|
Uterine Hypoplasia
Uterine hypoplasia, also known as naive uterus or infantile uterus, is a reproductive disorder characterized by hypoplasia of the uterus. It is usually due to pubertal failure/hypogonadism and may be treated with puberty induction using estrogens and/or progestogens. See also * Uterine hyperplasia * Uterine malformation A uterine malformation is a type of female genital malformation resulting from an abnormal development of the Müllerian duct(s) during embryogenesis. Symptoms range from amenorrhea, infertility, recurrent pregnancy loss, and pain, to normal funct ... References Congenital malformations of uterus and cervix {{symptom-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reproductive System Disease
A reproductive system disease is any disease of the reproductive system. Types Infections Reproductive tract infection (RTI) are infections that affect the reproductive tract, which is part of the Reproductive System. For females, reproductive tract infections can affect the upper reproductive tract (fallopian tubes, ovary and uterus) and the lower reproductive tract (vagina, cervix and vulva); for males these infections affect the penis, testicles, urethra or the vas deferens. The three types of reproductive tract infections are endogenous infections, iatrogenic infections and the more commonly known sexually transmitted infections. Each has its own specific causes and symptoms, caused by a bacterium, virus, fungus or other organism. Some infections are easily treatable and can be cured, some are more difficult, and some are non curable such as AIDS and herpes. Congenital abnormalities Examples of congenital abnormalities of the reproductive system include: *Kallmann syndrome - ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypoplasia
Hypoplasia (from Ancient Greek ὑπo- ''hypo-'' 'under' + πλάσις ''plasis'' 'formation'; adjective form ''hypoplastic'') is underdevelopment or incomplete development of a tissue or organ. Dictionary of Cell and Molecular Biology (11 March 2008) Although the term is not always used precisely, it properly refers to an inadequate or below-normal number of cells.Hypoplasia Stedman's Medical Dictionary. lww.com Hypoplasia is similar to |
Uterus
The uterus (from Latin ''uterus'', plural ''uteri'') or womb () is the organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans that accommodates the embryonic and fetal development of one or more embryos until birth. The uterus is a hormone-responsive sex organ that contains glands in its lining that secrete uterine milk for embryonic nourishment. In the human, the lower end of the uterus, is a narrow part known as the isthmus that connects to the cervix, leading to the vagina. The upper end, the body of the uterus, is connected to the fallopian tubes, at the uterine horns, and the rounded part above the openings to the fallopian tubes is the fundus. The connection of the uterine cavity with a fallopian tube is called the uterotubal junction. The fertilized egg is carried to the uterus along the fallopian tube. It will have divided on its journey to form a blastocyst that will implant itself into the lining of the uterus – the endometrium, where it will ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
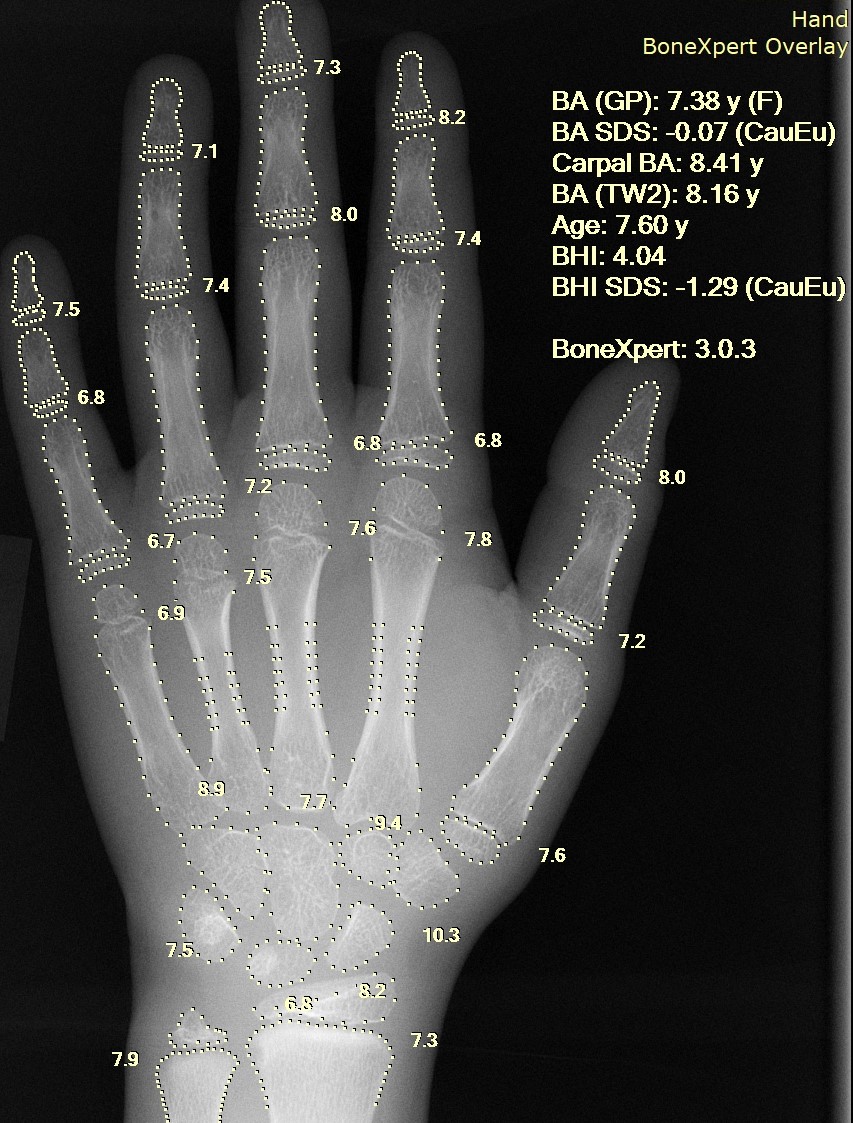
Delayed Puberty
Delayed puberty is when a person lacks or has incomplete development of specific sexual characteristics past the usual age of onset of puberty. The person may have no physical or hormonal signs that puberty has begun. In the United States, girls are considered to have delayed puberty if they lack breast development by age 13 or have not started menstruating by age 15. Boys are considered to have delayed puberty if they lack enlargement of the testicles by age 14. Delayed puberty affects about 2% of adolescents. Most commonly, puberty may be delayed for several years and still occur normally, in which case it is considered constitutional delay of growth and puberty, a common variation of healthy physical development. Delay of puberty may also occur due to various causes such as malnutrition, various systemic diseases, or defects of the reproductive system (hypogonadism) or the body's responsiveness to sex hormones. Initial workup for delayed puberty not due to a chronic condition in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypogonadism
Hypogonadism means diminished functional activity of the gonads—the testes or the ovaries—that may result in diminished production of sex hormones. Low androgen (e.g., testosterone) levels are referred to as hypoandrogenism and low estrogen (e.g., estradiol) as hypoestrogenism. These are responsible for the observed signs and symptoms in both males and females. Hypogonadism, commonly referred to by the symptom "low testosterone" or "Low T", can also decrease other hormones secreted by the gonads including progesterone, DHEA, anti-Müllerian hormone, activin, and inhibin. Sperm development (spermatogenesis) and release of the egg from the ovaries (ovulation) may be impaired by hypogonadism, which, depending on the degree of severity, may result in partial or complete infertility. In January 2020, the American College of Physicians issued clinical guidelines for testosterone treatment in adult men with age-related low levels of testosterone. The guidelines are supported b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puberty Induction
Delayed puberty is when a person lacks or has incomplete development of specific sexual characteristics past the usual age of onset of puberty. The person may have no physical or hormonal signs that puberty has begun. In the United States, girls are considered to have delayed puberty if they lack breast development by age 13 or have not started menstruating by age 15. Boys are considered to have delayed puberty if they lack enlargement of the testicles by age 14. Delayed puberty affects about 2% of adolescents. Most commonly, puberty may be delayed for several years and still occur normally, in which case it is considered constitutional delay of growth and puberty, a common variation of healthy physical development. Delay of puberty may also occur due to various causes such as malnutrition, various systemic diseases, or defects of the reproductive system (hypogonadism) or the body's responsiveness to sex hormones. Initial workup for delayed puberty not due to a chronic condition in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estrogen
Estrogen or oestrogen is a category of sex hormone responsible for the development and regulation of the female reproductive system and secondary sex characteristics. There are three major endogenous estrogens that have estrogenic hormonal activity: estrone (E1), estradiol (E2), and estriol (E3). Estradiol, an estrane, is the most potent and prevalent. Another estrogen called estetrol (E4) is produced only during pregnancy. Estrogens are synthesized in all vertebrates and some insects. Their presence in both vertebrates and insects suggests that estrogenic sex hormones have an ancient evolutionary history. Quantitatively, estrogens circulate at lower levels than androgens in both men and women. While estrogen levels are significantly lower in males than in females, estrogens nevertheless have important physiological roles in males. Like all steroid hormones, estrogens readily diffuse across the cell membrane. Once inside the cell, they bind to and activate estrogen receptors (E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progestogen
Progestogens, also sometimes written progestagens or gestagens, are a class of natural or synthetic steroid hormones that bind to and activate the progesterone receptors (PR). Progesterone is the major and most important progestogen in the body. The progestogens are named for their function in maintaining pregnancy (i.e., ''progestational''), although they are also present at other phases of the estrous and menstrual cycles. The progestogens are one of three types of sex hormones, the others being estrogens like estradiol and androgens/anabolic steroids like testosterone. In addition, they are one of the five major classes of steroid hormones, the others being the androgens, estrogens, glucocorticoids, and mineralocorticoids, as well as the neurosteroids. All endogenous progestogens are characterized by their basic 21-carbon skeleton, called a pregnane skeleton (C21). In similar manner, the estrogens possess an estrane skeleton (C18), and androgens, an androstane skeleton (C19). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uterine Hyperplasia
Uterine hyperplasia, or enlarged uterus, is a symptom, medical symptom in which the volume and size of the uterus in a female is abnormally high. It can be a symptom of medical conditions such as adenomyosis, uterine fibroids, ovarian cysts, and endometrial cancer. See also * Uterine hypoplasia References Noninflammatory disorders of female genital tract {{symptom-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uterine Malformation
A uterine malformation is a type of female genital malformation resulting from an abnormal development of the Müllerian duct(s) during embryogenesis. Symptoms range from amenorrhea, infertility, recurrent pregnancy loss, and pain, to normal functioning depending on the nature of the defect. Types The American Fertility Society (now American Society of Reproductive Medicine) Classification distinguishes: ; Class I—Müllerian agenesis (absent uterus). : This condition is represented by the hypoplasia or the agenesis (total absence) of the different parts of the uterus: :* Vaginal hypoplasia or agenesis :* Cervical hypoplasia or agenesis :* Fundal hypoplasia or agenesis (absence or hypoplasia of the fundus of the uterus) :* Tubal hypoplasia or agenesis (absence or hypoplasia of the Fallopian tubes) :* Combined hypoplasia the agenesis of different part of the uterus :This condition is also called Mayer-Rokitansky-Kuster-Hauser syndrome. The patient with MRKH syndrome will hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |