|
Versioning File System
A versioning file system is any computer file system which allows a computer file to exist in several versions at the same time. Thus it is a form of revision control. Most common versioning file systems keep a number of old copies of the file. Some limit the number of changes per minute or per hour to avoid storing large numbers of trivial changes. Others instead take periodic snapshots whose contents can be accessed using methods similar as those for normal file access. Similar technologies Backup A versioning file system is similar to a periodic backup, with several key differences. * Backups are normally triggered on a timed basis, while versioning occurs when the file changes. * Backups are usually system-wide or partition-wide, while versioning occurs independently on a file-by-file basis. * Backups are normally written to separate media, while versioning file systems write to the same hard drive (and normally the same folder, directory, or local partition). In comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Next3
Next3 is a journaling file system for Linux based on ext3 which adds snapshots support, yet retains compatibility to the ext3 on-disk format. Next3 is implemented as open-source software, licensed under the GPL license. Background A snapshot is a read-only copy of the file system frozen at a point in time. Versioning file systems like Next3 can internally track old versions of files and make snapshots available through a special namespace. Features Snapshots An advantage of copy-on-write is that when Next3 writes new data, the blocks containing the old data can be retained, allowing a snapshot version of the file system to be maintained. Next3 snapshots are created quickly, since all the data composing the snapshot is already stored; they are also space efficient, since any unchanged data is shared among the file system and its snapshots. Dynamically Provisioned Snapshots Space The traditional Linux Logical Volume Manager volume level snapshots implementation requires tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HAMMER (file System)
HAMMER is a high-availability 64-bit file system developed by Matthew Dillon for DragonFly BSD using B+ trees. Its major features include infinite NFS-exportable snapshots, master–multislave operation, configurable history retention, fsckless-mount, and checksums to deal with data corruption. HAMMER also supports data block deduplication, meaning that identical data blocks will be stored only once on a file system. A successor, HAMMER2, was announced in 2011 and became the default in Dragonfly 5.2 (April 2018). Features HAMMER file system provides configurable fine-grained and coarse-grained filesystem histories with online snapshots availability. Up to 65536 '' master'' (read–write) and ''slave'' (read-only) pseudo file systems (PFSs), with independent individual retention parameters and inode numbering, may be created for each file system; PFS may be mirrored to multiple slaves both locally or over network connection with near real-time performance. No file system ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Btrfs
Btrfs (pronounced as "better F S", "butter F S", "b-tree F S", or "B.T.R.F.S.") is a computer storage format that combines a file system based on the copy-on-write (COW) principle with a logical volume manager (distinct from Linux's LVM), developed together. It was created by Chris Mason in 2007 for use in Linux, and since November 2013, the file system's on-disk format has been declared stable in the Linux kernel. Btrfs is intended to address the lack of pooling, snapshots, integrity checking, data scrubbing, and integral multi-device spanning in Linux file systems. Mason, the principal Btrfs author, stated that its goal was "to let inuxscale for the storage that will be available. Scaling is not just about addressing the storage but also means being able to administer and to manage it with a clean interface that lets people see what's being used and makes it more reliable". History The core data structure of Btrfsthe copy-on-write B-treewas originally proposed by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apple File System
Apple File System (APFS) is a Proprietary software, proprietary file system developed and deployed by Apple Inc. for macOS macOS Sierra, Sierra (10.12.4) and later, iOS iOS 10 , 10.3, tvOS 10.2, watchOS 3.2, and all versions of iPadOS. It aims to fix HFS Plus#Criticisms, core problems of HFS Plus, HFS+ (also called Mac OS Extended), APFS's predecessor which had been in use since 1998. APFS is optimized for solid-state drive storage and supports encryption, Snapshot_(computer_storage) , snapshots, and improved handling of file system#metadata, metadata integrity. History Apple File System was announced at Apple Inc., Apple's Apple Worldwide Developers Conference, developers’ conference (WWDC) in June 2016 as a replacement for HFS Plus, HFS+, which had been in use since 1998. APFS was released for 64-bit computing, 64-bit iOS devices on March 27, 2017, with the release of iOS 10.3, and for macOS devices on September 25, 2017, with the release of MacOS High Sierra, macOS 10.1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
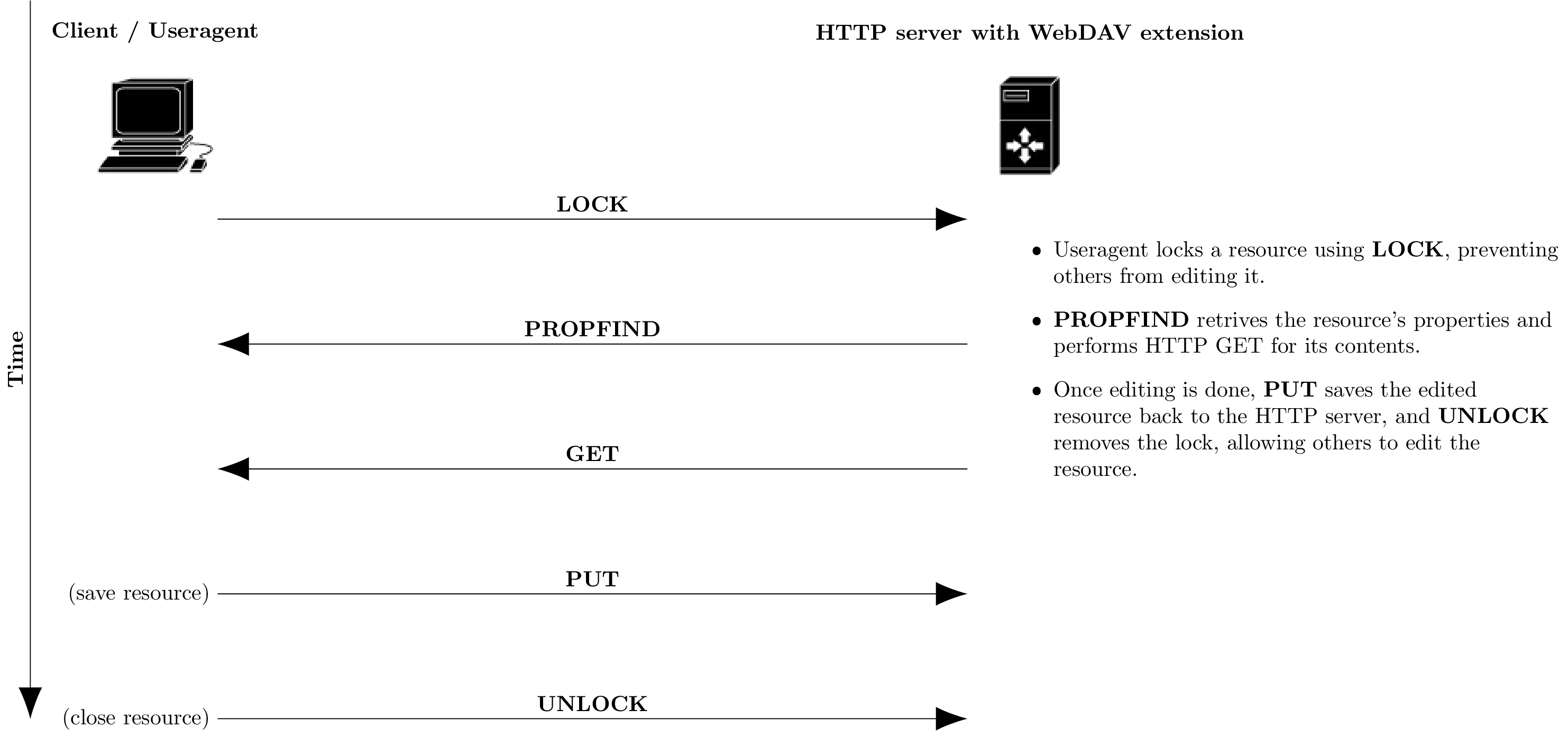
WebDAV
WebDAV (Web Distributed Authoring and Versioning) is a set of extensions to the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), which allows user agents to collaboratively author contents ''directly'' in an HTTP web server by providing facilities for concurrency control and namespace operations, thus allowing the Web to be viewed as a ''writeable, collaborative medium'' and not just a read-only medium. WebDAV is defined in by a working group of the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). The WebDAV protocol provides a framework for users to create, change and move documents on a server. The most important features include the maintenance of properties about an author or modification date, namespace management, collections, and overwrite protection. Maintenance of properties includes such things as the creation, removal, and querying of file information. Namespace management deals with the ability to copy and move web pages within a server's namespace. Collections deal with the creation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subversion (software)
Apache Subversion (often abbreviated SVN, after its command name ''svn'') is a version control system distributed as open source under the Apache License. Software developers use Subversion to maintain current and historical versions of files such as source code, web pages, and documentation. Its goal is to be a mostly compatible successor to the widely used Concurrent Versions System (CVS). The open source community has used Subversion widely: for example, in projects such as Apache Software Foundation, FreeBSD, SourceForge, and from 2006 to 2019, GCC. CodePlex was previously a common host for Subversion repositories. Subversion was created by CollabNet Inc. in 2000, and is now a top-level Apache project being built and used by a global community of contributors. History CollabNet founded the Subversion project in 2000 as an effort to write an open-source version-control system which operated much like CVS but which fixed the bugs and supplied some features missing in CVS. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SCO OpenServer
Xinuos OpenServer, previously SCO UNIX and SCO Open Desktop (SCO ODT), is a closed source computer operating system developed by Santa Cruz Operation (SCO), later acquired by SCO Group, and now owned by Xinuos. Early versions of OpenServer were based on UNIX System V, while the later OpenServer 10 is based on FreeBSD 10. However, OpenServer 10 has not received any updates since 2018 and is no longer marketed on Xinuos's website, while OpenServer 5 Definitive and 6 Definitive are still supported. History SCO UNIX/SCO Open Desktop In 1987 AT&T Corporation, Microsoft, and Sun Microsystems agreed to combine their versions of the Unix operating system. Santa Cruz Operation (SCO) sublicensed Microsoft's Xenix and wanted to retain the Xenix name, but AT&T said "If they want to call it Unix, they've got to use it the way it is. We don't want another set of variants". SCO UNIX was the successor to Xenix, derived from UNIX System V, UNIX System V Release 3.2 with an infusion of Xenix dev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HTFS
High Throughput File System (HTFS) is a journaling file system that was used by SCO OpenServer Xinuos OpenServer, previously SCO UNIX and SCO Open Desktop (SCO ODT), is a closed source computer operating system developed by Santa Cruz Operation (SCO), later acquired by SCO Group, and now owned by Xinuos. Early versions of OpenServer were .... The filesystem format is like that of an older SCO filesystem, the Extended Acer Filesystem (EAFS), but designed to be somewhat more future-proof. References Disk file systems {{compu-storage-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time Machine (macOS)
Time Machine is the backup mechanism of macOS, the desktop operating system developed by Apple. The software is designed to work with both local storage devices and network-attached disks, and is commonly used with external disk drives connected using either USB or Thunderbolt. It was first introduced in Mac OS X 10.5 Leopard, which was released in October 2007 and incrementally refined in subsequent releases of macOS. Time Machine was revamped in macOS 11 Big Sur to support APFS, thereby enabling "faster, more compact, and more reliable backups" than were possible previously. Overview Time Machine creates incremental backups of files that can be restored at a later date. It allows the user to restore the whole system or specific files. It also works within a number of applications such as Mail and iWork, making it possible to restore individual objects (e.g. emails, contacts, text documents, presentations) without leaving the application. For backups to a network drive, T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MacOS
macOS, previously OS X and originally Mac OS X, is a Unix, Unix-based operating system developed and marketed by Apple Inc., Apple since 2001. It is the current operating system for Apple's Mac (computer), Mac computers. Within the market of Desktop computer, desktop and laptop computers, it is the Usage share of operating systems#Desktop and laptop computers, second most widely used desktop OS, after Microsoft Windows and ahead of all Linux distributions, including ChromeOS and SteamOS. , the most recent release of macOS is MacOS Sequoia, macOS 15 Sequoia, the 21st major version of macOS. Mac OS X succeeded classic Mac OS, the primary Mac operating systems, Macintosh operating system from 1984 to 2001. Its underlying architecture came from NeXT's NeXTSTEP, as a result of NeXT#1997–2006: Acquisition by Apple, Apple's acquisition of NeXT, which also brought Steve Jobs back to Apple. The first desktop version, Mac OS X 10.0, was released on March 24, 2001. Mac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mac OS X Lion
OS X Lion, also known as Mac OS X Lion, (version 10.7) is the eighth major release of macOS, Apple's desktop and server operating system for Mac computers. A preview of OS X 10.7 Lion was publicly shown at the "Back to the Mac" Apple Special Event on October 20, 2010. It brought many developments made in Apple's iOS, such as an easily navigable display of installed applications, to the Mac, and includes support for the Mac App Store, as introduced in Mac OS X 10.6 Snow Leopard version 10.6.6. On February 24, 2011, the first developer's preview of Lion (11A390) was released to subscribers to the Apple Developer program. Other developer previews were subsequently released, with Lion Preview 4 (11A480b) being released at WWDC 2011. Lion was released to manufacturing on July 1, 2011, followed by its final release via the Mac App Store on July 20, 2011. Apple reported over one million Lion sales on the first day of its release. , OS X Lion had sold over six million copies wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |