|
Uropeltoidea
The Uropeltoidea, also known as uropeltoid snakes, are a superfamily of snakes that contains uropeltids (family Uropeltidae) and Asian pipesnakes (families Cylindrophiidae and Anomochilidae). As of 2018, Uropeltoidea contains 71 species, including the eponymous shield-tail snakes (genus '' Uropeltis'' with 23 species) and their relatives (32 species in 6 other genera), 13 species of Asian pipesnakes (genus ''Cylindrophis''), and 3 species of dwarf pipesnakes (genus '' Anomochilus''). The taxonomy of boas, pythons, and other henophidian snakes has long been debated, and ultimately the decision whether to assign a particular clade to a particular Linnaean rank (such as a superfamily, family, or subfamily In biological classification, a subfamily (Latin: ', plural ') is an auxiliary (intermediate) taxonomic rank, next below family but more inclusive than genus. Standard nomenclature rules end subfamily botanical names with "-oideae", and zoologi ...) is arbitrary. The clade na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snake
Snakes are elongated, Limbless vertebrate, limbless, carnivore, carnivorous reptiles of the suborder Serpentes . Like all other Squamata, squamates, snakes are ectothermic, amniote vertebrates covered in overlapping Scale (zoology), scales. Many species of snakes have skulls with several more joints than their lizard ancestors, enabling them to swallow prey much larger than their heads (cranial kinesis). To accommodate their narrow bodies, snakes' paired organs (such as kidneys) appear one in front of the other instead of side by side, and most have only one functional lung. Some species retain a pelvic girdle with a pair of vestigial claws on either side of the cloaca. Lizards have evolved elongate bodies without limbs or with greatly reduced limbs about twenty-five times independently via convergent evolution, leading to many lineages of legless lizards. These resemble snakes, but several common groups of legless lizards have eyelids and external ears, which snakes lack, altho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cylindrophiidae
The Cylindrophiidae are a monotypic Family (biology), family of secretive, semifossorial, non-venomous snakes containing the genus ''Cylindrophis'' found in southeastern Asia. These are burrowing snakes and most have a banded pattern on the belly. Currently, thirteen species are recognized, with no subspecies. Common names include Asian pipe snakes or Asian cylinder snakes. Geographic range ''Cylindrophis'' are found in southeastern Asia from Myanmar, Laos, Vietnam, Cambodia, Thailand, and the Malay Archipelago, including Singapore, both peninsular Malaysia and Sarawak, and Indonesia, including the Greater Sunda Islands (Borneo [including Sarawak and Brunei]), Sumatra, and Java, as well as some of their offshore islands), Sulawesi, the Lesser Sunda Islands (Lombok, Komodo, Flores, Sumbawa, Timor [including Timor-Leste]), and east to the Maluku Islands (Halmahera, Wetar, Damar, Babar, and into the Tanimbar Archipelago). The eastern distributional limit, sometimes given as the Aru I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cylindrophis
The Cylindrophiidae are a monotypic family of secretive, semifossorial, non-venomous snakes containing the genus ''Cylindrophis'' found in southeastern Asia. These are burrowing snakes and most have a banded pattern on the belly. Currently, thirteen species are recognized, with no subspecies. Common names include Asian pipe snakes or Asian cylinder snakes. Geographic range ''Cylindrophis'' are found in southeastern Asia from Myanmar, Laos, Vietnam, Cambodia, Thailand, and the Malay Archipelago, including Singapore, both peninsular Malaysia and Sarawak, and Indonesia, including the Greater Sunda Islands (Borneo [including Sarawak and Brunei]), Sumatra, and Java, as well as some of their offshore islands), Sulawesi, the Lesser Sunda Islands (Lombok, Komodo, Flores, Sumbawa, Timor [including Timor-Leste]), and east to the Maluku Islands (Halmahera, Wetar, Damar, Babar, and into the Tanimbar Archipelago). The eastern distributional limit, sometimes given as the Aru Islands off the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alethinophidia
:''Common names: advanced snakes.'' The Alethinophidia are an infraorder of snakes that includes all snakes other than blind snakes and thread snakes. Snakes have long been grouped into families within Alethinophidia based on their morphology, especially that of their teeth. More modern phylogenetic hypotheses using genetic data support the recognition of 19 extant families (see below), although the taxonomy of alethinophidian snakes has long been debated, and ultimately the decision whether to assign a particular clade to a particular Linnaean rank (such as a superfamily, family, or subfamily) is arbitrary. Etymology The infraorder name Alethinophidia derives from the two Ancient Greek words (), meaning "truthful, genuine", and (), meaning "snake". Fossil record Fossils of alethinophidians were found in Cenomanian (Middle Cretaceous) sites of Wadi Milk Formation in Wadi Abu Hashim, Sudan. ''Coniophis'' presents the vertebral morphology similar to modern-day Aniliidae. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
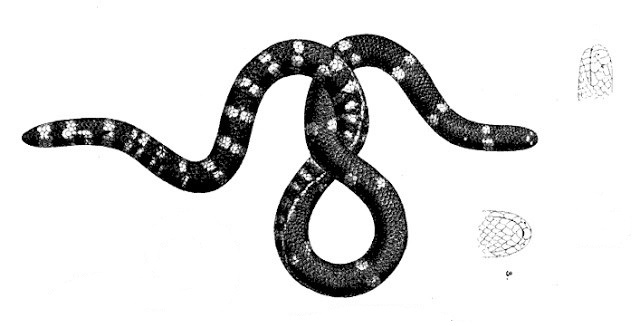
Uropeltis Maculata
''Uropeltis maculata'', also known commonly as the spotted earth snake and the spotted shieldtail, is a species of nonvenomous snake in the family Uropeltidae. The species is endemic to southern India. There are no subspecies that are recognized as being valid. Geographic range ''U. maculata'' is found in southern India in the Western Ghats: Anaimalai Hills and southern Kerala. No type locality was given in the original description. Beddome (1886) gives "Anaimalai, higher ranges elevation. Habitat The preferred natural habitats of ''U. maculata'' are forest and grassland, but it has also been found in agricultural plantations. Description ''U. maculata'' is dark brown or black both dorsally and ventrally, with several deep red blotches on the sides anteriorly, rarely along the full length of the body. It has similar deep red blotches about the tail. Adults may attain a total length (including tail) of 38 cm (15 inches). The dorsal scales are arranged in 17 rows ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uropeltidae
The Uropeltidae, also known Common name, commonly as the shieldtails or the shield-tailed snakes, are a Family (biology), family of primitive, nonvenomous, burrowing snakes native to peninsular India and Sri Lanka. The name is derived from the Greek words ('tail') and ('shield'), indicating the presence of the large keratinous shield at the tip of the tail. Seven or eight genus, genera are recognized, depending on whether ''Teretrurus rhodogaster'' is treated in its own genus or as part of ''Brachyophidium''. The family comprises over 50 species. These snakes are not well known in terms of their diversity, biology, and natural history. Description Snakes in the family Uropeltidae are small snakes, with adults growing to a total length (including tail) of . They are adapted to a fossorial way of life, which is apparent in their anatomy. The skull is primitive and inflexible, with a short, vertical quadrate bone and rigid jaws; the coronoid bone is still present in the lower jaw. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cylindrophis Rufus
The red-tailed pipe snake, red cylinder snake, or common pipe snake (''Cylindrophis ruffus'') is a nonvenomous cylindrophiid snake species found in Southeast Asia. No subspecies are currently recognized. Description Adults can grow to 39 in (1 m) in length.Burnie D, Wilson DE. 2001. Animal. Dorling Kindersley. 624 pp. . The dorsal scales are smooth, in 19 or 21 rows, with 186-245 ventrals, which are not quite twice as large as the contiguous dorsal scales; the anal plate is divided, and five to 10 subcaudals. Compared to other snakes, ''C. ruffus'' have a limited gape size. Their primary diet consists of long, thin prey animals including snakes, caecilians, and eels. Geographic range It is found in Myanmar and southern China (Fujian, Hong Kong and on Hainan Island), south into Vietnam, Laos, Cambodia, Thailand, the Malay Peninsula and the East Indies to Indonesia (the Riau Archipelago, Sumatra, Bangka, Borneo, Java, Sulawesi, Buton and the Sula Islands The Sula Islands Rege ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johannes Peter Müller
Johannes Peter Müller (14 July 1801 – 28 April 1858) was a German physiologist, comparative anatomy, comparative anatomist, ichthyology, ichthyologist, and herpetology, herpetologist, known not only for his discoveries but also for his ability to synthesize knowledge. The paramesonephric duct (Müllerian duct) was named in his honor. Life Early years and education Müller was born in Koblenz, Coblenz. He was the son of a poor shoemaker, and was about to be apprenticed to a saddler when his talents attracted the attention of his teacher, and he prepared himself to become a Roman Catholic Priest. During his Secondary school, college course in Koblenz, he devoted himself to the classics and made his own translations of Aristotle. At first, his intention was to become a priest. When he was eighteen, his love for natural science became dominant, and he turned to medicine, entering the University of Bonn in 1819. There he received his Doctor of Medicine, M.D. in 1822. He then studie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anomochilidae
The Anomochilidae, or anomochilids, are a monotypic family of snakes, created for the genus ''Anomochilus'', which currently contains three species. It is commonly called the dwarf pipe snake. Description Anomochilids are small snakes, with museum specimens measuring up to in total length (including tail). The eyes are reduced, and there are no teeth on the premaxiila, pterygoid, or palatine. A tracheal lung is absent. Anomochilids retain some pelvic elements, indicated externally by cloacal spurs. The tails are relatively short. Females have two well developed oviducts. Anomochilids have white or yellow patterns against a darker reddish background. Behaviour and habitat Anomochilids are probably fossorial. Diet Cranial and dentary morphology suggests that anomochilids probably eat small invertebrates. Reproduction One of the museum specimens of ''Anomochilus'' was found to contain four eggs, suggesting oviparity, but nothing else is known of anomochilid reproduction or behav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
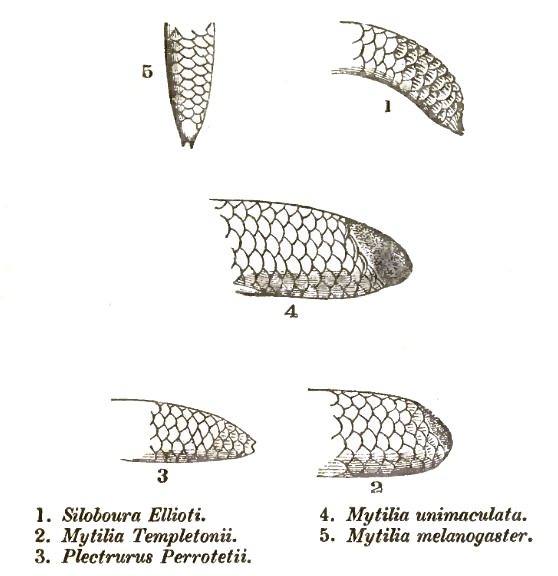
Uropeltis
:''Common names: shield tail snakes, earth snakes.'' ''Uropeltis'' is a genus of nonvenomous shield tail snakes endemic to Peninsular India. As of 2022, 26 species are recognized as being valid. Geographic range Most ''Uropeltis'' species are found in the hills of Peninsular India, mainly in the southwestern parts of the country, including the Western Ghats and, to some extent, also in the Eastern Ghats and in the hills of Central India. Description Species in the genus ''Uropeltis'' share the following characters. The eye is in the ocular shield. There are no supraoculars nor temporals. There is no mental groove. The tail is conical or obliquely truncated, terminating in a small scute, the end of which is square, or bicuspid with the points side by side. Boulenger GA (1893). ''Catalogue of the Snakes in the British Museum (Natural History). Volume I., Containing the Families ... Uropeltidæ ....'' London: Trustees of the British Museum (Natural History). (Taylor and Francis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anomochilus
The Anomochilidae, or anomochilids, are a monotypic family of snakes, created for the genus ''Anomochilus'', which currently contains three species. It is commonly called the dwarf pipe snake. Description Anomochilids are small snakes, with museum specimens measuring up to in total length (including tail). The eyes are reduced, and there are no teeth on the premaxiila, pterygoid, or palatine. A tracheal lung is absent. Anomochilids retain some pelvic elements, indicated externally by cloacal spurs. The tails are relatively short. Females have two well developed oviducts. Anomochilids have white or yellow patterns against a darker reddish background. Behaviour and habitat Anomochilids are probably fossorial. Diet Cranial and dentary morphology suggests that anomochilids probably eat small invertebrates. Reproduction One of the museum specimens of ''Anomochilus'' was found to contain four eggs, suggesting oviparity, but nothing else is known of anomochilid reproduction or behav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linnaean Taxonomy
Linnaean taxonomy can mean either of two related concepts: # The particular form of biological classification (taxonomy) set up by Carl Linnaeus, as set forth in his ''Systema Naturae'' (1735) and subsequent works. In the taxonomy of Linnaeus there are three kingdoms, divided into ''classes'', and they, in turn, into lower ranks in a hierarchical order. # A term for rank-based classification of organisms, in general. That is, taxonomy in the traditional sense of the word: rank-based scientific classification. This term is especially used as opposed to cladistic systematics, which groups organisms into clades. It is attributed to Linnaeus, although he neither invented the concept of ranked classification (it goes back to Plato and Aristotle) nor gave it its present form. In fact, it does not have an exact present form, as "Linnaean taxonomy" as such does not really exist: it is a collective (abstracting) term for what actually are several separate fields, which use similar approac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |