|
Ulvaria Obscura
''Ulvaria obscura'' is an intertidal and subtidal benthic marine algae found in temperate and Arctic ocean waters around the world. Ecology ''Ulvaria obscura'' is a common marine algae, typically identified in algal blooms referred to as "Green Tides". The species is distinct in its ability to produce the neurotransmitter dopamine as a herbivore defense mechanism. The species has a wide tolerance to various growth conditions, surviving temperatures between 5-29 °C, salinities from freshwater to complete saturation, and grows well under various light intensities. The species growth rate responds to increased dissolved inorganic nitrogen availability, making the species a possible indicator of anthropogenic pollution leading to eutrophication. Identification The thalli of ''Ulvaria obscura'' are bladelike, usually less than 5 cm tall and 8 cm thick, consisting of a single cell layer, and typically have between 2 and 6 pyrenoid Pyrenoids are sub-cellular m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intertidal
The intertidal zone, also known as the foreshore, is the area above water level at low tide and underwater at high tide (in other words, the area within the tidal range). This area can include several types of Marine habitat, habitats with various species of Marine life, life, such as seastars, Sea urchin, sea urchins, and many species of coral with regional differences in biodiversity. Sometimes it is referred to as the ''littoral zone'' or ''shore, seashore'', although those can be defined as a wider region. The well-known area also includes steep rocky Cliff, cliffs, sandy Beach, beaches, Bog, bogs or wetlands (e.g., vast Mudflat, mudflats). The area can be a narrow strip, as in Pacific island, Pacific islands that have only a narrow tidal range, or can include many meters of shoreline where shallow beach slopes interact with high tidal excursion. The peritidal zone is similar but somewhat wider, extending from above the highest tide level to below the lowest. Organisms in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subtidal
The neritic zone (or sublittoral zone) is the relatively shallow part of the ocean above the drop-off of the continental shelf, approximately in depth. From the point of view of marine biology it forms a relatively stable and well-illuminated environment for marine life, from plankton up to large fish and corals, while physical oceanography sees it as where the oceanic system interacts with the coast. Definition (marine biology), context, extra terminology In marine biology, the neritic zone, also called coastal waters, the coastal ocean or the sublittoral zone, refers to that zone of the ocean where sunlight reaches the ocean floor, that is, where the water is never so deep as to take it out of the photic zone. It extends from the low tide mark to the edge of the continental shelf, with a relatively shallow depth extending to about 200 meters (660 feet). Above the neritic zone lie the intertidal (or eulittoral) and supralittoral zones; below it the continental slope begi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benthic
The benthic zone is the ecological region at the lowest level of a body of water such as an ocean, lake, or stream, including the sediment surface and some sub-surface layers. The name comes from ancient Greek, βένθος (bénthos), meaning "the depths." Organisms living in this zone are called benthos and include microorganisms (e.g., bacteria and fungi) as well as larger invertebrates, such as crustaceans and polychaetes. Organisms here generally live in close relationship with the substrate and many are permanently attached to the bottom. The benthic boundary layer, which includes the bottom layer of water and the uppermost layer of sediment directly influenced by the overlying water, is an integral part of the benthic zone, as it greatly influences the biological activity that takes place there. Examples of contact soil layers include sand bottoms, rocky outcrops, coral, and bay mud. Description Oceans The benthic region of the ocean begins at the shore line (intertidal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marine Algae
Marine primary production is the chemical synthesis in the ocean of organic compounds from atmospheric or dissolved carbon dioxide. It principally occurs through the process of photosynthesis, which uses light as its source of energy, but it also occurs through chemosynthesis, which uses the oxidation or reduction of inorganic chemical compounds as its source of energy. Almost all life on Earth relies directly or indirectly on primary production. The organisms responsible for primary production are called primary producers or autotrophs. Most marine primary production is generated by a diverse collection of marine microorganisms called algae and cyanobacteria. Together these form the principal primary producers at the base of the ocean food chain and produce half of the world's oxygen. Marine primary producers underpin almost all marine animal life by generating nearly all of the oxygen and food marine animals need to exist. Some marine primary producers are also ecosystem en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
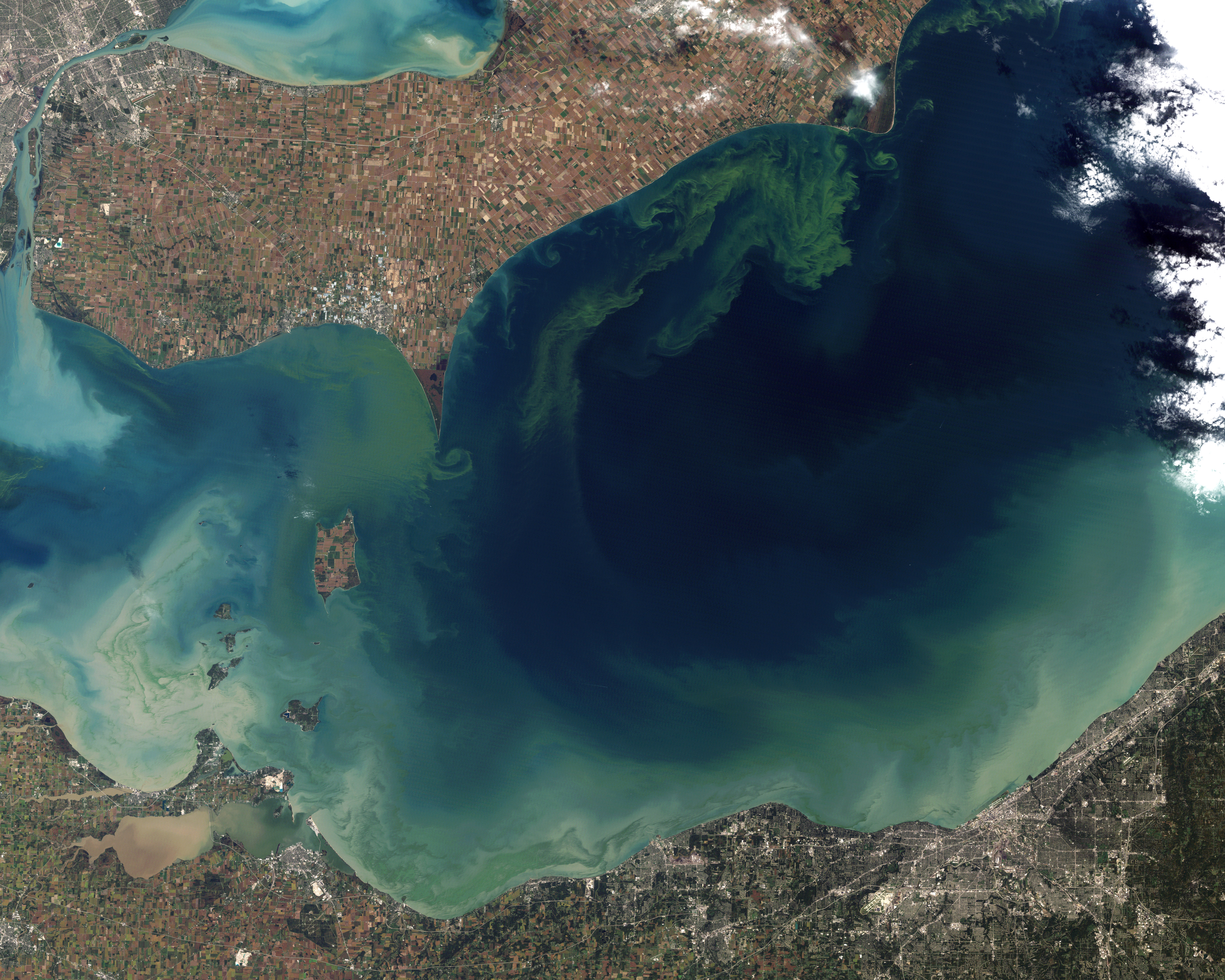
Algal Bloom
An algal bloom or algae bloom is a rapid increase or accumulation in the population of algae in freshwater or marine water systems. It is often recognized by the discoloration in the water from the algae's pigments. The term ''algae'' encompasses many types of aquatic photosynthetic organisms, both macroscopic multicellular organisms like seaweed and microscopic unicellular organisms like cyanobacteria. ''Algal bloom'' commonly refers to the rapid growth of microscopic unicellular algae, not macroscopic algae. An example of a macroscopic algal bloom is a kelp forest. Algal blooms are the result of a nutrient, like nitrogen or phosphorus from various sources (for example fertilizer runoff or other forms of nutrient pollution), entering the aquatic system and causing excessive growth of algae. An algal bloom affects the whole ecosystem. Consequences range from the benign feeding of higher trophic levels to more harmful effects like blocking sunlight from reaching other organ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a synapse. The cell receiving the signal, any main body part or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell. Neurotransmitters are released from synaptic vesicles into the synaptic cleft where they are able to interact with neurotransmitter receptors on the target cell. The neurotransmitter's effect on the target cell is determined by the receptor it binds. Many neurotransmitters are synthesized from simple and plentiful precursors such as amino acids, which are readily available and often require a small number of biosynthetic steps for conversion. Neurotransmitters are essential to the function of complex neural systems. The exact number of unique neurotransmitters in humans is unknown, but more than 100 have been identified. Common neurotransmitters include glutamate, GABA, acetylcholine, glycine and norepinephrine. Mechanism and cycle Synthes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dopamine
Dopamine (DA, a contraction of 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine) is a neuromodulatory molecule that plays several important roles in cells. It is an organic compound, organic chemical of the catecholamine and phenethylamine families. Dopamine constitutes about 80% of the catecholamine content in the brain. It is an amine synthesized by removing a carboxyl group from a molecule of its precursor (chemistry), precursor chemical, L-DOPA, which is biosynthesis, synthesized in the brain and kidneys. Dopamine is also synthesized in plants and most animals. In the brain, dopamine functions as a neurotransmitter—a chemical released by neurons (nerve cells) to send signals to other nerve cells. Neurotransmitters are synthesized in specific regions of the brain, but affect many regions systemically. The brain includes several distinct dopaminergic pathway, dopamine pathways, one of which plays a major role in the motivational component of reward system, reward-motivated behavior. The anticipa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herbivore
A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically adapted to eating plant material, for example foliage or marine algae, for the main component of its diet. As a result of their plant diet, herbivorous animals typically have mouthparts adapted to rasping or grinding. Horses and other herbivores have wide flat teeth that are adapted to grinding grass, tree bark, and other tough plant material. A large percentage of herbivores have mutualistic gut flora that help them digest plant matter, which is more difficult to digest than animal prey. This flora is made up of cellulose-digesting protozoans or bacteria. Etymology Herbivore is the anglicized form of a modern Latin coinage, ''herbivora'', cited in Charles Lyell's 1830 ''Principles of Geology''.J.A. Simpson and E.S.C. Weiner, eds. (2000) ''The Oxford English Dictionary'', vol. 8, p. 155. Richard Owen employed the anglicized term in an 1854 work on fossil teeth and skeletons. ''Herbivora'' is derived from Latin ''herba' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Illuminance
In photometry, illuminance is the total luminous flux incident on a surface, per unit area. It is a measure of how much the incident light illuminates the surface, wavelength-weighted by the luminosity function to correlate with human brightness perception.International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC): ''International Electrotechnical Vocabulary.'ref. 845-21-060, illuminance/ref> Similarly, luminous emittance is the luminous flux per unit area emitted from a surface. Luminous emittance is also known as luminous exitance. In SI units illuminance is measured in lux (lx), or equivalently in lumens per square metre ( lm· m−2). Luminous exitance is measured in lm·m−2 only, not lux. International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC): ''International Electrotechnical Vocabulary.'ref. 845-21-081, luminous exitance/ref> In the CGS system, the unit of illuminance is the phot, which is equal to . The foot-candle is a non-metric unit of illuminance that is used in photography. Ill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fertilizer
A fertilizer (American English) or fertiliser (British English; see spelling differences) is any material of natural or synthetic origin that is applied to soil or to plant tissues to supply plant nutrients. Fertilizers may be distinct from liming materials or other non-nutrient soil amendments. Many sources of fertilizer exist, both natural and industrially produced. For most modern agricultural practices, fertilization focuses on three main macro nutrients: nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K) with occasional addition of supplements like rock flour for micronutrients. Farmers apply these fertilizers in a variety of ways: through dry or pelletized or liquid application processes, using large agricultural equipment or hand-tool methods. Historically fertilization came from natural or organic sources: compost, animal manure, human manure, harvested minerals, crop rotations and byproducts of human-nature industries (i.e. fish processing waste, or bloodmeal from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthropogenic Hazard
Anthropogenic hazards are hazards caused by human action or inaction. They are contrasted with natural hazards. Anthropogenic hazards may adversely affect humans, other organisms, biomes, and ecosystems. They can even cause an omnicide. The frequency and severity of hazards are key elements in some risk analysis methodologies. Hazards may also be described in relation to the impact that they have. A hazard only exists if there is a pathway to exposure. As an example, the center of the earth consists of molten material at very high temperatures which would be a severe hazard if contact was made with the core. However, there is no feasible way of making contact with the core, therefore the center of the earth currently poses no hazard. Anthropogenic hazards can be grouped into societal hazards (criminality, civil disorder, terrorism, war, industrial hazards, engineering hazards, power outage, fire), hazards caused by transportation and environmental hazards. Societal hazards ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eutrophication
Eutrophication is the process by which an entire body of water, or parts of it, becomes progressively enriched with minerals and nutrients, particularly nitrogen and phosphorus. It has also been defined as "nutrient-induced increase in phytoplankton productivity". Water bodies with very low nutrient levels are termed oligotrophic and those with moderate nutrient levels are termed mesotrophic. Advanced eutrophication may also be referred to as dystrophic and hypertrophic conditions. Eutrophication can affect freshwater or salt water systems. In freshwater ecosystems it is almost always caused by excess phosphorus. In coastal waters on the other hand, the main contributing nutrient is more likely to be nitrogen, or nitrogen and phosphorus together. This depends on the location and other factors. When occurring naturally, eutrophication is a very slow process in which nutrients, especially phosphorus compounds and organic matter, accumulate in water bodies. These nutrients deriv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





_grazing_-_20050809.jpg)


