|
Varisi Language
Varisi is an indigenous language of Choiseul Province, Solomon Islands. External links * Paradisec The Pacific and Regional Archive for Digital Sources in Endangered Cultures (PARADISEC) is a cross-institutional project that supports work on endangered languages and cultures of the Pacific and the region around Australia. They digitise reel-to ... haa number of collections that include Varisi language materials. References Languages of the Solomon Islands Northwest Solomonic languages {{MesoMelanesian-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands is an island country consisting of six major islands and over 900 smaller islands in Oceania, to the east of Papua New Guinea and north-west of Vanuatu. It has a land area of , and a population of approx. 700,000. Its capital, Honiara, is located on the largest island, Guadalcanal. The country takes its name from the wider area of the Solomon Islands (archipelago), which is a collection of Melanesian islands that also includes the Autonomous Region of Bougainville (currently a part of Papua New Guinea), but excludes the Santa Cruz Islands. The islands have been settled since at least some time between 30,000 and 28,800 BCE, with later waves of migrants, notably the Lapita people, mixing and producing the modern indigenous Solomon Islanders population. In 1568, the Spanish navigator Álvaro de Mendaña was the first European to visit them. Though not named by Mendaña, it is believed that the islands were called ''"the Solomons"'' by those who later receiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malayo-Polynesian Languages
The Malayo-Polynesian languages are a subgroup of the Austronesian languages, with approximately 385.5 million speakers. The Malayo-Polynesian languages are spoken by the Austronesian peoples outside of Taiwan, in the island nations of Southeast Asia (Indonesian and Philippine Archipelago) and the Pacific Ocean, with a smaller number in continental Asia in the areas near the Malay Peninsula. Cambodia, Vietnam and the Chinese island Hainan serve as the northwest geographic outlier. Malagasy, spoken in the island of Madagascar off the eastern coast of Africa in the Indian Ocean, is the furthest western outlier. The languages spoken south-westward from central Micronesia until Easter Island are sometimes referred to as the Polynesian languages. Many languages of the Malayo-Polynesian family show the strong influence of Sanskrit and Arabic, as the western part of the region has been a stronghold of Hinduism, Buddhism, and, later, Islam. Two morphological characteristics of the M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oceanic Languages
The approximately 450 Oceanic languages are a branch of the Austronesian languages. The area occupied by speakers of these languages includes Polynesia, as well as much of Melanesia and Micronesia. Though covering a vast area, Oceanic languages are spoken by only two million people. The largest individual Oceanic languages are Eastern Fijian with over 600,000 speakers, and Samoan with an estimated 400,000 speakers. The Gilbertese (Kiribati), Tongan, Tahitian, Māori, Western Fijian and Tolai (Gazelle Peninsula) languages each have over 100,000 speakers. The common ancestor which is reconstructed for this group of languages is called Proto-Oceanic (abbr. "POc"). Classification The Oceanic languages were first shown to be a language family by Sidney Herbert Ray in 1896 and, besides Malayo-Polynesian, they are the only established large branch of Austronesian languages. Grammatically, they have been strongly influenced by the Papuan languages of northern New Guinea, but they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Oceanic Languages
The Western Oceanic languages is a linkage of Oceanic languages, proposed and studied by . Classification The West Oceanic linkage is made up of three sub-linkages:. * North New Guinea linkage * Meso-Melanesian linkage * Papuan Tip linkage The center of dispersal was evidently near the Willaumez Peninsula The Willaumez Peninsula is located on the north coast of New Britain in the West New Britain Province. It was named after Jean-Baptiste Philibert Willaumez Jean-Baptiste Philibert Willaumez (7 August 1763 – 17 May 1845) was a French sailor, ... on the north coast of New Britain. Notes References * * {{Austronesian languages Oceanic languages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meso-Melanesian Languages
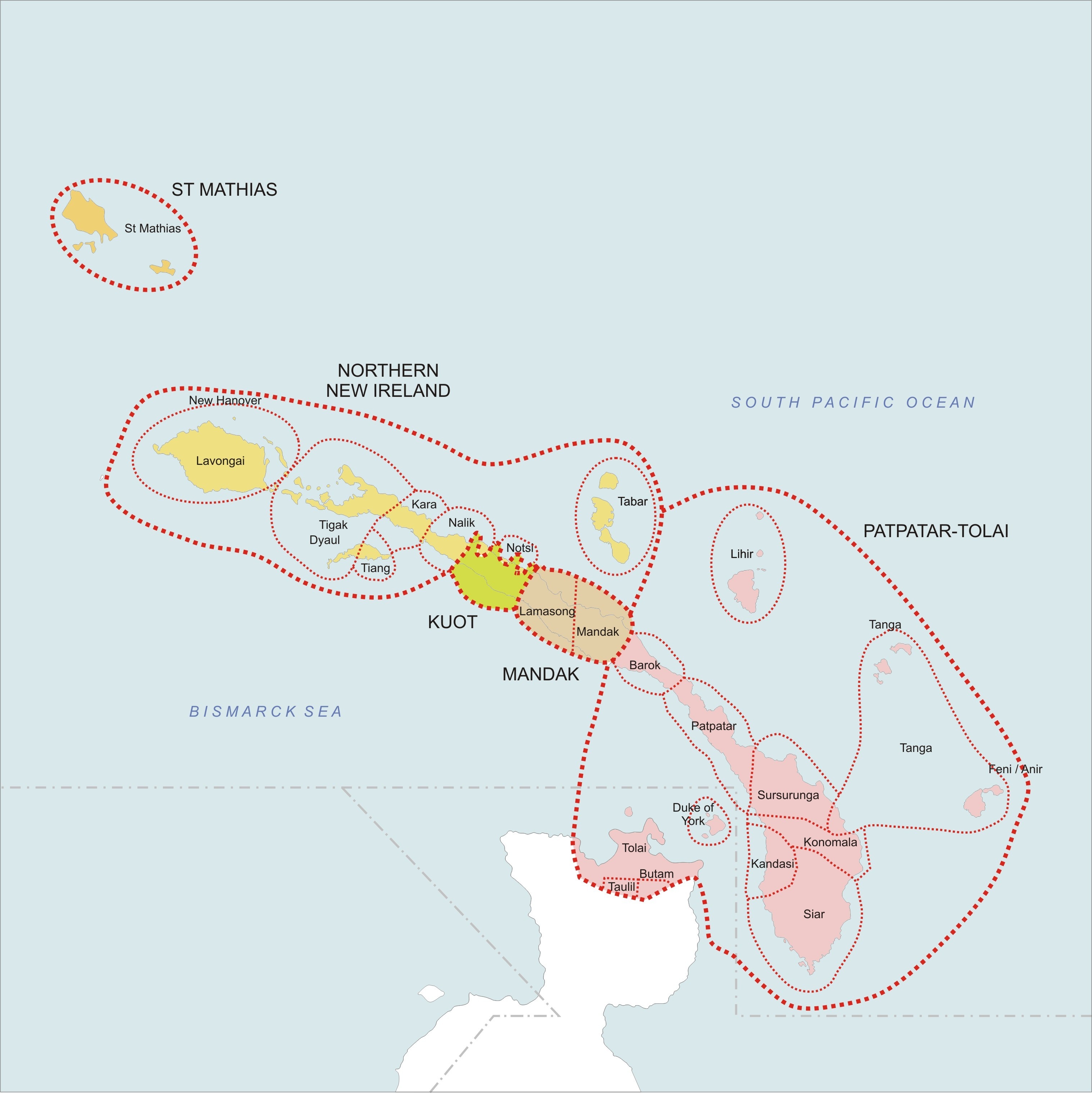
The Meso-Melanesian languages are a Linkage (linguistics), linkage of Oceanic languages spoken in the large Melanesian islands of New Ireland and the Solomon Islands east of New Guinea. Uneapa language, Bali is one of the most conservative languages. Composition The languages group as follows: *Willaumez Peninsula, Willaumez linkage: Bola language (Austronesian), Bola, Bulu language (Oceanic), Bulu, Meramera language, Meramera, Nakanai language, Nakanai *Bali–Vitu: Uneapa language, Bali (Uneapa), Vitu language, Vitu (Muduapa) [may be a single language] *New Ireland – Northwest Solomonic linkage **Tungag–Nalik family: Tigak language, Tigak, Tungag language, Tungag, Nalik language, Nalik, Laxudumau language, Laxudumau, Kara language (Papua New Guinea), Kara, Tiang language, Tiang **Tabar linkage: Mandara language, Madara (Tabar), Lihir language, Lihir, Notsi language, Notsi **Madak linkage: Barok language, Barok, Lavatbura-Lamusong language, Lavatbura-Lamusong, Madak langua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northwest Solomonic Languages
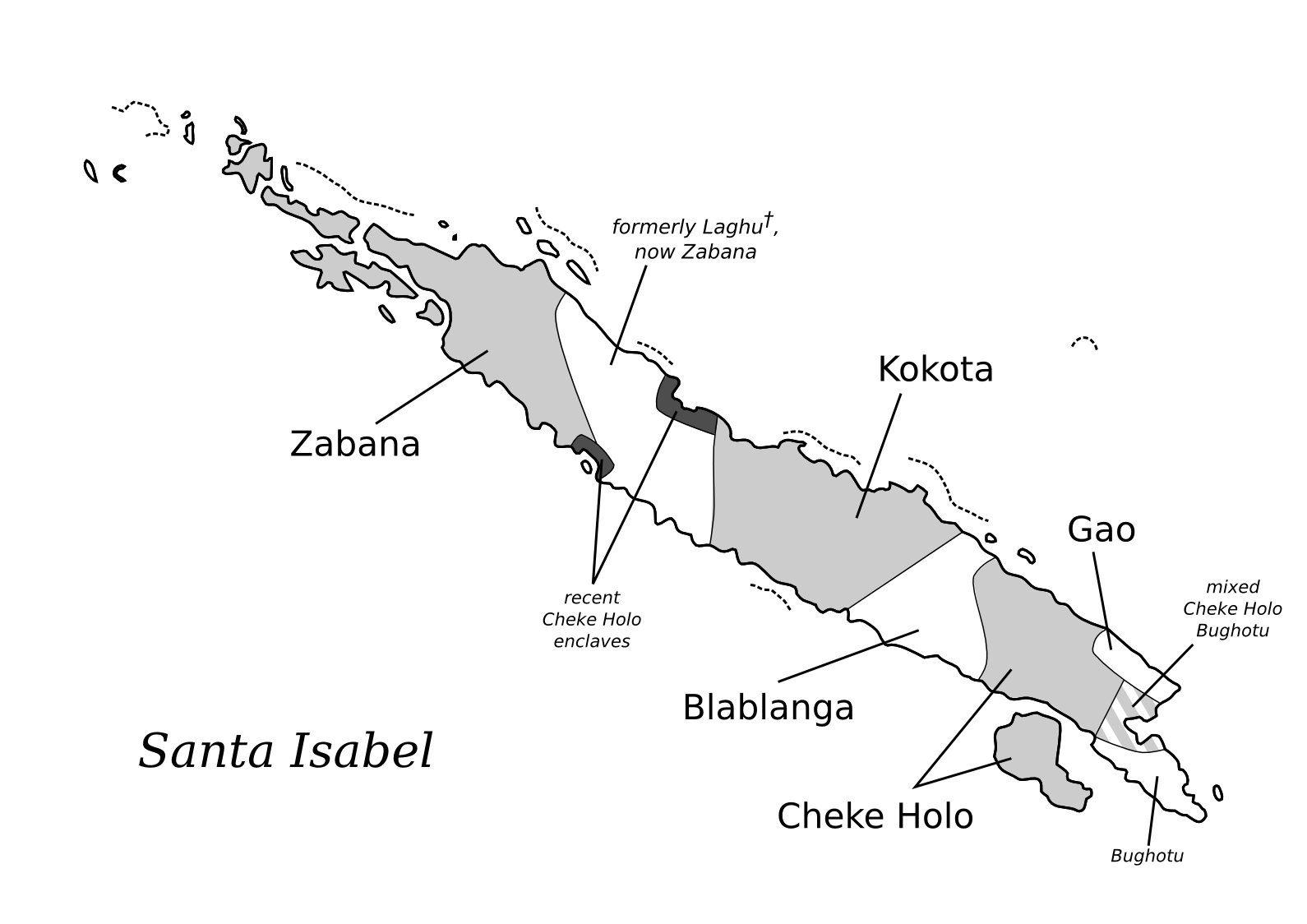
The family of Northwest Solomonic languages is a branch of the Oceanic languages. It includes the Austronesian languages of Bougainville and Buka in Papua New Guinea, and of Choiseul, New Georgia, and Santa Isabel (excluding Bugotu) in Solomon Islands. The unity of Northwest Solomonic and the number and composition of its subgroups, along with its relationship to other Oceanic groups, was established in pioneering work by Malcolm Ross. Languages Northwest Solomonic languages group as follows: * Nehan – North Bougainville linkage ** Nehan (Nissan) **Saposa–Tinputz: Hahon, Ratsua, Saposa (Taiof)– Teop, Tinputz **Buka: Halia– Hakö, Petats ** Papapana ** Solos * Piva–Bannoni family: Piva (Lawunuia), Bannoni * Mono–Uruavan family: Mono-Alu, Torau, Uruava *Choiseul linkage: Babatana (including Sisingga)– Ririo, Vaghua– Varisi *New Georgia – Ysabel family **New Georgia linkage: Simbo (Simbo Island), Roviana– Kusaghe, Marovo, Hoava, Vangunu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choiseul Languages
The family of Northwest Solomonic languages is a branch of the Oceanic languages. It includes the Austronesian languages of Bougainville and Buka in Papua New Guinea, and of Choiseul, New Georgia, and Santa Isabel (excluding Bugotu) in Solomon Islands. The unity of Northwest Solomonic and the number and composition of its subgroups, along with its relationship to other Oceanic groups, was established in pioneering work by Malcolm Ross. Languages Northwest Solomonic languages group as follows: * Nehan – North Bougainville linkage ** Nehan (Nissan) **Saposa–Tinputz: Hahon, Ratsua, Saposa (Taiof)– Teop, Tinputz **Buka: Halia– Hakö, Petats ** Papapana ** Solos * Piva–Bannoni family: Piva (Lawunuia), Bannoni * Mono–Uruavan family: Mono-Alu, Torau, Uruava *Choiseul linkage: Babatana (including Sisingga)– Ririo, Vaghua– Varisi *New Georgia – Ysabel family **New Georgia linkage: Simbo (Simbo Island), Roviana– Kusaghe, Marovo, Hoava, Vangunu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigenous Language
An indigenous language, or autochthonous language, is a language that is native to a region and spoken by indigenous peoples. This language is from a linguistically distinct community that originated in the area. Indigenous languages are not necessarily national languages but they can be; for example, Aymara is an official language of Bolivia. Also, national languages are not necessarily indigenous to the country. Many indigenous peoples worldwide have stopped passing on their ancestral languages to the next generation and have instead adopted the majority language as part of their acculturation into the majority culture. Furthermore, many indigenous languages have been subject to linguicide (language killing). Recognizing their vulnerability, the United Nations proclaimed 2019 the International Year of Indigenous Languages "to draw attention to the critical loss of indigenous languages and the urgent need to preserve, revitalize and promote indigenous languages." Disappearan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choiseul Province
Choiseul Province is one of the nine provinces of Solomon Islands. It lies southeast of Bougainville (part of Papua New Guinea), west of Santa Isabel Island, and north of Vella la Vella, Kolombangra & New Georgia. It has a population of 36,719 (as of 2020) The province has three major islands: Choiseul, Wagina, and Rob Roy. Choiseul Island (commonly known as Lauru to the natives) has a land area of ; Wagina's is ; Rob Roy's is . Taro Island, the capital of the province, has an area of . History Discovery and naming When the natives first arrived and discovered the big island, they called it Lauru. Then, in 1568, the Spanish explorer Álvaro de Mendaña de Neira rediscovered the island and named it San Marcos ('Saint Mark'). Mendana himself never set foot on Lauru. He called it San Marcos, because he saw the island from Santa Isabel on the Day of Saint Mark. 200 years later in 1768, the French explorer Louis Antoine de Bougainville saw the island again and named it C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paradisec
The Pacific and Regional Archive for Digital Sources in Endangered Cultures (PARADISEC) is a cross-institutional project that supports work on endangered languages and cultures of the Pacific and the region around Australia. They digitise reel-to-reel field tapes, have a mass data store and use international standards for metadata description. PARADISEC is part of the worldwide community of language archives (Delaman and the Open Language Archives Community). PARADISEC's main motivation is to ensure that unique recordings of small languages are themselves preserved for the future, and that researchers consider the future accessibility to their materials for other researchers, community members, or anyone who has an interest in such materials. Vanishing voices As the number of small languages in the world is reduced by many factors (urbanisation, colonial policies, the speakers' desire to learn languages which give access to resources), the tapes which may be their only record beco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Languages Of The Solomon Islands
Between 60 and 70 languages are spoken in the Solomon Islands Archipelago which covers a broader area than the nation state of Solomon Islands, and includes the island of Bougainville, which is an autonomous province of Papua New Guinea (PNG). The lingua franca of the archipelago is Pidgin, and the official language in both countries is English. Language families Most of the languages in the Solomon Islands are Austronesian languages. The Central Solomon languages such as Lavukaleve constitute an independent family. Two other language families are represented on Bougainville, which is geographically part of the Solomon Islands, if not within the national boundaries. The status of the Reefs – Santa Cruz languages were once thought to be non-Austronesian, but further research found them to be divergent Austronesian languages. The neighbouring languages of Vanikoro are also heavily relexified Austronesian languages. An indigenous sign language, Rennellese Sign Language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |