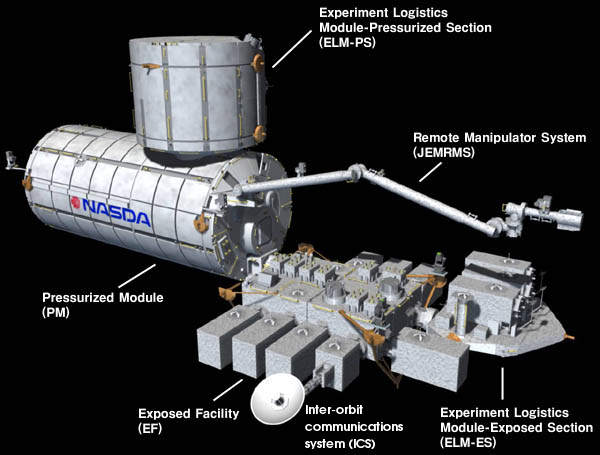
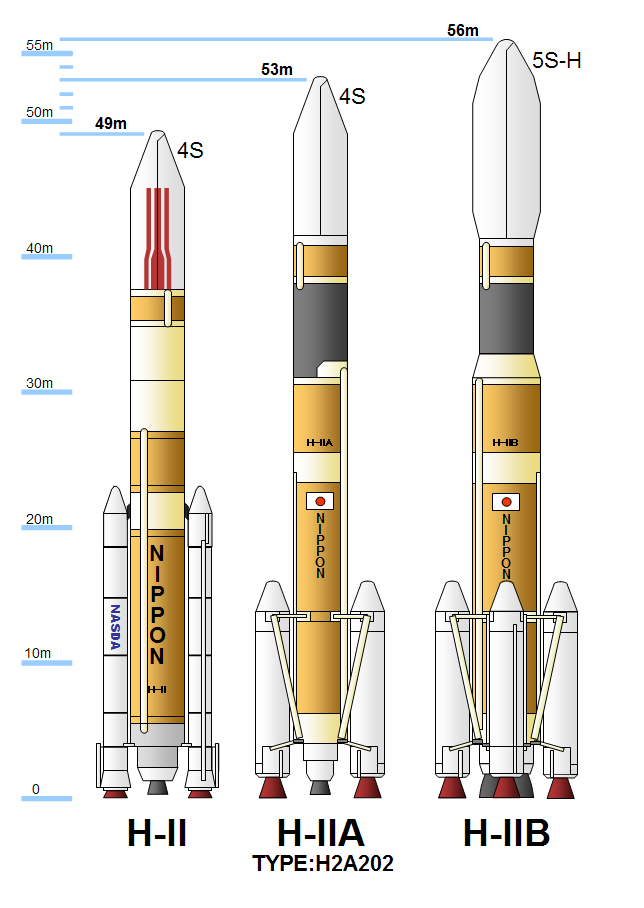
|
Usuda Deep Space Center
Usuda Deep Space Center is a facility of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency. It is a spacecraft tracking station in Saku, Nagano, opened in October, 1984. The main features of the station are two large beam waveguide antennas, an older 64 meter antenna and a newer 54 meter dish. Usuda was the first deep-space antenna constructed with beam-waveguide technology. Although this construction dramatically simplifies installation and maintenance of electronics, it was previously thought to offer poor noise performance. However, after the U.S. Jet Propulsion Lab (JPL) tested this antenna and found the noise performance was better than its conventional 64-meter antennas, it too switched to this method of construction for all subsequent antennas of their Deep Space Network (DSN). Because the 64 meter antenna is aging and is still in use over ten years after its designed service life, JAXA has built a new antenna nearby. Similar huge antennas are used by the deep space networks of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency
The is the Japanese national air and space agency. Through the merger of three previously independent organizations, JAXA was formed on 1 October 2003. JAXA is responsible for research, technology development and launch of satellites into orbit, and is involved in many more advanced missions such as asteroid exploration and possible human exploration of the Moon. Its motto is ''One JAXA'' and its corporate slogan is ''Explore to Realize'' (formerly ''Reaching for the skies, exploring space''). History On 1 October 2003, three organizations were merged to form the new JAXA: Japan's Institute of Space and Astronautical Science (ISAS), the National Aerospace Laboratory of Japan (NAL), and National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA). JAXA was formed as an Independent Administrative Institution administered by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) and the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications (MIC). Before the merger, ISA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saku, Nagano
is a city located in Nagano Prefecture, Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 99,131 in 41,522 households, and a population density of 230 persons per km². The total area of the city is . Geography Saku is located in east-central Nagano Prefecture in the Saku Basin of the upper reaches of the Shinano River. The city claims the distinction of containing the point furthest from the sea within Honshu island (actually this point lies within the former town of Usuda). Since the opening of Sakudaira Station on the Nagano Shinkansen, many people commute to Tokyo, which is one hour away. Surrounding municipalities *Nagano Prefecture ** Komoro, Chino, Tōmi ** Minamisaku District: Sakuho **Kitasaku District: Karuizawa, Miyota, Tateshina *Gunma Prefecture ** Kanra District: Shimonita, Nanmoku Climate The city has a climate characterized by characterized by hot and humid summers, and relatively mild winters (Köppen climate classification ''Dwa''). The average annu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beam Waveguide Antenna
A beam waveguide antenna is a particular type of antenna dish, at which waveguides are used to transmit the radio beam between the large steerable dish and the equipment for reception or transmission, like e.g. RF power amplifiers. Principle of operation Beam waveguide antennas are used in large radio telescopes and satellite communication stations as an alternative to the most common parabolic antenna design, the conventional "front fed" parabolic antenna. In front feed, the antenna feed, the small antenna that transmits or receives the radio waves reflected by the dish, is suspended at the focus, in front of the dish. However, this location causes a number of practical difficulties. In high performance systems, complex transmitter and receiver electronics must be located at the feed antenna. This feed equipment usually requires high maintenance; some examples are water cooling for transmitters and cryogenic cooling for sensitive receivers. With the large dishes used in these sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jet Propulsion Lab
The Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) is a federally funded research and development center and NASA field center in the City of La Cañada Flintridge, California, United States. Founded in the 1930s by Caltech researchers, JPL is owned by NASA and managed by the nearby California Institute of Technology (Caltech). The laboratory's primary function is the construction and operation of planetary robotic spacecraft, though it also conducts Earth-orbit and astronomy missions. It is also responsible for operating the NASA Deep Space Network. Among the laboratory's major active projects are the Mars 2020 mission, which includes the ''Perseverance'' rover and the '' Ingenuity'' Mars helicopter; the Mars Science Laboratory mission, including the ''Curiosity'' rover; the InSight lander (''Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport''); the ''Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter''; the ''Juno'' spacecraft orbiting Jupiter; the ''SMAP'' satellite for earth surface s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
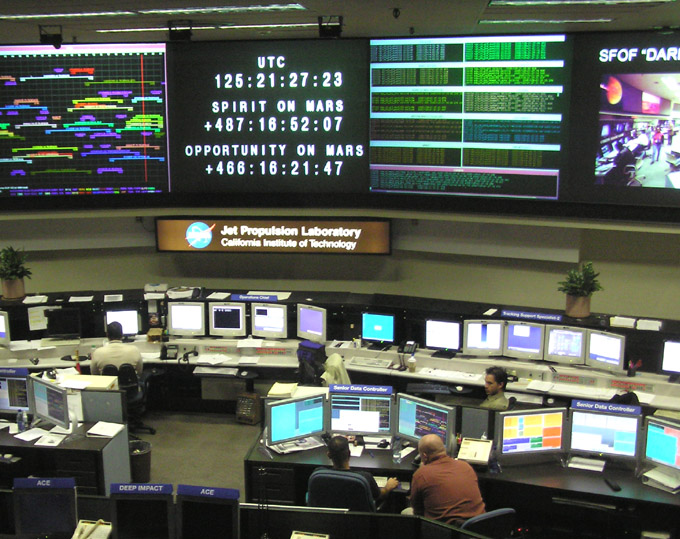
Deep Space Network
The NASA Deep Space Network (DSN) is a worldwide Telecommunications network, network of American spacecraft communication ground segment facilities, located in the United States (California), Spain (Madrid), and Australia (Canberra), that supports National Aeronautics and Space Administration, NASA's interplanetary spaceflight, interplanetary spacecraft missions. It also performs radio astronomy, radio and radar astronomy observations for the exploration of the Solar System and the universe, and supports selected Earth-orbiting missions. DSN is part of the NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL). General information DSN currently consists of three deep-space communications facilities placed approximately 120 degrees apart around the Earth. They are: * the Goldstone Deep Space Communications Complex () outside Barstow, California, Barstow, California. For details of Goldstone's contribution to the early days of space probe tracking, see Project Space Track (1957-1961), Project ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA Deep Space Network
The NASA Deep Space Network (DSN) is a worldwide network of American spacecraft communication ground segment facilities, located in the United States (California), Spain (Madrid), and Australia (Canberra), that supports NASA's interplanetary spacecraft missions. It also performs radio and radar astronomy observations for the exploration of the Solar System and the universe, and supports selected Earth-orbiting missions. DSN is part of the NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL). General information DSN currently consists of three deep-space communications facilities placed approximately 120 degrees apart around the Earth. They are: * the Goldstone Deep Space Communications Complex () outside Barstow, California. For details of Goldstone's contribution to the early days of space probe tracking, see Project Space Track; * the Madrid Deep Space Communications Complex (), west of Madrid, Spain; and * the Canberra Deep Space Communication Complex (CDSCC) in the Australian C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Deep Space Network
The Chinese Deep Space Network (CDSN) is a network of large antennas and communication facilities that are used for the interplanetary spacecraft missions of China. It is managed by the China Satellite Launch and Tracking Control Center General (CLTC), which reports to the People's Liberation Army Strategic Support Force Space Systems Department. They also deal with radio-astronomical and radar observations. The network was first needed for the lunar mission Chang'e 1, and since has been used to support subsequent missions to the Moon and Mars such as Chang'e 5, and Tianwen-1 missions. Similar deep space networks are run by the United States, Russia, European countries, Japan, and India. Introduction In principle, a Chinese deep space network has existed since 1993 with the commissioning of the Nanshan 25-meter telescope in the mountains south of Ürümqi. The 25-meter antenna of the Shanghai Astronomical Observatory was then not only able to participate in the Southern H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Deep Space Network
The Soviet Deep Space Network (or Russian Deep Space Network) was a network of large antennas and communication facilities that supports interplanetary spacecraft missions, and radio and radar astronomy observations for the exploration of the Solar System and the universe during Soviet times. It was built to support the space missions of the Soviet Union. Similar networks are run by the USA, China, Europe, Japan, and India. As of present, the Deep Space Network is maintained by Russia. History The first Soviet space communications network had 13 stations and was designed to track Earth orbiting satellites, not deep space probes.Don P. MitchelSoviet Telemetry Systems. Deep-Space Communication Centers./ref> Interplanetary missions require larger antennas, more powerful transmitters, and more sensitive receivers, and an effort was started in 1959 to support the planned 1960 launch of the Venera series of missions to Venus and the Mars program of spacecraft to Mars. The select ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ESTRACK
The European Space Tracking (ESTRACK) network consists of a number of ground-based space-tracking stations belonging to the European Space Agency (ESA), and operated by the European Space Operations Centre (ESOC) in Darmstadt, Germany. The stations support various ESA spacecraft and facilitate communications between ground operators and scientific probes such as XMM-Newton, Mars Express, BepiColombo, Gaia. Similar networks are run by the USA, China, Russia, Japan, and India. Composition The Core ESTRACK network is composed of seven ESA-owned ground stations and the ESTRACK Control Centre in the ESOC. Four of the stations are used for tracking satellites and launchers near Earth and three are used for tracking deep-space probes. Service contracts with commercially operated ground stations and cooperation agreements with international partners allows the network to track satellites that aren't in view of the ESA owned ground stations. ESA stations Core Ground Stations * Kourou S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Deep Space Network
Indian Deep Space Network (IDSN) is a network of large antennas and communication facilities operated by the Indian Space Research Organisation to support the interplanetary spacecraft missions of India. Its hub is located at Byalalu, Ramanagar in the state of Karnataka in India. It was inaugurated on 17 October 2008 by the former ISRO chairman G. Madhavan Nair. Similar networks are run by USA, China, Russia, Europe, and Japan. Introduction The network consists of the ISRO Telemetry, Tracking and Command Network (ISTRAC), augmented by a fully steerable and a DSN antenna which improves the visibility duration when compared with the existing ISTRAC system. The Indian Deep Space Network implements a baseband system adhering to Consultative Committee for Space Data Systems (CCSDS) Standards, thus facilitating cross-support among the Telemetry Tracking Command (TTC) agencies. The two antennas at the Byalalu complex have built-in support facilities. A fibre optic link will pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sagamihara Campus
Sagamihara Campus is a facility of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) in Sagamihara, Kanagawa Prefecture. Gallery file:ISAS Sagamihara Campus Gate.jpg, Entrance gate file:M-3SII exhibition model.jpg, M-3SII launch vehicle file:M-V on exhibition.jpg, M-V launch vehicle file:Astro-E2.jpg, Suzaku of before vibration test. file:Astro-E2 in the Clean Room.jpeg, Suzaku in Cleanroom A cleanroom or clean room is an engineered space, which maintains a very low concentration of airborne particulates. It is well isolated, well-controlled from contamination, and actively cleansed. Such rooms are commonly needed for scientif ... for test. References External links Sagamihara CampusJAXA Sagamihara CampusISAS Space program of Japan Space technology research institutes {{Japan-org-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Program Of Japan
The is the Japanese national air and space agency. Through the merger of three previously independent organizations, JAXA was formed on 1 October 2003. JAXA is responsible for research, technology development and launch of satellites into orbit, and is involved in many more advanced missions such as asteroid exploration and possible human exploration of the Moon. Its motto is ''One JAXA'' and its corporate slogan is ''Explore to Realize'' (formerly ''Reaching for the skies, exploring space''). History On 1 October 2003, three organizations were merged to form the new JAXA: Japan's Institute of Space and Astronautical Science (ISAS), the National Aerospace Laboratory of Japan (NAL), and National Space Development Agency of Japan (NASDA). JAXA was formed as an Independent Administrative Institution administered by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) and the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications (MIC). Before the merger, ISAS w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |