|
Van Der Vecht's Gland
Van der Vecht's gland or Van der Vecht's organ is a gland which is located in an area of modified cuticle on the rearmost gastral sternite of female wasps. This gland secretes chemicals which are important in the determination and maintenance of the hierarchy of groups of eusocial wasps and are used in the defence of the nests in others. In the Asian giant hornet (''Vespa mandarinia'') the van der Vecht's gland is used to scent mark hives of honey bees to attract other members of their colony to cooperatively attack the hive; the only known case of the gland's use to scent mark a food source. In the cleptoparasitic paper wasp '' Polistes semenowi'' the female usurps the host foundress, usually '' Polistes dominula'' and uses an enlarged Van der Vecht's gland to produce large quantities of hydrocarbons and to control the host workers, and even sometimes the host foundress. The gland was discovered by, and named in honour of, the Dutch entomologist Jacobus van der Vecht. At least ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
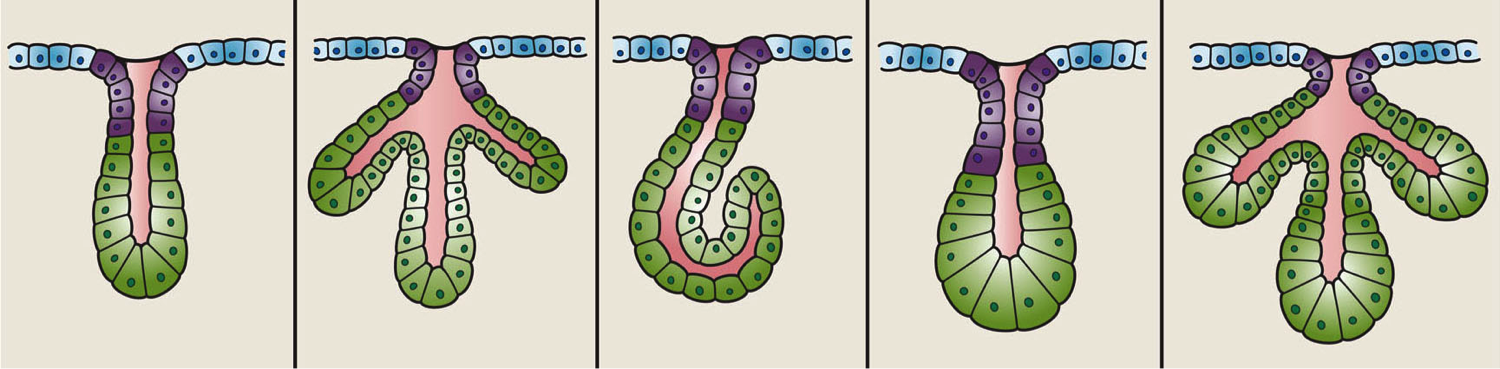
Gland
In animals, a gland is a group of cells in an animal's body that synthesizes substances (such as hormones) for release into the bloodstream (endocrine gland) or into cavities inside the body or its outer surface (exocrine gland). Structure Development Every gland is formed by an ingrowth from an epithelial surface. This ingrowth may in the beginning possess a tubular structure, but in other instances glands may start as a solid column of cells which subsequently becomes tubulated. As growth proceeds, the column of cells may split or give off offshoots, in which case a compound gland is formed. In many glands, the number of branches is limited, in others (salivary, pancreas) a very large structure is finally formed by repeated growth and sub-division. As a rule, the branches do not unite with one another, but in one instance, the liver, this does occur when a reticulated compound gland is produced. In compound glands the more typical or secretory epithelium is found forming t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entomologist
Entomology () is the scientific study of insects, a branch of zoology. In the past the term "insect" was less specific, and historically the definition of entomology would also include the study of animals in other arthropod groups, such as arachnids, myriapods, and crustaceans. This wider meaning may still be encountered in informal use. Like several of the other fields that are categorized within zoology, entomology is a taxon-based category; any form of scientific study in which there is a focus on insect-related inquiries is, by definition, entomology. Entomology therefore overlaps with a cross-section of topics as diverse as molecular genetics, behavior, neuroscience, biomechanics, biochemistry, systematics, physiology, developmental biology, ecology, morphology, and paleontology. Over 1.3 million insect species have been described, more than two-thirds of all known species. Some insect species date back to around 400 million years ago. They have many kinds of intera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insect Anatomy
Insect morphology is the study and description of the physical form of insects. The terminology used to describe insects is similar to that used for other arthropods due to their shared evolutionary history. Three physical features separate insects from other arthropods: they have a body divided into three regions (called tagmata) (head, thorax, and abdomen), have three pairs of legs, and mouthparts located ''outside'' of the head capsule. It is this position of the mouthparts which divides them from their closest relatives, the non-insect hexapods, which includes Protura, Diplura, and Collembola. There is enormous variation in body structure amongst insect species. Individuals can range from 0.3 mm ( fairyflies) to 30 cm across ( great owlet moth); have no eyes or many; well-developed wings or none; and legs modified for running, jumping, swimming, or even digging. These modifications allow insects to occupy almost every ecological niche on the planet, except the deep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vespinae
The subfamily Vespinae contains the largest and best-known eusocial wasps, including true hornets (the genus ''Vespa''), and the "yellowjackets" (genera ''Dolichovespula'' and ''Vespula''). The remaining genus, ''Provespa'', is a small, poorly known group of nocturnal wasps from Southeast Asia. One genus, ''Palaeovespa'', has been described from the Eocene fossil record, from Colorado. Collectively, the group can be found on all continents except Antarctica, and several of these wasps are invasive species An invasive species otherwise known as an alien is an introduced organism that becomes overpopulated and harms its new environment. Although most introduced species are neutral or beneficial with respect to other species, invasive species ad ..., introduced beyond their native ranges, and can be major pests. References Vespidae Biological pest control wasps Extant Eocene first appearances {{Vespidae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polistinae
The Polistinae is a subfamily of eusocial wasps belonging to the Family (biology), family Vespidae. They are closely related to the more familiar wasps (“yellowjackets” as they are called in North America) and true hornets of the subfamily Vespinae, containing four tribes. With about 1,100 species total, it is the second-most diverse subfamily within the Vespidae, and while most species are tropical or subtropical, they include some of the most frequently encountered large wasps in temperate regions. The Polistinae are also known as paper wasps, which is a misleading term, since other wasps (including the wasps in the subfamily Vespinae) also build nests out of paper, and because some epiponine wasps (e.g., ''Polybia emaciata'') build theirs out of mud, nonetheless, the name "paper wasp" seems to apply mostly, but not exclusively, to the Polistinae, especially the Polistini. Many polistines, such as ''Polistes fuscatus,'' ''Polistes annularis'', and ''Polistes exclamans'', m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stenogastrinae
The Stenogastrinae are a subfamily of social wasps included in the family Vespidae. They are sometimes called hover wasps owing to the particular hovering flight of some species. Their morphology and biology present interesting peculiarities. Systematic position The first reports on stenogastrine wasps can be found in a book of Guérin de Méneville (1831) with the first known species, ''Stenogaster fulgipennis''. Henri Louis Frédéric de Saussure treated their systematic position and remarked that these wasps were, in all their characters, entirely intermediate between the two subfamilies of Eumeninae and Vespinae. In 1927, Anton von Schulthess-Rechberg created the new genus ''Parischnogaster'' for some species living in the Oriental region. Dutch entomologist Jacobus van der Vecht created four new genera including species from the entire area of distribution and described tens of new species. He revised the two Papuan genera'' Anischnogaster'' and ''Stenogaster '' and the or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subfamily
In biological classification, a subfamily (Latin: ', plural ') is an auxiliary (intermediate) taxonomic rank, next below family but more inclusive than genus. Standard nomenclature rules end subfamily botanical names with "-oideae", and zoological names with "-inae". See also * International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants * International Code of Zoological Nomenclature * Rank (botany) * Rank (zoology) In biological classification, taxonomic rank is the relative level of a group of organisms (a taxon) in an ancestral or hereditary hierarchy. A common system consists of species, genus, family, order, class, phylum, kingdom, domain. While ... Sources {{biology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polistes
Wasps of the cosmopolitan genus ''Polistes'' (the only genus in the tribe Polistini) are the most familiar of the polistine wasps, and are the most common type of paper wasp in North America. Walter Ebeling coined the vernacular name "umbrella wasps" for this genus in 1975 to distinguish it from other types of paper wasp, in reference to the form of their nests. It is also the single largest genus within the family Vespidae, with over 300 recognized species and subspecies. Their innate preferences for nest-building sites leads them to commonly build nests on human habitation, where they can be very unwelcome; although generally not aggressive, they can be provoked into defending their nests. All species are predatory, and they may consume large numbers of caterpillars, in which respect they are generally considered beneficial. The European paper wasp, ''Polistes dominula'', was introduced into the US about 1981 and has quickly spread throughout most of the country, in most cases ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family (taxonomy), family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomy (biology), taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacobus Van Der Vecht
Jacobus van der Vecht (5 July 1906 – 15 March 1992), nicknamed Jaap, was a Dutch entomologist who specialised in Hymenoptera, especially those of the East Indies and New Guinea. Early life Van der Vecht was born in The Hague on 5 July 1906. His father, the Master of the Wine Cellars at the court of the then Queen Dowager of the Netherlands, Emma of Waldeck and Pyrmont, had an interest in natural history and reared butterflies as a hobby. He enjoyed taking his sons on walks to study nature and this encouraged a passion for biology in Jacobus. Van der Vecht left school in The Hague and enrolled to study Biology at the ''Leiden University, Rijksuniversiteit Leiden''. Here he began to study the Aculeata, Aculeate Hymenoptera especially the taxonomy of bees, concentrating on the large mining bee genus ''Andrena'' and the wasps in the family Sphecidae. He graduated with a master's degree in 1928. Career After graduating Van der Vecht took a position in the Dutch East Indies at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dutch People
The Dutch (Dutch: ) are an ethnic group and nation native to the Netherlands. They share a common history and culture and speak the Dutch language. Dutch people and their descendants are found in migrant communities worldwide, notably in Aruba, Suriname, Guyana, Curaçao, Argentina, Brazil, Canada,Based on Statistics Canada, Canada 2001 Censusbr>Linkto Canadian statistics. Australia, South Africa, New Zealand and the United States.According tFactfinder.census.gov The Low Countries were situated around the border of France and the Holy Roman Empire, forming a part of their respective peripheries and the various territories of which they consisted had become virtually autonomous by the 13th century. Under the Habsburgs, the Netherlands were organised into a single administrative unit, and in the 16th and 17th centuries the Northern Netherlands gained independence from Spain as the Dutch Republic. The high degree of urbanization characteristic of Dutch society was attained at a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuticle (insect Anatomy)
The cuticle forms the major part of the integument of the Arthropoda. It includes most of the material of the exoskeleton of the insects, Crustacea, Arachnida, and Myriapoda. Morphology In arthropods, the integument, the external "skin", or "shell", is the product of a single layer of ectodermal epithelium. That layer is attached to the external or distal surface of the deepest layer, the non-cellular internal membrane of the integument. That non-cellular membrane is called the basement membrane. The layer of epithelium on the basement membrane produces the cuticle, which begins as a tough, flexible layer of chitin. Such thin, flexible chitin is the major structural part of the integument where flexibility is necessary, such as in bodily parts that must stretch to contain accumulated liquids, or that form joints between rigid parts of the exoskeleton. In other parts of the cuticle the function of the integument demands more rigid materials, such as armoured regions or the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)


