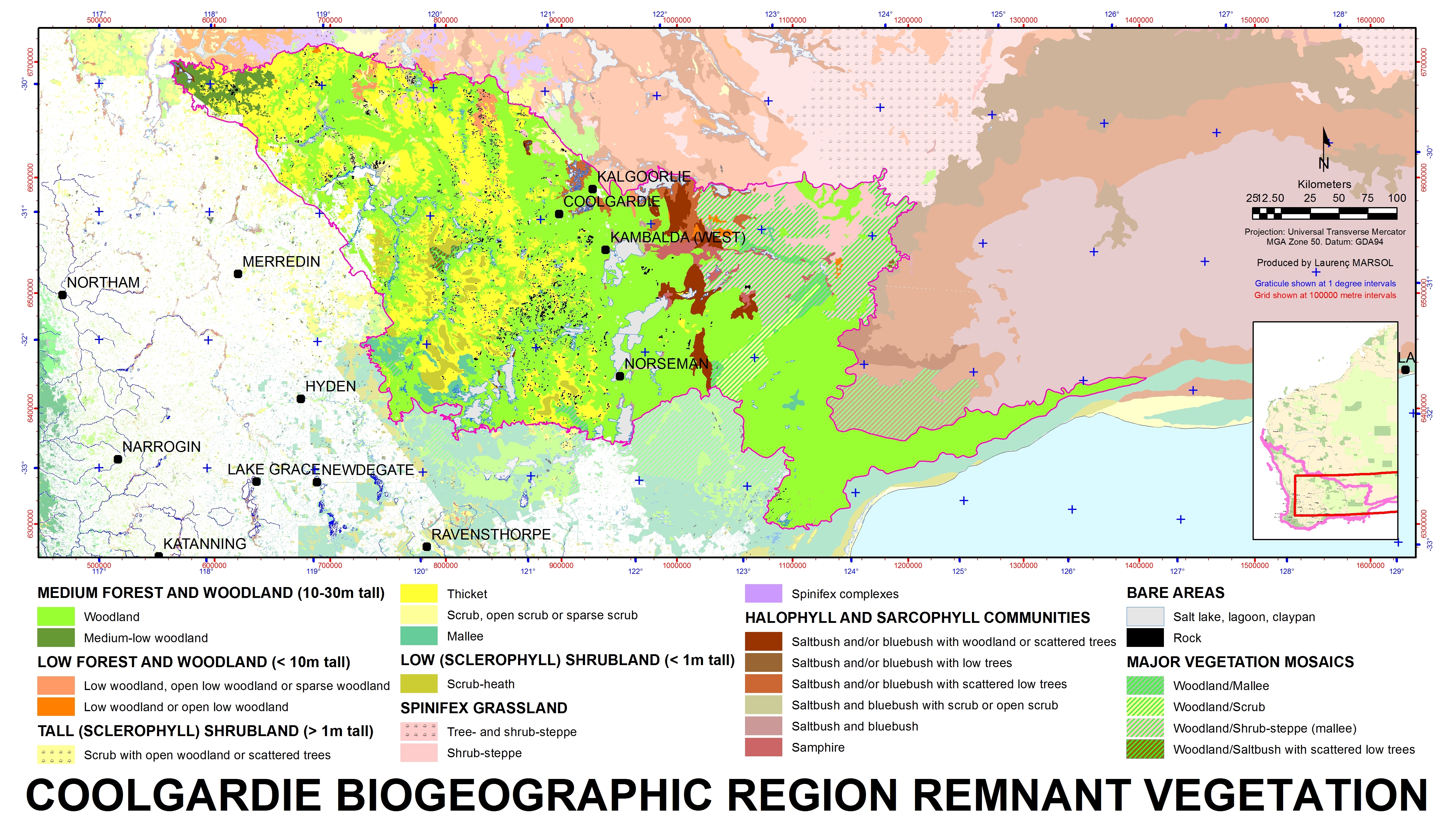
Coolgardie (biogeographic Region)
Coolgardie is an Australian bioregion consisting of an area of low hills and plains of infertile sandy soil in Western Australia. It has an area of . It includes much of the Great Western Woodlands. Location and description This is a transition zone between the Mediterranean climate of Australia's south-west coast and the country's dry interior. The poor soil makes it unsuitable for agriculture but Coolgardie has been a gold and nickel mining area. It is bounded on the north by the arid Murchison bioregion, characterised by open Mulga woodlands and steppe. The low shrublands of the arid Nullarbor Plain lie to the east. The Mallee bioregion adjoins Coolgardie on the south. The Avon Wheatbelt bioregion is to the west. The Coolgardie bioregion, together with the coastal Hampton bioregion to the southeast, constitute the Coolgardie woodlands ecoregion defined by the World Wildlife Fund. Flora and fauna The low hills are home to woodland of endemic species of eucalyptus while t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avon Wheatbelt
The Avon Wheatbelt is a bioregion in Western Australia. It has an area of . It is considered part of the larger Southwest Australia savanna ecoregion. Geography The Avon Wheatbelt bioregion is mostly a gently undulating landscape with low relief. It lies on the Yilgarn Craton, an ancient block of crystalline rock, which was uplifted in the Tertiary and dissected by rivers. The craton is overlain by laterite deposits, which in places have decomposed into yellow sandplains, particularly on low hills. Steep-sided erosional gullies, known as breakaways, are common. Beecham, Brett (2001). "Avon Wheatbelt 2 (AW2 - Re-juvenated Drainage subregion)" in ''A Biodiversity Audit of Western Australia’s 53 Biogeographical Subregions in 2002''. Department of Conservation and Land Management, Government of Western Australia, November 2001. Accessed 15 May 2022/ref> In the south and west (the Katanning subregion), streams are mostly perennial, and feed rivers which drain westwards to empty in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forrestania Airport
Forrestania Airport is located at Forrestania, Western Australia. See also * List of airports in Western Australia This is a list of airports in the Australian state of Western Australia. __TOC__ List of airports The list is sorted by the name of the community served, click the sort buttons in the table header to switch listing order. Airports named in bo ... * Aviation transport in Australia References External links Airservices Aerodromes & Procedure Charts Airports in Western Australia {{WesternAustralia-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bullabulling, Western Australia
Bullabulling (spelled "Bulla Bulling" until 1944) is a small townsite located 526 km (327 mi) east of Perth, Western Australia on the Great Eastern Highway in the Goldfields-Esperance region. The town was gazetted in 1898, when the population of the town was 160 (140 males and 20 females). Its central feature was the Rock Hotel roadhouse (also known as Rock Tavern), which closed around 2015. Bullabulling is also the location of a reservoir which forms part of the Goldfields Water Supply Scheme. From here, the water gravitates (i.e. moves without pumping) to Coolgardie and Kalgoorlie. In 1996, Bullabulling was registered as a place of cultural heritage significance. References Towns in Western Australia {{WesternAustralia-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walgoolan, Western Australia
Walgoolan is a small town located in the eastern Wheatbelt region of Western Australia. It is situated between Merredin and Bodallin along the Great Eastern Highway. Originating as a railway siding on the main eastern railway, Walgoolan was established between 1895 and 1899. Land was set aside for a townsite in 1913 and lots were surveyed in 1922. The townsite was gazetted in 1923. The name of the town is Aboriginal in origin and means ''place where the short bushes grow''. Following World War I, nearly 100 settlers took up land in the area, which were cleared and planted with cereal crops, mostly wheat. The town was a thriving community with five schools, tennis courts, a cricket club, Country Women's Association and Wheat Growers Union. Tenders for the construction of a brick and cement hall in the town were called for in 1926. The hall was opened and being used for recitals and other community events the following year. The Westonia Road board held a referendum among ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verticordia Fimbrilepis
''Verticordia fimbrilepis'', commonly known as shy featherflower, is a flowering plant in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae and is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It is a small, bushy shrub with one openly branched main stem at its base, small, pointed leaves and rounded groups of pink flowers near the ends of the branches. Description ''Verticordia fimbrilepis'' is a shrub which grows to a height and width of about and which has one openly branched stem at its base. The leaves lower on the stems are linear in shape, almost round in cross-section, long with a rounded end with a sharp point. Those near the flowers are more oblong to narrow egg-shaped. The flowers are arranged in rounded groups on stalks long near the ends of the branches. The floral cup is broadly top-shaped, about long, glabrous but slightly rough. The sepals are pink, sometimes white, long, with 5 to 7 hairy lobes. The petals are also pink or white, and are long, egg-shaped with long, coarse hai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verticordia Pityrhops
''Verticordia pityrhops'', commonly known as East Mount Barren featherflower or pine-like featherflower, is a flowering plant in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae and is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It is a single-stemmed shrub which is densely-branched with crowded narrow linear leaves giving the impression of a miniature pine tree. When it flowers in autumn, the shrub is completely covered with masses of very small, honey-scented, pinkish-purple flowers. Description ''Verticordia pityrhops'' is a shrub with a single, thick, densely branched main stem and a few side branches and which grows to a height of and wide, although some specimens grow to as high as . Its leaves are dark green and crowded, narrow linear, almost needle-like, long with a pointed tip. The flowers are scented and arranged in corymb-like groups near the ends of the branches, each flower on a stalk long. The floral cup is top-shaped, about long, smooth but hairy. The sepals are about long, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |