|
Up (game Theory)
Combinatorial game theory is a branch of mathematics and theoretical computer science that typically studies sequential games with perfect information. Study has been largely confined to two-player games that have a ''position'' that the players take turns changing in defined ways or ''moves'' to achieve a defined winning condition. Combinatorial game theory has not traditionally studied games of chance or those that use imperfect or incomplete information, favoring games that offer perfect information in which the state of the game and the set of available moves is always known by both players. However, as mathematical techniques advance, the types of game that can be mathematically analyzed expands, thus the boundaries of the field are ever changing. Scholars will generally define what they mean by a "game" at the beginning of a paper, and these definitions often vary as they are specific to the game being analyzed and are not meant to represent the entire scope of the field. C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematicians Playing Konane
A mathematician is someone who uses an extensive knowledge of mathematics in their work, typically to solve mathematical problems. Mathematicians are concerned with numbers, data, quantity, structure, space, models, and change. History One of the earliest known mathematicians were Thales of Miletus (c. 624–c.546 BC); he has been hailed as the first true mathematician and the first known individual to whom a mathematical discovery has been attributed. He is credited with the first use of deductive reasoning applied to geometry, by deriving four corollaries to Thales' Theorem. The number of known mathematicians grew when Pythagoras of Samos (c. 582–c. 507 BC) established the Pythagorean School, whose doctrine it was that mathematics ruled the universe and whose motto was "All is number". It was the Pythagoreans who coined the term "mathematics", and with whom the study of mathematics for its own sake begins. The first woman mathematician recorded by history was Hypatia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Game Theory
Game theory is the study of mathematical models of strategic interactions among rational agents. Myerson, Roger B. (1991). ''Game Theory: Analysis of Conflict,'' Harvard University Press, p.&nbs1 Chapter-preview links, ppvii–xi It has applications in all fields of social science, as well as in logic, systems science and computer science. Originally, it addressed two-person zero-sum games, in which each participant's gains or losses are exactly balanced by those of other participants. In the 21st century, game theory applies to a wide range of behavioral relations; it is now an umbrella term for the science of logical decision making in humans, animals, as well as computers. Modern game theory began with the idea of mixed-strategy equilibria in two-person zero-sum game and its proof by John von Neumann. Von Neumann's original proof used the Brouwer fixed-point theorem on continuous mappings into compact convex sets, which became a standard method in game theory and mathema ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science (journal)
''Science'', also widely referred to as ''Science Magazine'', is the peer-reviewed academic journal of the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) and one of the world's top academic journals. It was first published in 1880, is currently circulated weekly and has a subscriber base of around 130,000. Because institutional subscriptions and online access serve a larger audience, its estimated readership is over 400,000 people. ''Science'' is based in Washington, D.C., United States, with a second office in Cambridge, UK. Contents The major focus of the journal is publishing important original scientific research and research reviews, but ''Science'' also publishes science-related news, opinions on science policy and other matters of interest to scientists and others who are concerned with the wide implications of science and technology. Unlike most scientific journals, which focus on a specific field, ''Science'' and its rival ''Nature (journal), Nature'' c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer-assisted Proof
A computer-assisted proof is a mathematical proof that has been at least partially generated by computer. Most computer-aided proofs to date have been implementations of large proofs-by-exhaustion of a mathematical theorem. The idea is to use a computer program to perform lengthy computations, and to provide a proof that the result of these computations implies the given theorem. In 1976, the four color theorem was the first major theorem to be verified using a computer program. Attempts have also been made in the area of artificial intelligence research to create smaller, explicit, new proofs of mathematical theorems from the bottom up using automated reasoning techniques such as heuristic search. Such automated theorem provers have proved a number of new results and found new proofs for known theorems. Additionally, interactive proof assistants allow mathematicians to develop human-readable proofs which are nonetheless formally verified for correctness. Since these proofs ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solved Game
A solved game is a game whose outcome (win, lose or draw) can be correctly predicted from any position, assuming that both players play perfectly. This concept is usually applied to abstract strategy games, and especially to games with full information and no element of chance; solving such a game may use combinatorial game theory and/or computer assistance. Overview A two-player game can be solved on several levels: ;Ultra-weak : Prove whether the first player will win, lose or draw from the initial position, given perfect play on both sides. This can be a non-constructive proof (possibly involving a strategy-stealing argument) that need not actually determine any moves of the perfect play. ;Weak : Provide an algorithm that secures a win for one player, or a draw for either, against any possible moves by the opponent, from the beginning of the game. ;Strong : Provide an algorithm that can produce perfect moves from any position, even if mistakes have already been made on one or b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
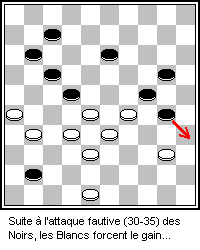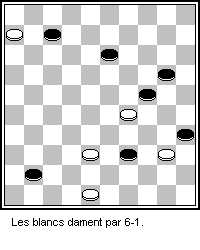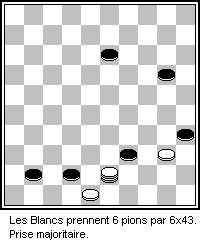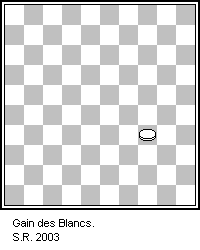
Checkers
Checkers (American English), also known as draughts (; British English), is a group of strategy board games for two players which involve diagonal moves of uniform game pieces and mandatory captures by jumping over opponent pieces. Checkers is developed from alquerque. The term "checkers" derives from the checkered board which the game is played on, whereas "draughts" derives from the verb "to draw" or "to move". The most popular forms of checkers in Anglophone countries are American checkers (also called English draughts), which is played on an 8×8 checkerboard; Russian draughts, Turkish draughts both on an 8x8 board, and International draughts, played on a 10×10 board – the latter is widely played in many countries worldwide. There are many other variants played on 8×8 boards. Canadian checkers and Singaporean/Malaysian checkers (also locally known as ''dum'') are played on a 12×12 board. American checkers was weakly solved in 2007 by a team of Canadian computer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solved Game
A solved game is a game whose outcome (win, lose or draw) can be correctly predicted from any position, assuming that both players play perfectly. This concept is usually applied to abstract strategy games, and especially to games with full information and no element of chance; solving such a game may use combinatorial game theory and/or computer assistance. Overview A two-player game can be solved on several levels: ;Ultra-weak : Prove whether the first player will win, lose or draw from the initial position, given perfect play on both sides. This can be a non-constructive proof (possibly involving a strategy-stealing argument) that need not actually determine any moves of the perfect play. ;Weak : Provide an algorithm that secures a win for one player, or a draw for either, against any possible moves by the opponent, from the beginning of the game. ;Strong : Provide an algorithm that can produce perfect moves from any position, even if mistakes have already been made on one or b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strategy-stealing Argument
In combinatorial game theory, the strategy-stealing argument is a general argument that shows, for many two-player games, that the second player cannot have a guaranteed winning strategy. The strategy-stealing argument applies to any symmetric game (one in which either player has the same set of available moves with the same results, so that the first player can "use" the second player's strategy) in which an extra move can never be a disadvantage. A key property of a strategy stealing argument is that it proves that the first player can win (or possibly draw) the game without actually constructing such a strategy. So, although it might tell you that there exists a winning strategy, the proof gives you no information about what that strategy is. The argument works by obtaining a contradiction. A winning strategy is assumed to exist for the second player, who is using it. But then, roughly speaking, after making an arbitrary first move – which by the conditions above is not a disa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Game Complexity
Combinatorial game theory has several ways of measuring game complexity. This article describes five of them: state-space complexity, game tree size, decision complexity, game-tree complexity, and computational complexity. Measures of game complexity State-space complexity The state-space complexity of a game is the number of legal game positions reachable from the initial position of the game. When this is too hard to calculate, an upper bound can often be computed by also counting (some) illegal positions, meaning positions that can never arise in the course of a game. Game tree size The game tree size is the total number of possible games that can be played: the number of leaf nodes in the game tree rooted at the game's initial position. The game tree is typically vastly larger than the state space because the same positions can occur in many games by making moves in a different order (for example, in a tic-tac-toe game with two X and one O on the board, this position co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha–beta Pruning
Alpha–beta pruning is a search algorithm that seeks to decrease the number of nodes that are evaluated by the minimax algorithm in its search tree. It is an adversarial search algorithm used commonly for machine playing of two-player games (Tic-tac-toe, Chess, Connect 4, etc.). It stops evaluating a move when at least one possibility has been found that proves the move to be worse than a previously examined move. Such moves need not be evaluated further. When applied to a standard minimax tree, it returns the same move as minimax would, but prunes away branches that cannot possibly influence the final decision. History Allen Newell and Herbert A. Simon who used what John McCarthy calls an "approximation" in 1958 wrote that alpha–beta "appears to have been reinvented a number of times". Arthur Samuel had an early version for a checkers simulation. Richards, Timothy Hart, Michael Levin and/or Daniel Edwards also invented alpha–beta independently in the United States. McC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Search Algorithm
In computer science, a search algorithm is an algorithm designed to solve a search problem. Search algorithms work to retrieve information stored within particular data structure, or calculated in the search space of a problem domain, with either discrete or continuous values. algorithms are Although search engines use search algorithms, they belong to the study of information retrieval, not algorithmics. The appropriate search algorithm often depends on the data structure being searched, and may also include prior knowledge about the data. Search algorithms can be made faster or more efficient by specially constructed database structures, such as search trees, hash maps, and database indexes. Search algorithms can be classified based on their mechanism of searching into three types of algorithms: linear, binary, and hashing. Linear search algorithms check every record for the one associated with a target key in a linear fashion. Binary, or half-interval, searches repeatedly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Automated Planning And Scheduling
Automation describes a wide range of technologies that reduce human intervention in processes, namely by predetermining decision criteria, subprocess relationships, and related actions, as well as embodying those predeterminations in machines. Automation has been achieved by various means including Mechanical system, mechanical, hydraulic, pneumatic, electrical, electronic devices, and computers, usually in combination. Complicated systems, such as modern factories, airplanes, and ships typically use combinations of all of these techniques. The benefit of automation includes labor savings, reducing waste, savings in electricity costs, savings in material costs, and improvements to quality, accuracy, and precision. Automation includes the use of various equipment and control systems such as machinery, processes in factories, boilers, and heat-treating ovens, switching on telephone networks, steering, and stabilization of ships, aircraft, and other applications and vehicles with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |