|
Umbilical Vein
The umbilical vein is a vein present during fetal development that carries oxygenated blood from the placenta into the growing fetus. The umbilical vein provides convenient access to the central circulation of a neonate for restoration of blood volume and for administration of glucose and drugs. The blood pressure inside the umbilical vein is approximately 20 mmHg.Wang, Y. Vascular biology of the placenta. in Colloquium Series on Integrated Systems Physiology: from Molecule to Function. 2010. Morgan & Claypool Life Sciences. Fetal circulation The unpaired umbilical vein carries oxygen and nutrient rich blood derived from fetal-maternal blood exchange at the chorionic villi. More than two-thirds of fetal hepatic circulation is via the main portal vein, while the remainder is shunted from the left portal vein via the ductus venosus to the inferior vena cava, eventually being delivered to the fetal right atrium. Closure Closure of the umbilical vein usually occurs after the umbilica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fetal Circulation
In humans, the circulatory system is different before and after birth. The fetal circulation is composed of the placenta, umbilical blood vessels encapsulated by the umbilical cord, heart and systemic blood vessels. A major difference between the fetal circulation and postnatal circulation is that the lungs are not used during the fetal stage resulting in the presence of shunts to move oxygenated blood and nutrients from the placenta to the fetal tissue. At birth, the start of breathing and the severance of the umbilical cord prompt various changes that quickly transforms fetal circulation into postnatal circulation. Oxygenation, nutrient, and waste exchange Placenta The placenta functions as the exchange site of nutrients and wastes between the maternal and fetal circulation. Water, glucose, amino acids, vitamins, and inorganic salts freely diffuse across the placenta along with oxygen. Two umbilical arteries carry deoxygenated blood and waste from the fetus to the placenta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
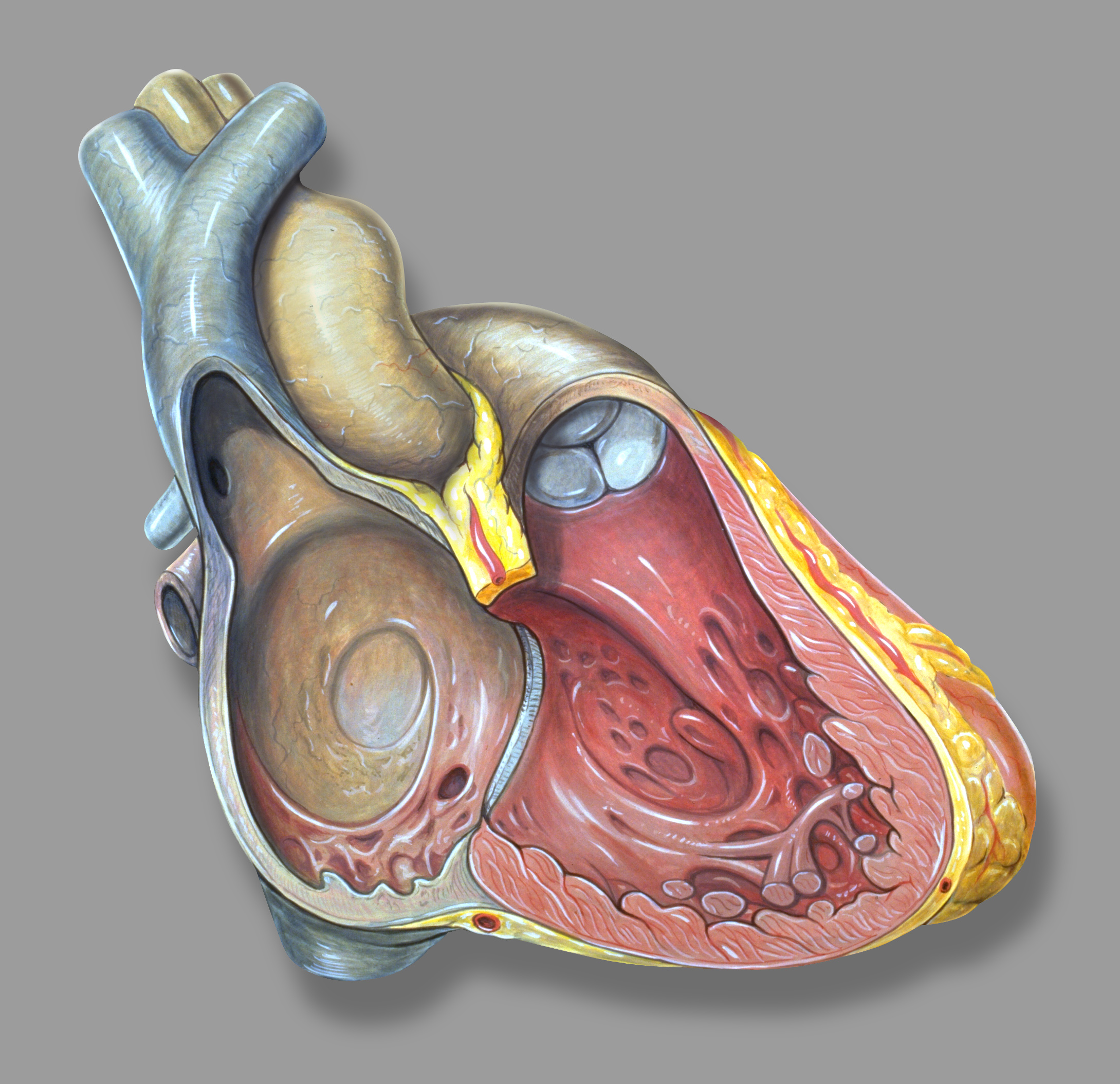
Right Atrium
The atrium ( la, ātrium, , entry hall) is one of two upper chambers in the heart that receives blood from the circulatory system. The blood in the atria is pumped into the heart ventricles through the atrioventricular valves. There are two atria in the human heart – the left atrium receives blood from the pulmonary circulation, and the right atrium receives blood from the venae cavae of the systemic circulation. During the cardiac cycle the atria receive blood while relaxed in diastole, then contract in systole to move blood to the ventricles. Each atrium is roughly cube-shaped except for an ear-shaped projection called an atrial appendage, sometimes known as an auricle. All animals with a closed circulatory system have at least one atrium. The atrium was formerly called the 'auricle'. That term is still used to describe this chamber in some other animals, such as the ''Mollusca''. They have thicker muscular walls than the atria do. Structure Humans have a four-chambered h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caput Medusae
Caput medusae is the appearance of distended and engorged superficial epigastric veins, which are seen radiating from the umbilicus across the abdomen. The name ''caput medusae'' (Latin for "head of Medusa") originates from the apparent similarity to Medusa's head, which had venomous snakes in place of hair. It is also a sign of portal hypertension. It is caused by dilation of the paraumbilical veins, which carry oxygenated blood from mother to fetus ''in utero'' and normally close within one week of birth, becoming re-canalised due to portal hypertension caused by liver failure. Differential diagnosis Inferior vena cava obstruction * Produces abdominal collateral veins to bypass the blocked inferior vena cava and permit venous return from the legs. Determine the direction of flow in the veins below the umbilicus. After pushing down on the prominent vein, blood will: * flow toward the legs → caput medusae * flow toward the head → inferior vena cava obstruction. See also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liver
The liver is a major Organ (anatomy), organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it is located in the quadrant (anatomy), right upper quadrant of the abdomen, below the thoracic diaphragm, diaphragm. Its other roles in metabolism include the regulation of Glycogen, glycogen storage, decomposition of red blood cells, and the production of hormones. The liver is an accessory digestive organ that produces bile, an alkaline fluid containing cholesterol and bile acids, which helps the fatty acid degradation, breakdown of fat. The gallbladder, a small pouch that sits just under the liver, stores bile produced by the liver which is later moved to the small intestine to complete digestion. The liver's highly specialized biological tissue, tissue, consisting mostly of hepatocytes, regulates a w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vascular Resistance
Vascular resistance is the resistance that must be overcome to push blood through the circulatory system and create flow. The resistance offered by the systemic circulation is known as the systemic vascular resistance (SVR) or may sometimes be called by the older term total peripheral resistance (TPR), while the resistance offered by the pulmonary circulation is known as the pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR). Systemic vascular resistance is used in calculations of blood pressure, blood flow, and cardiac function. Vasoconstriction (i.e., decrease in blood vessel diameter) increases SVR, whereas vasodilation (increase in diameter) decreases SVR. Units for measuring Units for measuring vascular resistance are dyn·s·cm−5, pascal seconds per cubic metre (Pa·s/m3) or, for ease of deriving it by pressure (measured in mmHg) and cardiac output (measured in L/min), it can be given in mmHg·min/L. This is numerically equivalent to hybrid resistance units (HRU), also known as Wood un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vessel Occlusion
Vascular occlusion is a blockage of a blood vessel, usually with a clot. It differs from thrombosis in that it can be used to describe any form of blockage, not just one formed by a clot. When it occurs in a major vein, it can, in some cases, cause deep vein thrombosis. The condition is also relatively common in the retina, and can cause partial or total loss of vision. An occlusion can often be diagnosed using Doppler sonography (a form of ultrasound). Some medical procedures, such as embolisation, involve occluding a blood vessel to treat a particular condition. This can be to reduce pressure on aneurysms (weakened blood vessels) or to restrict a haemorrhage. It can also be used to reduce blood supply to tumours or growths in the body, and therefore restrict their development. Occlusion can be carried out using a ligature; by implanting small coils which stimulate the formation of clots; or, particularly in the case of cerebral aneurysms, by clipping. See also * Central ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scar
A scar (or scar tissue) is an area of fibrous tissue that replaces normal skin after an injury. Scars result from the biological process of wound repair in the skin, as well as in other organs, and tissues of the body. Thus, scarring is a natural part of the healing process. With the exception of very minor lesions, every wound (e.g., after accident, disease, or surgery) results in some degree of scarring. An exception to this are animals with complete regeneration, which regrow tissue without scar formation. Scar tissue is composed of the same protein ( collagen) as the tissue that it replaces, but the fiber composition of the protein is different; instead of a random basketweave formation of the collagen fibers found in normal tissue, in fibrosis the collagen cross-links and forms a pronounced alignment in a single direction. This collagen scar tissue alignment is usually of inferior functional quality to the normal collagen randomised alignment. For example, scars in the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portal Hypertension
Portal hypertension is abnormally increased portal venous pressure – blood pressure in the portal vein and its branches, that drain from most of the intestine to the liver. Portal hypertension is defined as a hepatic venous pressure gradient greater than 5 mmHg. Cirrhosis (a form of chronic liver failure) is the most common cause of portal hypertension; other, less frequent causes are therefore grouped as non-cirrhotic portal hypertension. When it becomes severe enough to cause symptoms or complications, treatment may be given to decrease portal hypertension itself or to manage its complications. Signs and symptoms Signs and symptoms of portal hypertension include: * Ascites (free fluid in the peritoneal cavity), ** Abdominal pain or tenderness (when bacteria infect the ascites, as in spontaneous bacterial peritonitis). * Increased spleen size (splenomegaly), which may lead to lower platelet counts (thrombocytopenia) * Anorectal varices * Swollen veins on the anterior abdomin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis, also known as liver cirrhosis or hepatic cirrhosis, and end-stage liver disease, is the impaired liver function caused by the formation of scar tissue known as fibrosis due to damage caused by liver disease. Damage causes tissue repair and subsequent formation of scar tissue, which over time can replace normal functioning tissue, leading to the impaired liver function of cirrhosis. The disease typically develops slowly over months or years. Early symptoms may include tiredness, weakness, loss of appetite, unexplained weight loss, nausea and vomiting, and discomfort in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen. As the disease worsens, symptoms may include itchiness, swelling in the lower legs, fluid build-up in the abdomen, jaundice, bruising easily, and the development of spider-like blood vessels in the skin. The fluid build-up in the abdomen may become spontaneously infected. More serious complications include hepatic encephalopathy, bleeding from dilated veins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Pressure
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term "blood pressure" refers to the pressure in the large arteries. Blood pressure is usually expressed in terms of the systolic pressure (maximum pressure during one heartbeat) over diastolic pressure (minimum pressure between two heartbeats) in the cardiac cycle. It is measured in millimeters of mercury ( mmHg) above the surrounding atmospheric pressure. Blood pressure is one of the vital signs—together with respiratory rate, heart rate, oxygen saturation, and body temperature—that healthcare professionals use in evaluating a patient's health. Normal resting blood pressure, in an adult is approximately systolic over diastolic, denoted as "120/80 mmHg". Globally, the average blood pressure, age standardized, has remained about the same since 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lobe (anatomy)
In anatomy, a lobe is a clear anatomical division or extension of an organ (as seen for example in the brain, lung, liver, or kidney) that can be determined without the use of a microscope at the gross anatomy level. This is in contrast to the much smaller lobule, which is a clear division only visible under the microscope. Interlobar ducts connect lobes and interlobular ducts connect lobules. Examples of lobes *The four main lobes of the brain **the frontal lobe **the parietal lobe **the occipital lobe **the temporal lobe *The three lobes of the human cerebellum **the flocculonodular lobe **the anterior lobe **the posterior lobe *The two lobes of the thymus *The two and three lobes of the lungs **Left lung: superior and inferior **Right lung: superior, middle, and inferior *The four lobes of the liver **Left lobe of liver **Right lobe of liver **Quadrate lobe of liver **Caudate lobe of liver *The renal lobes of the kidney *Earlobes Examples of lobules *the cortical lobules o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Falciform Ligament Of The Liver
In human anatomy, the falciform ligament () is a ligament that attaches the liver to the front body wall and divides the liver into the left lobe and right lobe. The falciform ligament is a broad and thin fold of peritoneum, its base being directed downward and backward and its apex upward and forward. It droops down from the hilum of the liver. Structure The falciform ligament stretches obliquely from the front to the back of the abdomen, with one surface in contact with the peritoneum behind the right rectus abdominis muscle and the diaphragm, and the other in contact with the left lobe of the liver. The ligament stretches from the underside of the diaphragm to the posterior surface of the sheath of the right rectus abdominis muscle, as low down as the umbilicus; by its right margin it extends from the notch on the anterior margin of the liver, as far back as the posterior surface. It is composed of two layers of peritoneum closely united together. Its base or free edge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)