|
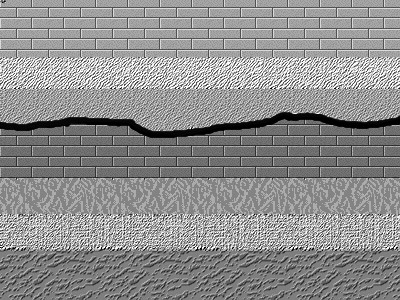
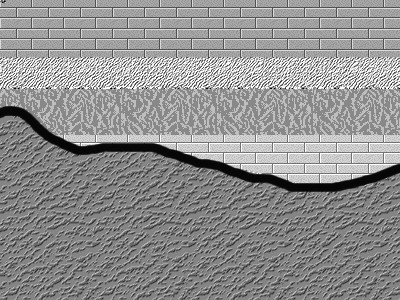
Unconformities
An unconformity is a buried erosional or non-depositional surface separating two rock masses or strata of different ages, indicating that sediment deposition was not continuous. In general, the older layer was exposed to erosion for an interval of time before deposition of the younger layer, but the term is used to describe any break in the sedimentary geologic record. The significance of angular unconformity (see below) was shown by James Hutton, who found examples of Hutton's Unconformity at Jedburgh in 1787 and at Siccar Point in 1788. The rocks above an unconformity are younger than the rocks beneath (unless the sequence has been overturned). An unconformity represents time during which no sediments were preserved in a region or were subsequently eroded before the next deposition. The local record for that time interval is missing and geologists must use other clues to discover that part of the geologic history of that area. The interval of geologic time not represented i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraconformity
An unconformity is a buried erosional or non-depositional surface separating two rock masses or strata of different ages, indicating that sediment deposition was not continuous. In general, the older layer was exposed to erosion for an interval of time before deposition of the younger layer, but the term is used to describe any break in the sedimentary geologic record. The significance of angular unconformity (see below) was shown by James Hutton, who found examples of Hutton's Unconformity at Jedburgh in 1787 and at Siccar Point in 1788. The rocks above an unconformity are younger than the rocks beneath (unless the sequence has been overturned). An unconformity represents time during which no sediments were preserved in a region or were subsequently eroded before the next deposition. The local record for that time interval is missing and geologists must use other clues to discover that part of the geologic history of that area. The interval of geologic time not represented i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angular Unconformity
An unconformity is a buried erosional or non-depositional surface separating two rock masses or strata of different ages, indicating that sediment deposition was not continuous. In general, the older layer was exposed to erosion for an interval of time before deposition of the younger layer, but the term is used to describe any break in the sedimentary geologic record. The significance of angular unconformity (see below) was shown by James Hutton, who found examples of Hutton's Unconformity at Jedburgh in 1787 and at Siccar Point in 1788. The rocks above an unconformity are younger than the rocks beneath (unless the sequence has been overturned). An unconformity represents time during which no sediments were preserved in a region or were subsequently eroded before the next deposition. The local record for that time interval is missing and geologists must use other clues to discover that part of the geologic history of that area. The interval of geologic time not represented i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disconformity
An unconformity is a buried erosional or non-depositional surface separating two rock masses or strata of different ages, indicating that sediment deposition was not continuous. In general, the older layer was exposed to erosion for an interval of time before deposition of the younger layer, but the term is used to describe any break in the sedimentary geologic record. The significance of angular unconformity (see below) was shown by James Hutton, who found examples of Hutton's Unconformity at Jedburgh in 1787 and at Siccar Point in 1788. The rocks above an unconformity are younger than the rocks beneath (unless the sequence has been overturned). An unconformity represents time during which no sediments were preserved in a region or were subsequently eroded before the next deposition. The local record for that time interval is missing and geologists must use other clues to discover that part of the geologic history of that area. The interval of geologic time not represented i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hutton's Unconformity
Hutton's Unconformity is a name given to various notable geological sites in Scotland identified by the 18th-century Scottish geologist James Hutton as places where the junction between two types of rock formations can be seen. This geological phenomenon marks the location where rock formations created at different times and by different forces adjoin. For Hutton, such an unconformity provided evidence for his Plutonist theories of uniformitarianism and the age of Earth. An unconformity is any break in the normal progression of sedimentary deposits, which are laid the newer on top of the older. In his search, Hutton and colleagues examined rock outcrops and cliffs, both riverside and sea, and found several locations where two adjoining rock types had been laid bare, the most noted being at Siccar Point on the coast of Berwickshire. Theory of rock formations Hutton hit on a variety of ideas to explain the rock formations he saw, and, after a quarter century of work, he read ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diastem
In geology, a diastem (plural: diastems) is a short interruption in sedimentation with little or no erosion. They can also be described as very short unconformities (more precisely as very short paraconformities).In 1917 Joseph barrel of USA estimated the rate of deposition of succession from the available radiometric age. His accumulation showed that the strata accumulation was at the rate of thousands of years per foot rather than hundreds. He stated that diastems are universal in sedimentary rocks and explain them as a product of fluctuation of base level. Definition The International Commission on Stratigraphy defines a diastem as " short interruption in deposition with little or no erosion before resumption of sedimentation" Duration Studies indicate that the age contained in diastems ranges from a few hundred to a few thousand years in shelf settings as well as throughout the Paleozoic The Paleozoic (or Palaeozoic) Era is the earliest of three geologic eras of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hutton Unconformity , Jedburgh
Hutton may refer to: Places ;Antarctica * Hutton Cliffs, Ross Island * Hutton Mountains ;Australia * Hutton Sandstone Formation ;Canada * Hutton, Alberta, a locality * Hutton, British Columbia, a railway point * Hutton railway station, British Columbia ;England * Hutton, Cumbria, a civil parish * Hutton, Essex, a former village, now a commuter suburb of Brentwood * Hutton, Lancashire, a village and civil parish * Hutton, Somerset, a village and civil parish * Hutton Cranswick, East Riding of Yorkshire, formed by the merger of two villages still referred to by their separate names * Hutton Village, a village near Guisborough in North Yorkshire ;Scotland * Hutton, Scottish Borders, a village * Hutton Castle, Scottish Borders * Hutton oilfield, North Sea ;United States * Hutton, Indiana, an unincorporated town * Hutton, Maryland, an unincorporated community * Hutton Township, Coles County, Illinois Outer space * Hutton (lunar crater) * Hutton (Martian crater) * 613 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleosols
In the geosciences, paleosol (''palaeosol'' in Great Britain and Australia) is an ancient soil that formed in the past. The precise definition of the term in geology and paleontology is slightly different from its use in soil science. In geology and paleontology, a paleosol is a former soil preserved by burial underneath either sediments (alluvium or loess) or volcanic deposits (volcanic ash), which in the case of older deposits have lithified into rock. In Quaternary geology, sedimentology, paleoclimatology, and geology in general, it is the typical and accepted practice to use the term "paleosol" to designate such "''fossil soils''" found buried within sedimentary and volcanic deposits exposed in all continents. In soil science the definition differs only slightly: ''paleosols'' are soils formed long ago that have no relationship in their chemical and physical characteristics to the present-day climate or vegetation. Such soils are found within extremely old continenta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mississippian (geology)
The Mississippian ( , also known as Lower Carboniferous or Early Carboniferous) is a subperiod in the geologic timescale or a subsystem of the geologic record. It is the earlier of two subperiods of the Carboniferous period lasting from roughly 358.9 to 323.2 million years ago. As with most other geochronologic units, the rock beds that define the Mississippian are well identified, but the exact start and end dates are uncertain by a few million years. The Mississippian is so named because rocks with this age are exposed in the Mississippi Valley. The Mississippian was a period of marine transgression in the Northern Hemisphere: the sea level was so high that only the Fennoscandian Shield and the Laurentian Shield were dry land. The cratons were surrounded by extensive delta systems and lagoons, and carbonate sedimentation on the surrounding continental platforms, covered by shallow seas. In North America, where the interval consists primarily of marine limestones, it is t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horni Pocernice
Prague 20, also known as Horní Počernice (German ''Ober Potschernitz''), is a municipal district (''městská část'') in Prague. It is located in the eastern part of the city. It is formed by one cadastre Horní Počernice. , there were 15,404 inhabitants living in Prague 20. The administrative district (''správní obvod'') of the same name is identical with the municipal district Prague 20. Twin towns * Brunsbüttel Brunsbüttel () is a town in the district of Dithmarschen, in Schleswig-Holstein, northern Germany that lies at the mouth of the Elbe river, near the North Sea. It is the location of the western entrance to the Kiel Canal. History The earliest r ..., Germany (2004) External links Prague 20 - Horní Počernice - Official homepage Districts of Prague {{Prague-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleosol
In the geosciences, paleosol (''palaeosol'' in Great Britain and Australia) is an ancient soil that formed in the past. The precise definition of the term in geology and paleontology is slightly different from its use in soil science. In geology and paleontology, a paleosol is a former soil preserved by burial underneath either sediments (alluvium or loess) or volcanic deposits (volcanic ash), which in the case of older deposits have lithified into rock. In Quaternary geology, sedimentology, paleoclimatology, and geology in general, it is the typical and accepted practice to use the term "paleosol" to designate such "''fossil soils''" found buried within sedimentary and volcanic deposits exposed in all continents. In soil science the definition differs only slightly: ''paleosols'' are soils formed long ago that have no relationship in their chemical and physical characteristics to the present-day climate or vegetation. Such soils are found within extremely old continental c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Briançonnais Modèles 7F
Briançonnais may refer to: *the people of Briançon *, a natural region of France *Briançonnais zone The Briançonnais zone or Briançonnais terrane is a piece of continental crust found in the Penninic nappes of the Alps. According to some paleogeographic reconstructions the rocks of the Briançonnais zone were in fact a part of the microconti ..., a piece of continental crust See also * Republic of the Escartons, sometimes called the Briançonnais {{dab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |