|
Urbach Energy
The Urbach Energy, or Urbach Edge, is a parameter typically denoted E_, with dimensions of energy, used to quantify energetic disorder in the band edges of a semiconductor. It is evaluated by fitting the absorption coefficient as a function of energy to an exponential function. It is often used to describe electron transport in structurally disordered semiconductors such a hydrogenated amorphous silicon. Introduction In the simplest description of a semiconductor, a single parameter is used to quantify the onset of optical absorption: the band gap, E_. In this description, semiconductors are described as being able to absorb photons above E_, but are transparent to photons below E_. However, the density of states in 3 dimensional semiconductors increases further from the band gap (this is not generally true in lower dimensional semiconductors however). For this reason, the absorption coefficient, \alpha, increases with energy. The Urbach Energy quantifies the ''steepness'' of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy
In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek: ἐνέργεια, ''enérgeia'', “activity”) is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of heat and light. Energy is a conserved quantity—the law of conservation of energy states that energy can be converted in form, but not created or destroyed. The unit of measurement for energy in the International System of Units (SI) is the joule (J). Common forms of energy include the kinetic energy of a moving object, the potential energy stored by an object (for instance due to its position in a field), the elastic energy stored in a solid object, chemical energy associated with chemical reactions, the radiant energy carried by electromagnetic radiation, and the internal energy contained within a thermodynamic system. All living organisms constantly take in and release energy. Due to mass–energy equivalence, any object th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exponential Function
The exponential function is a mathematical function denoted by f(x)=\exp(x) or e^x (where the argument is written as an exponent). Unless otherwise specified, the term generally refers to the positive-valued function of a real variable, although it can be extended to the complex numbers or generalized to other mathematical objects like matrices or Lie algebras. The exponential function originated from the notion of exponentiation (repeated multiplication), but modern definitions (there are several equivalent characterizations) allow it to be rigorously extended to all real arguments, including irrational numbers. Its ubiquitous occurrence in pure and applied mathematics led mathematician Walter Rudin to opine that the exponential function is "the most important function in mathematics". The exponential function satisfies the exponentiation identity e^ = e^x e^y \text x,y\in\mathbb, which, along with the definition e = \exp(1), shows that e^n=\underbrace_ for positi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronic Band Structures
Electronic may refer to: *Electronics, the science of how to control electric energy in semiconductor * ''Electronics'' (magazine), a defunct American trade journal *Electronic storage, the storage of data using an electronic device *Electronic commerce or e-commerce, the trading in products or services using computer networks, such as the Internet *Electronic publishing or e-publishing, the digital publication of books and magazines using computer networks, such as the Internet *Electronic engineering, an electrical engineering discipline Entertainment *Electronic (band), an English alternative dance band ** ''Electronic'' (album), the self-titled debut album by British band Electronic *Electronic music, a music genre *Electronic musical instrument *Electronic game, a game that employs electronics See also *Electronica, an electronic music genre *Consumer electronics Consumer electronics or home electronics are electronic ( analog or digital) equipment intended for everyd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photothermal Deflection Spectroscopy
Photothermal spectroscopy is a group of high sensitivity spectroscopy techniques used to measure optical absorption and thermal characteristics of a sample. The basis of photothermal spectroscopy is the change in thermal state of the sample resulting from the absorption of radiation. Light absorbed and not lost by emission results in heating. The heat raises temperature thereby influencing the thermodynamic properties of the sample or of a suitable material adjacent to it. Measurement of the temperature, pressure, or density changes that occur due to optical absorption are ultimately the basis for the photothermal spectroscopic measurements. As with photoacoustic spectroscopy, photothermal spectroscopy is an indirect method for measuring optical absorption, because it is not based on the direct measure of the light which is involved in the absorption. In another sense, however, photothermal (and photoacoustic) methods measure ''directly'' the absorption, rather than e.g. calculate it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Activation Energy
In chemistry and physics, activation energy is the minimum amount of energy that must be provided for compounds to result in a chemical reaction. The activation energy (''E''a) of a reaction is measured in joules per mole (J/mol), kilojoules per mole (kJ/mol) or kilocalories per mole (kcal/mol). Activation energy can be thought of as the magnitude of the potential barrier (sometimes called the energy barrier) separating minima of the potential energy surface pertaining to the initial and final thermodynamic state. For a chemical reaction to proceed at a reasonable rate, the temperature of the system should be high enough such that there exists an appreciable number of molecules with translational energy equal to or greater than the activation energy. The term "activation energy" was introduced in 1889 by the Swedish scientist Svante Arrhenius. Other uses Although less commonly used, activation energy also applies to nuclear reactions and various other physical phenomena. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
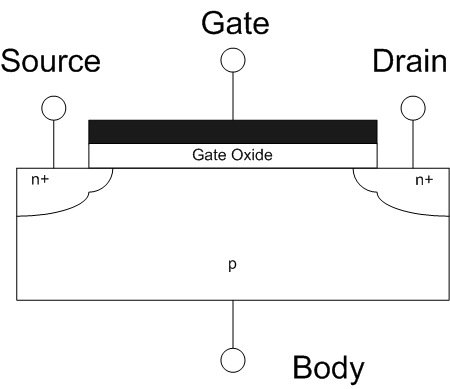
Field-effect Transistor
The field-effect transistor (FET) is a type of transistor that uses an electric field to control the flow of current in a semiconductor. FETs ( JFETs or MOSFETs) are devices with three terminals: ''source'', ''gate'', and ''drain''. FETs control the flow of current by the application of a voltage to the gate, which in turn alters the conductivity between the drain and source. FETs are also known as unipolar transistors since they involve single-carrier-type operation. That is, FETs use either electrons (n-channel) or holes (p-channel) as charge carriers in their operation, but not both. Many different types of field effect transistors exist. Field effect transistors generally display very high input impedance at low frequencies. The most widely used field-effect transistor is the MOSFET (metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor). History The concept of a field-effect transistor (FET) was first patented by Austro-Hungarian physicist Julius Edgar Lilienfeld in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronvolt
In physics, an electronvolt (symbol eV, also written electron-volt and electron volt) is the measure of an amount of kinetic energy gained by a single electron accelerating from rest through an electric potential difference of one volt in vacuum. When used as a unit of energy, the numerical value of 1 eV in joules (symbol J) is equivalent to the numerical value of the charge of an electron in coulombs (symbol C). Under the 2019 redefinition of the SI base units, this sets 1 eV equal to the exact value Historically, the electronvolt was devised as a standard unit of measure through its usefulness in electrostatic particle accelerator sciences, because a particle with electric charge ''q'' gains an energy after passing through a voltage of ''V.'' Since ''q'' must be an integer multiple of the elementary charge ''e'' for any isolated particle, the gained energy in units of electronvolts conveniently equals that integer times the voltage. It is a common unit of energy with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kodak
The Eastman Kodak Company (referred to simply as Kodak ) is an American public company that produces various products related to its historic basis in analogue photography. The company is headquartered in Rochester, New York, and is incorporated in New Jersey. Kodak provides packaging, functional printing, graphic communications, and professional services for businesses around the world. Its main business segments are Print Systems, Enterprise Inkjet Systems, Micro 3D Printing and Packaging, Software and Solutions, and Consumer and Film. It is best known for photographic film products. Kodak was founded by George Eastman and Henry A. Strong on May 23, 1892. During most of the 20th century, Kodak held a dominant position in photographic film. The company's ubiquity was such that its " Kodak moment" tagline entered the common lexicon to describe a personal event that deserved to be recorded for posterity. Kodak began to struggle financially in the late 1990s, as a result o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silver Bromide
Silver bromide (AgBr) is a soft, pale-yellow, water-insoluble salt well known (along with other silver halides) for its unusual sensitivity to light. This property has allowed silver halides to become the basis of modern photographic materials. AgBr is widely used in photographic films and is believed by some to have been used for making the Shroud of Turin. The salt can be found naturally as the mineral bromargyrite. Preparation Although the compound can be found in mineral form, AgBr is typically prepared by the reaction of silver nitrate with an alkali bromide, typically potassium bromide: :AgNO3(aq) + KBr(aq) → AgBr(s)+ KNO3(aq) Although less convenient, the compound can also be prepared directly from its elements. Modern preparation of a simple, light-sensitive surface involves forming an emulsion of silver halide crystals in a gelatine, which is then coated onto a film or other support. The crystals are formed by precipitation in a controlled environment to produce s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Density Of States
In solid state physics and condensed matter physics, the density of states (DOS) of a system describes the number of modes per unit frequency range. The density of states is defined as D(E) = N(E)/V , where N(E)\delta E is the number of states in the system of volume V whose energies lie in the range from E to E+\delta E. It is mathematically represented as a distribution by a probability density function, and it is generally an average over the space and time domains of the various states occupied by the system. The density of states is directly related to the dispersion relations of the properties of the system. High DOS at a specific energy level means that many states are available for occupation. Generally, the density of states of matter is continuous. In isolated systems however, such as atoms or molecules in the gas phase, the density distribution is discrete, like a spectral density. Local variations, most often due to distortions of the original system, are often refe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material which has an electrical conductivity value falling between that of a conductor, such as copper, and an insulator, such as glass. Its resistivity falls as its temperature rises; metals behave in the opposite way. Its conducting properties may be altered in useful ways by introducing impurities (" doping") into the crystal structure. When two differently doped regions exist in the same crystal, a semiconductor junction is created. The behavior of charge carriers, which include electrons, ions, and electron holes, at these junctions is the basis of diodes, transistors, and most modern electronics. Some examples of semiconductors are silicon, germanium, gallium arsenide, and elements near the so-called " metalloid staircase" on the periodic table. After silicon, gallium arsenide is the second-most common semiconductor and is used in laser diodes, solar cells, microwave-frequency integrated circuits, and others. Silicon is a critical elem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Two-dimensional Semiconductor
A two-dimensional semiconductor (also known as 2D semiconductor) is a type of natural semiconductor with thicknesses on the atomic scale. Geim and Novoselov et al. initiated the field in 2004 when they reported a new semiconducting material graphene, a flat monolayer of carbon atoms arranged in a 2D materials, 2D honeycomb lattice. A 2D monolayer semiconductor is significant because it exhibits stronger piezoelectric coupling than traditionally employed bulk forms. This coupling could enable applications. One research focus is on designing nanoelectronic components by the use of graphene as electrical conductor, hexagonal boron nitride as electrical insulator, and a transition metal dichalcogenide as semiconductor. Materials Graphene Graphene, consisting of single sheets of carbon atoms, has high electron mobility and high thermal conductivity. One issue regarding graphene is its lack of a band gap, which poses a problem in particular with digital electronics because it is unabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |