|
Universal Soil Loss Equation
The Universal Soil Loss Equation (USLE) is a widely used mathematical model that describes soil erosion processes. Erosion models play critical roles in soil and water resource conservation and nonpoint source pollution assessments, including: sediment load assessment and inventory, conservation planning and design for sediment control, and for the advancement of scientific understanding. The USLE or one of its derivatives are main models used by United States government agencies to measure water erosion. The USLE was developed in the U.S., based on soil erosion data collected beginning in the 1930s by the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) Soil Conservation Service (now the USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service). The model has been used for decades for purposes of conservation planning both in the United States where it originated and around the world, and has been used to help implement the United States' multibillion-dollar conservation program. The Revised Universal S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematical Model
A mathematical model is a description of a system using mathematical concepts and language. The process of developing a mathematical model is termed mathematical modeling. Mathematical models are used in the natural sciences (such as physics, biology, earth science, chemistry) and engineering disciplines (such as computer science, electrical engineering), as well as in non-physical systems such as the social sciences (such as economics, psychology, sociology, political science). The use of mathematical models to solve problems in business or military operations is a large part of the field of operations research. Mathematical models are also used in music, linguistics, and philosophy (for example, intensively in analytic philosophy). A model may help to explain a system and to study the effects of different components, and to make predictions about behavior. Elements of a mathematical model Mathematical models can take many forms, including dynamical systems, statisti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conceptual Model
A conceptual model is a representation of a system. It consists of concepts used to help people knowledge, know, understanding, understand, or simulation, simulate a subject the model represents. In contrast, physical models are physical object such as a toy model that may be assembled and made to work like the object it represents. The term may refer to models that are formed after a wikt:concept#Noun, conceptualization or generalization process. Conceptual models are often abstractions of things in the real world, whether physical or social. Semantics, Semantic studies are relevant to various stages of process of concept formation, concept formation. Semantics is basically about concepts, the meaning that thinking beings give to various elements of their experience. Overview Models of concepts and models that are conceptual The term ''conceptual model'' is normal. It could mean "a model of concept" or it could mean "a model that is conceptual." A distinction can be made bet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
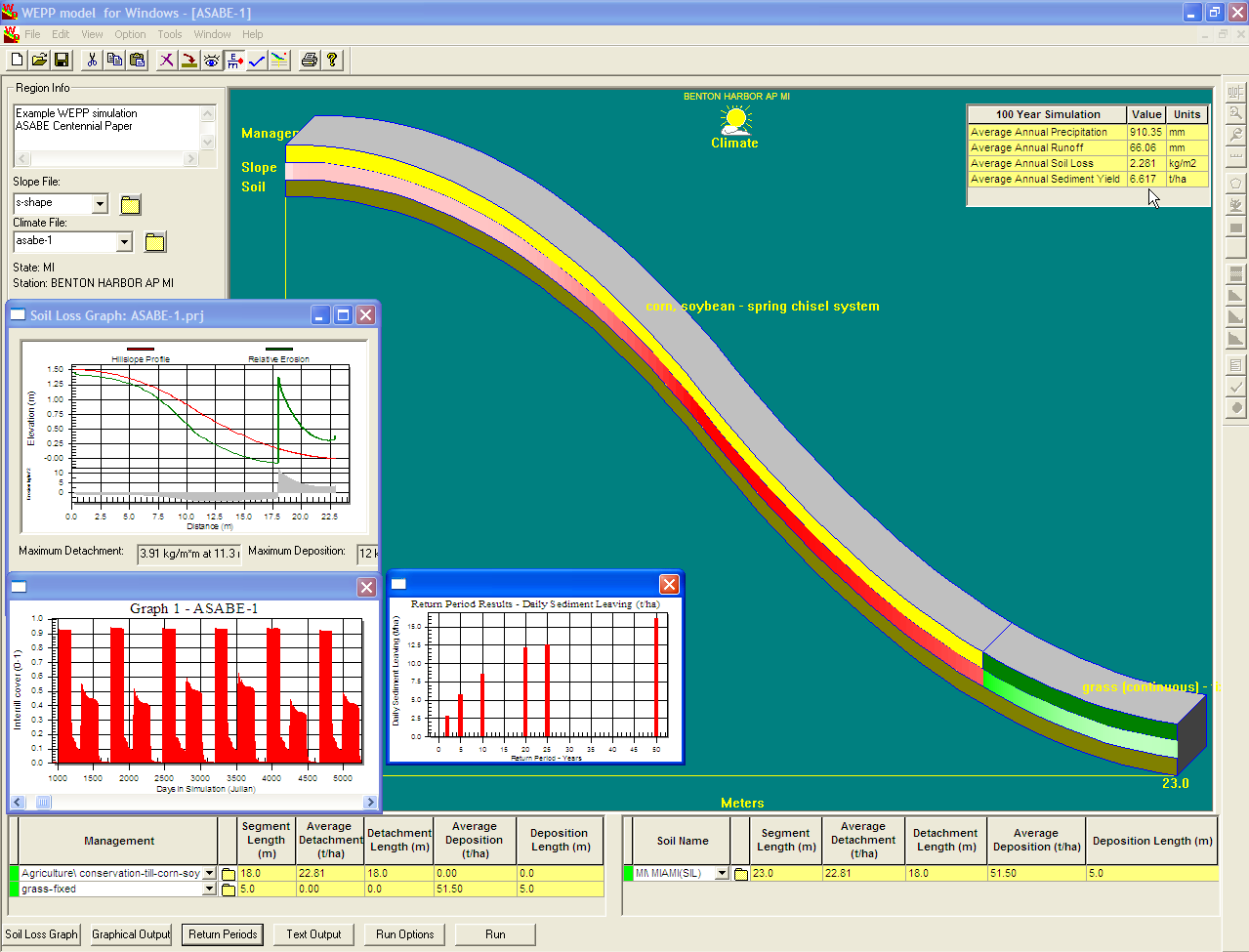
WEPP
The Water Erosion Prediction Project (WEPP) model is a Hydrological_transport_model#Physically based_models, physically based soil erosion, erosion simulation model built on the fundamentals of hydrology, plant science, hydraulics, and soil erosion, erosion mechanics. The model was developed by an interagency team of scientists to replace the Universal Soil Loss Equation (USLE) and has been widely used in the United States and the world. WEPP requires four inputs, i.e., climate, topography, soil, and management (vegetation); and provides various types of outputs, including water balance (surface runoff, subsurface flow, and evapotranspiration), Erosion, soil detachment and Deposition (chemistry), deposition at points along the slope, Sediment transport, sediment delivery, and vegetation growth. The WEPP model has been improved continuously since its public delivery in 1995, and is applicable for a variety of areas (e.g., cropland, rangeland, forestry, fisheries, and surface coal minin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erosion Control
Erosion control is the practice of preventing or controlling wind or water erosion in agriculture, land development, coastal areas, river banks and construction. Effective erosion controls handle surface runoff and are important techniques in preventing water pollution, soil loss, wildlife habitat loss and human property loss. Usage Erosion controls are used in natural areas, agricultural settings or urban environments. In urban areas erosion controls are often part of stormwater runoff management programs required by local governments. The controls often involve the creation of a physical barrier, such as vegetation or rock, to absorb some of the energy of the wind or water that is causing the erosion. They also involve building and maintaining storm drains. On construction sites they are often implemented in conjunction with sediment controls such as sediment basins and silt fences. Bank erosion is a natural process: without it, rivers would not meander and change course. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CPESC
{{Unreferenced, date=July 2020 Certified Professional in Erosion and Sediment Control (CPESC) is a qualification indicating the holder has educational training, expertise and experience in controlling erosion and sedimentation, and met certification standards. Eligibility requirements * Each applicant must successfully pass a written examination designed to determine proficiency in the principles, practices, and legislation of erosion and sediment control. Applicants must also meet one of the following requirements: *# Earn a BS degree A Bachelor of Science (BS, BSc, SB, or ScB; from the Latin ') is a bachelor's degree awarded for programs that generally last three to five years. The first university to admit a student to the degree of Bachelor of Science was the University of ... or higher plus three years of professional level experience in the soil erosion and sediment control profession *# Complete seven years or more of professional level experience in the erosion and s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nomograph
A nomogram (from Greek , "law" and , "line"), also called a nomograph, alignment chart, or abac, is a graphical calculating device, a two-dimensional diagram designed to allow the approximate graphical computation of a mathematical function. The field of nomography was invented in 1884 by the French engineer Philbert Maurice d'Ocagne (1862–1938) and used extensively for many years to provide engineers with fast graphical calculations of complicated formulas to a practical precision. Nomograms use a parallel coordinate system invented by d'Ocagne rather than standard Cartesian coordinates. A nomogram consists of a set of n scales, one for each variable in an equation. Knowing the values of n-1 variables, the value of the unknown variable can be found, or by fixing the values of some variables, the relationship between the unfixed ones can be studied. The result is obtained by laying a straightedge across the known values on the scales and reading the unknown value from where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Soil And Water Conservation
The ''Journal of Soil and Water Conservation'' is a bimonthly peer-reviewed journal of conservation science, practice, and policy. The journal is published by the Soil and Water Conservation Society The Soil and Water Conservation Society (SWCS) is a professional and scientific membership society. The mission of the organization is to foster the science and art of natural resource management for sustainability. The society was formed in 1945 .... Earth and atmospheric sciences journals Soil science journals {{soil-sci-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tillage
Tillage is the agricultural preparation of soil by mechanical agitation of various types, such as digging, stirring, and overturning. Examples of human-powered tilling methods using hand tools include shoveling, picking, mattock work, hoeing, and raking. Examples of draft-animal-powered or mechanized work include ploughing (overturning with moldboards or chiseling with chisel shanks), rototilling, rolling with cultipackers or other rollers, harrowing, and cultivating with cultivator shanks (teeth). Tillage that is deeper and more thorough is classified as primary, and tillage that is shallower and sometimes more selective of location is secondary. Primary tillage such as ploughing tends to produce a rough surface finish, whereas secondary tillage tends to produce a smoother surface finish, such as that required to make a good seedbed for many crops. Harrowing and rototilling often combine primary and secondary tillage into one operation. "Tillage" can also mean the lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fallow
Fallow is a farming technique in which arable land is left without sowing for one or more vegetative cycles. The goal of fallowing is to allow the land to recover and store organic matter while retaining moisture and disrupting pest life cycles and soil borne pathogens by temporarily removing their hosts. Crop rotation systems typically called for some of a farmer's fields to be left fallow each year. The increase in intensive farming, including the use of cover crops in lieu of fallow practices, has caused a loss of acreage of fallow land, as well as field margins, hedges, and wasteland. This has reduced biodiversity; fallows have been the primary habitat for farmland bird populations. Fallow syndrome Fallow syndrome is when a crop has insufficient nutrient uptake due to the lack of arbuscular mycorhizae (AM fungi) in the soil following a fallow period. Crops such as corn that are prone to fallow syndrome should not follow a period of fallow, but instead should follow a cover ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topographic
Topography is the study of the forms and features of land surfaces. The topography of an area may refer to the land forms and features themselves, or a description or depiction in maps. Topography is a field of geoscience and planetary science and is concerned with local detail in general, including not only relief, but also natural, artificial, and cultural features such as roads, land boundaries, and buildings. In the United States, topography often means specifically ''relief'', even though the USGS topographic maps record not just elevation contours, but also roads, populated places, structures, land boundaries, and so on. Topography in a narrow sense involves the recording of relief or terrain, the three-dimensional quality of the surface, and the identification of specific landforms; this is also known as geomorphometry. In modern usage, this involves generation of elevation data in digital form (DEM). It is often considered to include the graphic representation of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erodibility
Erodability (or erodibility) is the inherent yielding or nonresistance of soils and rocks to erosion. A high erodability implies that the same amount of work exerted by the erosion processes leads to a larger removal of material. Because the mechanics behind erosion depend upon the competence and coherence of the material, erodability is treated in different ways depending on the type of surface that eroded. Soils Soil erodibility is a lumped parameter that represents an integrated annual value of the soil profile reaction to the process of soil detachment and transport by raindrops and surface flow. The most commonly used model for predicting soil loss from water erosion is the '' Universal Soil Loss Equation (USLE)'' (also known as the K-factor technique), which estimates the average annual soil loss A as: :A = R K L S C P where ''R'' is thrainfall erosivity factor ''K'' is the soil erodibility, ''L'' and ''S'' are topographic factors representing length and slope, and ''C'' and ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rainfall
Rain is water droplets that have condensed from atmospheric water vapor and then fall under gravity. Rain is a major component of the water cycle and is responsible for depositing most of the fresh water on the Earth. It provides water for hydroelectric power plants, crop irrigation, and suitable conditions for many types of ecosystems. The major cause of rain production is moisture moving along three-dimensional zones of temperature and moisture contrasts known as weather fronts. If enough moisture and upward motion is present, precipitation falls from convective clouds (those with strong upward vertical motion) such as cumulonimbus (thunder clouds) which can organize into narrow rainbands. In mountainous areas, heavy precipitation is possible where upslope flow is maximized within windward sides of the terrain at elevation which forces moist air to condense and fall out as rainfall along the sides of mountains. On the leeward side of mountains, desert climates can exi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |