|
United Arab List (1977)
The United Arab List ( he, רשימה ערבית מאוחדת, rtl=yes, ''Reshima Aravit Meuhedet'') was an Arab satellite list in Israel during the late 1970s and early 1980s. It is not connected to the modern day United Arab List. History The UAL was established on 8 March 1977, during the eighth Knesset by the merger of the Arab List for Bedouins and Villagers and Progress and Development.Mergers and Splits Among Parliamentary Groups Knesset Both were Israeli Arab parties associated with the Labor Party, and had merged into it the Labor-dominated |
Hamad Abu Rabia
Sheikh Hamad Abu Rabia ( ar, حماد أبو ربيعة, he, חמאד אבו-רביעה; born 1929, died 12 January 1981) was a Bedouin Israeli politician and a member of the Knesset. Biography Abu Rabia was born and grew up in the Negev, where he attended elementary school. He attended high school in Hebron. At the age of 18 he became sheikh of his tribe and took interest in fostering its education. Abu Rabia was first elected to the Knesset in 1973 on the Arab List for Bedouins and Villagers, becoming the first Bedouin to serve in the Knesset. In 1974 the party joined the Alignment, but broke away again in 1976. The following year it merged into the original United Arab List. He was re-elected in the 1977 elections, and became a member of the Committee for Public Services. The United Arab List had won a single seat, which Abu Rabia and Jabr Muadi Sheikh Jabr Muadi ( ar, جبر داهش معدي; he, ג'בר מועדי, born 1 April 1919, died 19 May 2009) was an Israel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jabr Muadi
Sheikh Jabr Muadi ( ar, جبر داهش معدي; he, ג'בר מועדי, born 1 April 1919, died 19 May 2009) was an Israeli Druze politician who served as a member of the Knesset for seven different parties between 1951 and 1981. Biography Born in Yirka in British-controlled Palestine, Muadi was first elected to the Knesset in 1951 as a member of the Democratic List for Israeli Arabs. Although he lost his seat in the 1955 elections, he returned to the Knesset on 13 February 1956 as a replacement for Seif el-Din el-Zubi. He lost his seat again in the 1959 elections. He returned to the Knesset again after being elected on the Cooperation and Brotherhood list in 1961. He retained his seat in the 1965 elections. The following year Cooperation and Brotherhood merged with Progress and Development to form Cooperation and Development. The two parties split again on 1 January 1967, and on 11 April, Muadi broke away to form his own single-member faction, the Druze Party, which he r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
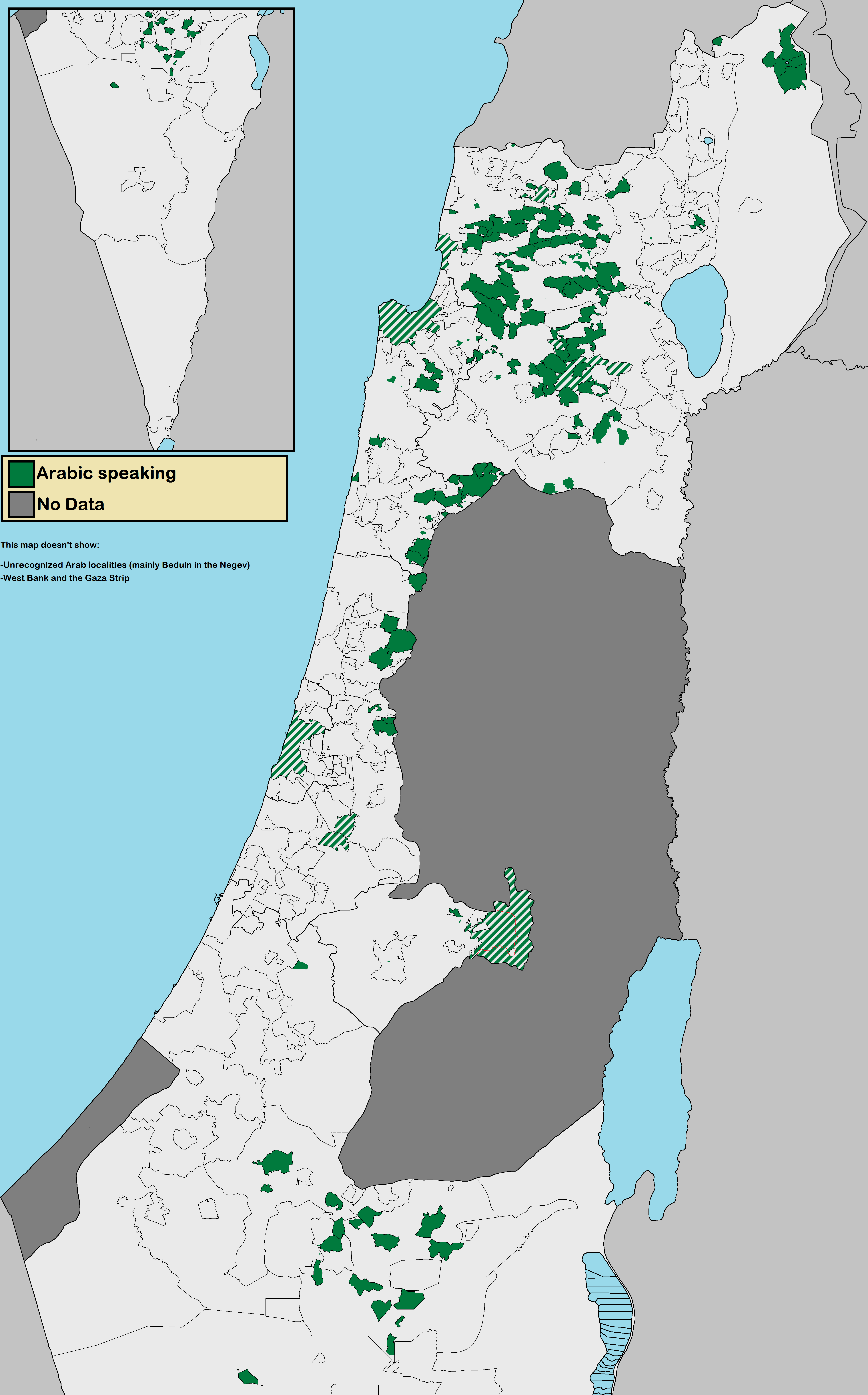
Arab Political Parties In Israel
The Arab citizens of Israel are the largest ethnic minority in the country. They comprise a hybrid community of Israeli citizens with a heritage of Palestinian citizenship, mixed religions (Muslim, Christian or Druze), bilingual in Arabic and Hebrew, and with varying social identities. Self-identification as Palestinian citizens of Israel has sharpened in recent years, alongside distinct identities including Galilee and Negev Bedouin, the Druze people, and Arab Christians and Arab Muslims who do not identify as Palestinians. In Arabic, commonly used terms to refer to Israel's Arab population include 48-Arab ( ar, عرب 48, Arab Thamaniya Wa-Arba'in, label=none) and 48-Palestinian (). Since the Nakba, the Palestinians that have remained within Israel's 1948 borders have been colloquially known as "48-Arabs". In Israel itself, Arab citizens are commonly referred to as Israeli-Arabs or simply as ''Arabs''; international media often uses the term Arab-Israeli to distinguish Arab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Political Parties Established In 1977
Politics (from , ) is the set of activities that are associated with making decisions in groups, or other forms of power relations among individuals, such as the distribution of resources or status. The branch of social science that studies politics and government is referred to as political science. It may be used positively in the context of a "political solution" which is compromising and nonviolent, or descriptively as "the art or science of government", but also often carries a negative connotation.. The concept has been defined in various ways, and different approaches have fundamentally differing views on whether it should be used extensively or limitedly, empirically or normatively, and on whether conflict or co-operation is more essential to it. A variety of methods are deployed in politics, which include promoting one's own political views among people, negotiation with other political subjects, making laws, and exercising internal and external force, including wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Defunct Political Parties In Israel
{{Disambiguation ...
Defunct (no longer in use or active) may refer to: * ''Defunct'' (video game), 2014 * Zombie process or defunct process, in Unix-like operating systems See also * * :Former entities * End-of-life product * Obsolescence Obsolescence is the state of being which occurs when an object, service, or practice is no longer maintained or required even though it may still be in good working order. It usually happens when something that is more efficient or less risky r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Election Threshold
The electoral threshold, or election threshold, is the minimum share of the primary vote that a candidate or political party requires to achieve before they become entitled to representation or additional seats in a legislature. This limit can operate in various ways, e.g. in party-list proportional representation systems where an electoral threshold requires that a party must receive a specified minimum percentage of votes (e.g. 5%), either nationally or in a particular electoral district, to obtain seats in the legislature. In Single transferable voting the election threshold is called the quota and not only the first choice but also the next-indicated choices are used to determine whether or not a party passes the electoral threshold (and it is possible to be elected under STV even if a candidate does not pass the election threshold). In MMP systems the election threshold determines which parties are eligible for the top-up seats. The effect of an electoral threshold is to d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1981 Israeli Legislative Election
Knesset elections were held in Israel on 30 June 1981. The ruling Likud won one more seat than the opposition Alignment, in line with many polls which had predicted a tight race. Voter turnout was 78.5%, with Likud receiving around ten thousand more than the Alignment. This elections highlighted the polarization in the country. Background Prior to the elections, Menachem Begin's government faced instability due to internal conflict amongst coalition partners and international pressures, as well as issues with corruption, and failure to pass legislation. Discontent with the government was growing, and 40% of people agreed that "the major problems facing the state and the entire political system must be changed and a strong government of leaders and independent of parties should take control". Parliament factions The table below lists the parliamentary factions represented in the 9th Knesset. Electoral system The 120 seats in the Knesset were elected by closed list proportiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1977 Israeli Legislative Election
Legislative elections were held in Israel on 17 May 1977 to elect the ninth Knesset. For the first time in Israeli political history, the right wing, led by Likud, won a plurality of seats, ending almost 30 years of rule by the left-wing Alignment and its predecessor, Mapai. The dramatic shift in Israeli politics caused by the outcome led to it becoming known as "the revolution" (Hebrew: המהפך, ''HaMahapakh''), a phrase coined by TV anchor Haim Yavin when he announced the election results live on television with the words "Ladies and gentlemen—a revolution!" (Hebrew: !גבירותי ורבותי—מהפך, ''Gvirotai veRabotai—Mahapakh!''). The election saw the beginning of a period lasting almost two decades where the left- and right-wing blocs held roughly equal numbers of seats in the Knesset. Voter turnout was 79%. History The Alignment was re-elected in December 1973, following the Yom Kippur War, but continued in-fighting and investigation into Israel's prepare ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seif-El-Din El-Zubi
Seif el-Din el-Zoubi ar, سيف الدين الزعبي, he, סַיִף אֵל־דִּין אֶל־זעֻבִּי; in Hebrew his name was most often written without niqqud (as is standard) as . (1913 – 26 June 1986) was an Israeli-Arab politician. Biography El-Zoubi was born in 1913 in Nazareth, where he attended high school. During the British Mandate of Palestine, he was active in the Haganah, and later received the Fighter of the State Decoration. In 1949 he was elected to the Knesset as the leader of the Democratic List of Nazareth. He was re-elected in 1951 on the Democratic List for Israeli Arabs, and 1955, but resigned from the Knesset on 13 February 1956. In 1959, he became mayor of Nazareth, the city's first Muslim mayor in decades, and held the post until 1965, when he returned to the Knesset on the Progress and Development list, which briefly merged into Cooperation and Development before regaining its independence. He was re-elected in 1969, and was appointed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knesset
The Knesset ( he, הַכְּנֶסֶת ; "gathering" or "assembly") is the unicameral legislature of Israel. As the supreme state body, the Knesset is sovereign and thus has complete control of the entirety of the Israeli government (with the exception of checks and balances from the courts and local governments). The Knesset passes all laws, elects the president and prime minister (although the latter is ceremonially appointed by the President), approves the cabinet, and supervises the work of the government, among other things. In addition, the Knesset elects the state comptroller. It also has the power to waive the immunity of its members, remove the president and the state comptroller from office, dissolve the government in a constructive vote of no confidence, and to dissolve itself and call new elections. The prime minister may also dissolve the Knesset. However, until an election is completed, the Knesset maintains authority in its current composition. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progress And Development
Progress and Development ( he, קידמה ופיתוח, ''Kidma VePituah''; ar, تقدم وتطور) was an Arab satellite list in Israel. History Progress and Development was established in 1959, drawing its support from the Galilee area. Like other Israeli Arab parties at the time, it was associated with David Ben-Gurion's Mapai party, as Ben-Gurion was keen to include Israeli Arabs in the functioning of the state in order to prove Jews and Arabs could co-exist peacefully and productively. In the 1959 elections, the party won 1.3% of the votes and two seats, making it the most popular Israeli Arab party in the Knesset. Its seats were taken by Ahmed A-Dahar and Elias Nakhleh. Because of its association with Mapai, the party joined the governing coalition. In the 1961 elections the party increased its share of the vote to 1.6%, though it was overtaken as the most popular Israeli Arab party by Cooperation and Brotherhood, who won 1.9% of the vote. Despite its increased vote, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alignment (political Party)
The Alignment ( he, המערך, HaMa'arakh) was the name of two political alliances in Israel, both of which ended their existence by merging into the Israeli Labor Party. The first Alignment was a 1965 alliance of Mapai and Ahdut HaAvoda. The two parties continued to exist independently, but submitted joint electoral lists. Often called the Labor Alignment, the alliance lasted three years until a merger with Rafi in 1968 created the unitary Israeli Labor Party. The following year the Labor Party formed an alliance with Mapam, readopting the Alignment name. The two constituent parties remained separate, but with combined electoral campaigns and candidate lists. The second version of the Alignment lasted for more than two decades. At its formation in 1969, the second Alignment had 63 of 120 Knesset seats, the only time a parliamentary group in Israel has ever held a parliamentary majority. Although its majority was lost in the 1969 election, the 56 seats won by the Alignment re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |