|
Unicameral Bone Cyst
A unicameral bone cyst, also known as a simple bone cyst, is a cavity filled with a yellow-colored fluid. It is considered to be benign since it does not spread beyond the bone. Unicameral bone cysts can be classified into two categories: active and latent. An active cyst is adjacent to the epiphyseal plate and tends to grow until it fills the entire diaphysis, the shaft, of the bone; depending on the invasiveness of the cyst, it can cause a pathological fracture or even destroy the epiphyseal plate leading to the permanent shortening of the bone. A latent cyst is located away from the epiphyseal plate and is more likely to heal with treatment. It is typically diagnosed in under 20 year olds. Although unicameral bone cysts can form in any bone structure, it is predominantly found in the proximal humerus and proximal femur; additionally, it affects males twice as often as females. Signs and symptoms Most unicameral bone cysts do not cause any symptoms and are discovered as accident ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves to generate images of the organs in the body. MRI does not involve X-rays or the use of ionizing radiation, which distinguishes it from CT and PET scans. MRI is a medical application of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) which can also be used for imaging in other NMR applications, such as NMR spectroscopy. MRI is widely used in hospitals and clinics for medical diagnosis, staging and follow-up of disease. Compared to CT, MRI provides better contrast in images of soft-tissues, e.g. in the brain or abdomen. However, it may be perceived as less comfortable by patients, due to the usually longer and louder measurements with the subject in a long, confining tube, though "Open" MRI designs mostly relieve this. Additionally, implants and oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
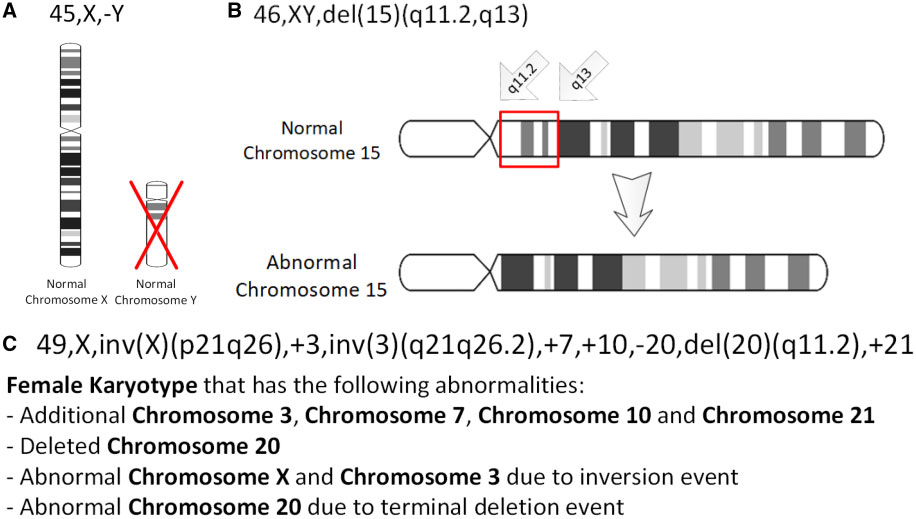
Deletion (genetics)
In genetics, a deletion (also called gene deletion, deficiency, or deletion mutation) (sign: Δ) is a mutation (a genetic aberration) in which a part of a chromosome or a sequence of DNA is left out during DNA replication. Any number of nucleotides can be deleted, from a single base to an entire piece of chromosome. Some chromosomes have fragile spots where breaks occur which result in the deletion of a part of chromosome. The breaks can be induced by heat, viruses, radiations, chemicals. When a chromosome breaks, a part of it is deleted or lost, the missing piece of chromosome is referred to as deletion or a deficiency. For synapsis to occur between a chromosome with a large intercalary deficiency and a normal complete homolog, the unpaired region of the normal homolog must loop out of the linear structure into a deletion or compensation loop. The smallest single base deletion mutations occur by a single base flipping in the template DNA, followed by template DNA strand sli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cauterization
Cauterization (or cauterisation, or cautery) is a medical practice or technique of burning a part of a body to remove or close off a part of it. It destroys some tissue in an attempt to mitigate bleeding and damage, remove an undesired growth, or minimize other potential medical harm, such as infections when antibiotics are unavailable. The practice was once widespread for treatment of wounds. Its utility before the advent of antibiotics was said to be effective at more than one level: *To prevent exsanguination *To close amputations Cautery was historically believed to prevent infection, but current research shows that cautery actually increases the risk for infection by causing more tissue damage and providing a more hospitable environment for bacterial growth. Actual cautery refers to the metal device, generally heated to a dull red glow, that a physician applies to produce blisters, to stop bleeding of a blood vessel, and for other similar purposes., page 16. The main forms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Septum
In biology, a septum (Latin for ''something that encloses''; plural septa) is a wall, dividing a cavity or structure into smaller ones. A cavity or structure divided in this way may be referred to as septate. Examples Human anatomy * Interatrial septum, the wall of tissue that is a sectional part of the left and right atria of the heart * Interventricular septum, the wall separating the left and right ventricles of the heart * Lingual septum, a vertical layer of fibrous tissue that separates the halves of the tongue. *Nasal septum: the cartilage wall separating the nostrils of the nose * Alveolar septum: the thin wall which separates the alveoli from each other in the lungs * Orbital septum, a palpebral ligament in the upper and lower eyelids * Septum pellucidum or septum lucidum, a thin structure separating two fluid pockets in the brain * Uterine septum, a malformation of the uterus * Vaginal septum, a lateral or transverse partition inside the vagina * Intermuscular sep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trephine
A trephine (; from Greek ''trypanon'', meaning an instrument for boring). is a surgical instrument with a cylindrical blade. It can be of one of several dimensions and designs depending on what it is meant to be used for. They may be specially designed for obtaining a cylindrically shaped core of bone that can be used for tests and bone studies, cutting holes in bones (e.g., the skull) or for cutting out a round piece of the cornea for eye surgery. A cylindrically shaped core of bone (or bone biopsy) obtained with a bone marrow trephine is usually examined in the histopathology department of a hospital under a microscope. It shows the pattern and cellularity of the bone marrow as it lay in the bone and is a useful diagnostic tool in certain circumstances such as bone marrow cancer and leukemia. See also *Trepanning *Trepanation in Mesoamerica *Instruments used in general surgery There are many different surgical specialties, some of which require very specific kinds o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acromion
In human anatomy, the acromion (from Greek: ''akros'', "highest", ''ōmos'', "shoulder", plural: acromia) is a bony process on the scapula (shoulder blade). Together with the coracoid process it extends laterally over the shoulder joint. The acromion is a continuation of the scapular spine, and hooks over anteriorly. It articulates with the clavicle (collar bone) to form the acromioclavicular joint. Structure The acromion forms the summit of the shoulder, and is a large, somewhat triangular or oblong process, flattened from behind forward, projecting at first lateralward, and then curving forward and upward, so as to overhang the glenoid fossa.''Gray's Anatomy'' 1918, see infobox It starts from the base of acromion which marks its projecting point emerging from the spine of scapula. Surfaces Its superior surface, directed upward, backward, and lateralward, is convex, rough, and gives attachment to some fibers of the deltoideus, and in the rest of its extent is subcutaneous. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fowler's Position
In medicine, Fowler's position is a standard patient position in which the patient is seated in a semi-sitting position (45-60 degrees) and may have knees either bent or straight. Variations in the angle are denoted by high Fowler, indicating an upright position at approximately 90 degrees and semi-Fowler, 30 to 45 degrees; and low Fowler, where the head is slightly elevated." It is an intervention used to promote oxygenation via maximum chest expansion and is implemented during events of respiratory distress. Fowler's position facilitates the relaxing of tension of the abdominal muscles, allowing for improved breathing. In immobile patients and infants, the Fowler's position alleviates compression of the chest that occurs due to gravity. Fowler's position increases comfort during eating and other activities, is used in postpartum women to improve uterine drainage, and in infants when signs of respiratory distress are present. Fowler's position is also used when oral or nasal gas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methylprednisolone Acetate
Methylprednisolone acetate, sold under the brand names Depo-Medrol among others, is a synthetic glucocorticoid corticosteroid and a corticosteroid ester—specifically the C21 acetate ester of methylprednisolone—which is used in clinical and veterinary medicine. It has been formulated as an aqueous suspension for intramuscular, intra-articular, soft tissue, and intralesional injection alone and in combination with lidocaine, a local anesthetic. Methylprednisolone acetate was previously suspended with polyethylene glycol but is no longer formulated with this excipient due to concerns about possible toxicity. Depo methylprednisolone acetate is a depot injection and is absorbed slowly with a duration Duration may refer to: * The amount of time elapsed between two events * Duration (music) – an amount of time or a particular time interval, often cited as one of the fundamental aspects of music * Duration (philosophy) – a theory of time and ... of weeks to months with a sing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bone Grafting
Bone grafting is a surgical procedure that replaces missing bone in order to repair bone fractures that are extremely complex, pose a significant health risk to the patient, or fail to heal properly. Some small or acute fractures can be cured without bone grafting, but the risk is greater for large fractures like compound fractures. Bone generally has the ability to regenerate completely but requires a very small fracture space or some sort of scaffold to do so. Bone grafts may be autologous (bone harvested from the patient's own body, often from the iliac crest), allograft (cadaveric bone usually obtained from a bone bank), or synthetic (often made of hydroxyapatite or other naturally occurring and biocompatible substances) with similar mechanical properties to bone. Most bone grafts are expected to be resorbed and replaced as the natural bone heals over a few months' time. The principles involved in successful bone grafts include osteoconduction (guiding the reparative growth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curettage
Curettage ( or ), in medical procedures, is the use of a curette (French, meaning scoopMosby's Medical, Nursing & Allied Health Dictionary, Fourth Edition, Mosby-Year Book 1994, p. 422) to remove tissue by scraping or scooping. Curettages are also a declining method of abortion. It has been replaced by vacuum aspiration over the last decade. Curettage has been used to treat teeth affected by periodontitis. Curettage is also a major method used for removing osteoid osteoma and osteoblastoma. Curettage with subsequent culture is more accurate than ulcer base swan culture or aspiration and culture for diabetic foot ulcers. Curettage is also used when excising a chalazion of the eyelid. See also * Dilation and curettage Dilation (or dilatation) and curettage (D&C) refers to the dilation (widening/opening) of the cervix and surgical removal of part of the lining of the uterus and/or contents of the uterus by scraping and scooping (curettage). It is a gynecolog ... Refe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoplasm
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists in growing abnormally, even if the original trigger is removed. This abnormal growth usually forms a mass, when it may be called a tumor. ICD-10 classifies neoplasms into four main groups: benign neoplasms, in situ neoplasms, malignant neoplasms, and neoplasms of uncertain or unknown behavior. Malignant neoplasms are also simply known as cancers and are the focus of oncology. Prior to the abnormal growth of tissue, as neoplasia, cells often undergo an abnormal pattern of growth, such as metaplasia or dysplasia. However, metaplasia or dysplasia does not always progress to neoplasia and can occur in other conditions as well. The word is from Ancient Greek 'new' and 'formation, creation'. Types A neoplasm can be benign, potentially ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FET Protein Family
The FET protein family (also known as the TET protein family consists of three similarly structured and functioning proteins. They and the genes in the FET gene family which encode them (i.e. form the pre-messenger RNAs that are converted to the messenger RNAs responsible for their production) are: 1) the EWSR1 protein encoded by the ''EWSR1'' gene (also termed the ''Ewing sarcoma RNA binding protein, EWS RNA binding protein 1,'' or ''bK984G1.4'' gene) located at band 12.2 of the long (i.e. "q") arm of chromosome 22; 2) the FUS (i.e. fused in sarcoma) protein encoded by the ''FUS'' gene (also termed the ''FUS RNA binding protein, TLS, asTLS, ALS6, ETM4, FUS1, POMP75, altFUS'', or ''HNRNPP2'' gene) located at band 16 on the short arm of chromosome 16; and 3) the TAF15 protein encoded by the ''TAF15'' gene (also termed the ''TATA-box binding protein associated factor 15, Npl3, RBP56, TAF2N'', or ''TAFII68'' gene) located at band 12 on the long arm of chromosome 7 The FET in this prot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |