|
Vanishing Bile Duct Syndrome
Vanishing bile duct syndrome is a loose collection of diseases which leads to the injury to hepatic bile ducts and eventual ductopenia. Signs and symptoms The presentation is dependent upon the underlying cause. The course can be rapid or chronic. * Fatigue * Anorexia * Abdominal pain * Weight loss * Pruritus * Hyperlipidemia * Malabsorption * Fat-soluble vitamin deficiencies * Elevated alkaline phosphatase * Elevated gamma-glutamyltransferase * Elevated conjugated bilirubin Cause Congenital In fetal and neonatal life the ductal plates are remodeled. The malformations can be atretic or fibrocystic. Atretic causes * Intrahepatic bile duct atresia (Alagille syndrome) (ALGS2 MIM:610205 and ALGS1 MIM:118450) * Extrahepatic bile duct atresia Fibrocystic causes * Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease * Congential hepatic fibrosis * Caroli's disease * Von Meyenburg complex Chromosomal associations * Trisomy 17, 18 and 21 Genetic associations * Cystic fibrosis * Alpha 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastroenterology
Gastroenterology (from the Greek gastḗr- “belly”, -énteron “intestine”, and -logía "study of") is the branch of medicine focused on the digestive system and its disorders. The digestive system consists of the gastrointestinal tract, sometimes referred to as the ''GI tract,'' which includes the esophagus, stomach, small intestine and large intestine as well as the accessory organs of digestion which includes the pancreas, gallbladder, and liver. The digestive system functions to move material through the GI tract via peristalsis, break down that material via digestion, absorb nutrients for use throughout the body, and remove waste from the body via defecation. Physicians who specialize in the medical specialty of gastroenterology are called gastroenterologists or sometimes ''GI doctors''. Some of the most common conditions managed by gastroenterologists include gastroesophageal reflux disease, gastrointestinal bleeding, irritable bowel syndrome, irritable bowel dise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
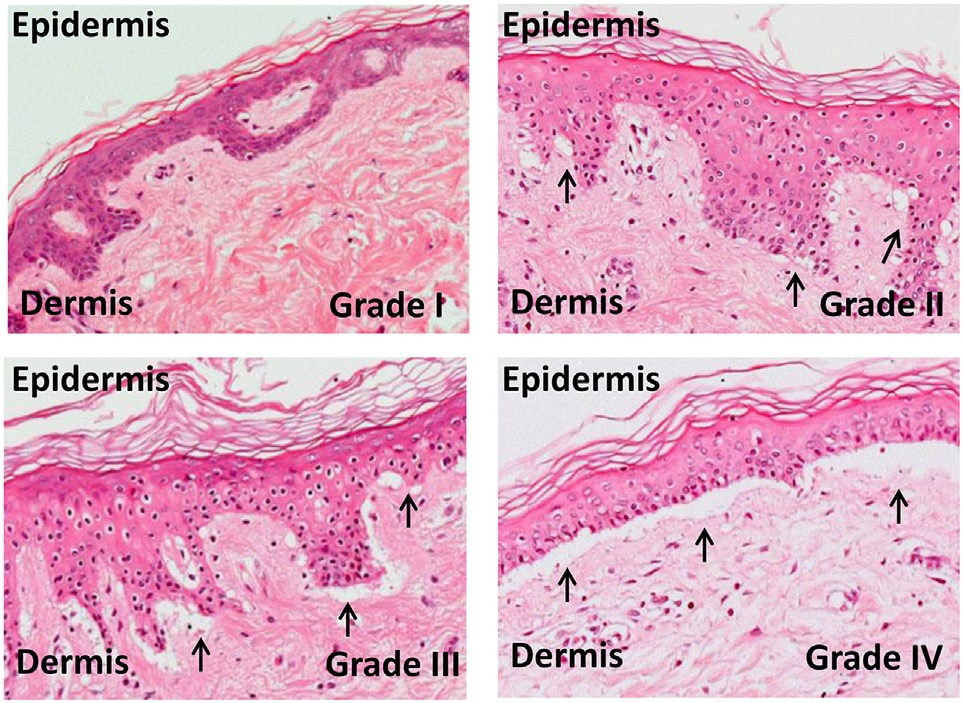
Ductopenia
Ductopenia refers to a reduction in the number of ducts in an organ, in particular the absence of bile ducts of the expected size in the portal tract of the liver. It is the histological hallmark of vanishing bile duct syndrome (typically <0.5 s per ). The most common cause of ductopenia is . Other causes of ductopenia include failing , |
Alagille Syndrome
Alagille syndrome is a genetic disorder that affects primarily the liver and the heart. Problems associated with the disorder generally become evident in infancy or early childhood. The disorder is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern, and the estimated prevalence of Alagille syndrome is 1 in every 30,000 to 1 in every 40,000 live births. It is named after the French pediatrician Daniel Alagille, who first described the condition in 1969. Signs and symptoms The severity of the disorder can vary within the same family, with symptoms ranging from so mild as to go unnoticed, to severe heart and/or liver disease that requires transplantation. It is uncommon, but Alagille syndrome can be a life-threatening disease with a mortality rate of 10%. The majority of deaths from ALGS are typically due to heart complications or chronic liver failure. Liver Signs and symptoms arising from liver damage in Alagille syndrome may include a yellowish tinge in the skin and the whites of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byler's Disease
Progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis (PFIC) is a group of familial cholestatic conditions caused by defects in biliary epithelial transporters. The clinical presentation usually occurs first in childhood with progressive cholestasis. This usually leads to failure to thrive, cirrhosis, and the need for liver transplantation. Types Types of progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis are as follows: * Type 1 (OMIM #211600), also called Byler disease * Type 2 (OMIM #601847), also called ABCB11 deficiency or BSEP deficiency * Type 3 (OMIM #602347), also called ABCB4 deficiency or MDR3 deficiency * Type 4 (OMIM #615878), from mutation in ''TJP2'' Signs and symptoms The onset of the disease is usually before age 2, but patients have been diagnosed with PFIC even into adolescence. Of the three entities, PFIC-1 usually presents earliest. Patients usually present in early childhood with cholestasis, jaundice, and failure to thrive. Intense pruritus is characteristic; in pati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hodgkin's Lymphoma
Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) is a type of lymphoma, in which cancer originates from a specific type of white blood cell called lymphocytes, where multinucleated Reed–Sternberg cells (RS cells) are present in the patient's lymph nodes. The condition was named after the English physician Thomas Hodgkin, who first described it in 1832. Symptoms may include fever, night sweats, and weight loss. Often, nonpainful enlarged lymph nodes occur in the neck, under the arm, or in the groin. Those affected may feel tired or be itchy. The two major types of Hodgkin lymphoma are classic Hodgkin lymphoma and nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma. About half of cases of Hodgkin lymphoma are due to Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) and these are generally the classic form. Other risk factors include a family history of the condition and having HIV/AIDS. Diagnosis is conducted by confirming the presence of cancer and identifying RS cells in lymph node biopsies. The virus-positive cases are classified ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graft-versus-host Disease
Graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) is a syndrome, characterized by inflammation in different organs. GvHD is commonly associated with bone marrow transplants and stem cell transplants. White blood cells of the donor's immune system which remain within the donated tissue (the graft) recognize the recipient (the host) as foreign (non-self). The white blood cells present within the transplanted tissue then attack the recipient's body's cells, which leads to GvHD. This should not be confused with a transplant rejection, which occurs when the immune system of the transplant recipient rejects the transplanted tissue; GvHD occurs when the donor's immune system's white blood cells reject the recipient. The underlying principle (alloimmunity) is the same, but the details and course may differ. GvHD can also occur after a blood transfusion if the blood products used have not been irradiated or treated with an approved pathogen reduction system. Types In the clinical setting, graft-versus-hos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ursodeoxycholic Acid
Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA), also known as ursodiol, is a secondary bile acid, produced in humans and most other species from metabolism by intestinal bacteria. It is synthesized in the liver in some species, and was first identified in bile of bears of genus ''Ursus'', from which its name derived. In purified form, it has been used to treat or prevent several diseases of the liver or bile ducts. It is available as a generic medication. Medical uses UDCA has been used as medical therapy in gallstone disease (cholelithiasis) and for biliary sludge. UDCA helps reduce the cholesterol saturation of bile and leads to gradual dissolution of cholesterol-rich gallstones. UDCA may be given after bariatric surgery to prevent cholelithiasis, which commonly occurs due to the rapid weight loss producing biliary cholesterol oversaturation and also biliary dyskinesia secondary hormonal changes. Primary biliary cholangitis UDCA is used as therapy in primary biliary cholangitis (PBC; previou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunosuppression
Immunosuppression is a reduction of the activation or efficacy of the immune system. Some portions of the immune system itself have immunosuppressive effects on other parts of the immune system, and immunosuppression may occur as an adverse reaction to treatment of other conditions. In general, deliberately induced immunosuppression is performed to prevent the body from rejecting an organ transplant. Additionally, it is used for treating graft-versus-host disease after a bone marrow transplant, or for the treatment of auto-immune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, Sjögren's syndrome, or Crohn's disease. This is typically done using medications, but may involve surgery (splenectomy), plasmapheresis, or radiation. A person who is undergoing immunosuppression, or whose immune system is weak for some other reasons (such as chemotherapy or HIV), is said to be ''immunocompromised''. Deliberately induced Administration of immunosuppressive medic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organ Transplant
Organ transplantation is a medical procedure in which an organ is removed from one body and placed in the body of a recipient, to replace a damaged or missing organ. The donor and recipient may be at the same location, or organs may be transported from a donor site to another location. Organs and/or tissues that are transplanted within the same person's body are called autografts. Transplants that are recently performed between two subjects of the same species are called allografts. Allografts can either be from a living or cadaveric source. Organs that have been successfully transplanted include the heart, kidneys, Liver transplantation, liver, Lung transplantation, lungs, Pancreas transplantation, pancreas, Intestinal transplant, intestine, Thymus transplantation, thymus and uterus transplantation, uterus. Tissues include Bone grafting, bones, tendons (both referred to as musculoskeletal grafts), corneal transplantation, corneae, skin grafting, skin, Artificial heart valve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatology
Hepatology is the branch of medicine that incorporates the study of liver, gallbladder, biliary tree, and pancreas as well as management of their disorders. Although traditionally considered a sub-specialty of gastroenterology, rapid expansion has led in some countries to doctors specializing solely on this area, who are called hepatologists. Diseases and complications related to viral hepatitis and alcohol are the main reason for seeking specialist advice. More than two billion people have been infected with hepatitis B virus at some point in their life, and approximately 350 million have become persistent carriers. Up to 80% of liver cancers can be attributed to either hepatitis B or hepatitis C virus. In terms of mortality, the former is second only to smoking among known agents causing cancer. With more widespread implementation of vaccination and strict screening before blood transfusion, lower infection rates are expected in the future. In many countries, however, overall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_mixed_cellulary_type.jpg)