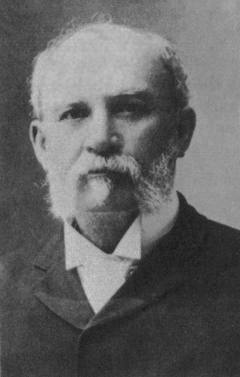|
Ululani Lewai Baker
Ululani Lewai Peleiōhōlani Baker (1858 – October 5, 1902) was a Hawaiian high chiefess and the last Governess of the island of Hawaii from 1886 to 1888. During her tenure, she was given the honorific Her Excellency, the Governess of Hawaii.; Life Ululani was born 1858. Her parents were High Chief Noah Peleiōhōlani and Kamanu. Considered of high rank, her father's family descended from the high chiefs of Maui. She received her Hawaiian language name ''Liwai'' or ''Lewai'' from an incident in the 18th-century reign of King Kalaniʻōpuʻu. According to tradition, Kalaniʻōpuʻu hanged his '' kahuna'' Naonaoaina after the latter was unable to dig freshwater from the cliffs of Mōʻīlele, near Kalae in the district of Kaʻū. She shared this same traditional name with distant cousin John Liwai Ena. She married John Tamatoa Baker, who famously served as one of the model of the Kamehameha Statues. They had no children. During the reign of King Kalākaua, Ululani was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Governors Of Hawaii (island)
The Governor of Hawaii Island ( haw, Kiaaina o na Mokupuni o Hawaii) was the Governor, royal governor or viceroy of the Hawaii (island), Island of Hawaii during the Hawaiian Kingdom, Kingdom of Hawaii. The Governor of Hawaii was usually a Hawaiian chief or prince and could even be a woman. There were no restriction of women in government in the House of Nobles or Governorship of the islands. The Governor had authority over the island of Hawaii, the biggest island in the kingdom, and it was up to the governor to appoint lieutenant governors to assisted them. The governor had replaced the old Aliʻis of the islands, but sovereignty remained with the king. The island governors were under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of the Interior (Hawaii), Ministers of the Interiors. Role The 1840 Constitution of the Hawaiian Kingdom, 1840 Constitution of the Kingdom of Hawaii states: Abolition After King Kalākaua was forced to sign the 1887 Constitution of the Hawaiian Kingdom, Bayonet Con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kamehameha Statues
Several ''Kamehameha'' statues honor the monarch who founded the Kingdom of Hawaii. Original work The pictured statue stands prominently in front of Aliiolani Hale in Honolulu, Hawaii. The statue had its origins in 1878 when Walter M. Gibson, a member of the Hawaiian government at the time, wanted to commemorate the 100-year arrival of Captain Cook to the Hawaiian Islands. The legislature appropriated $10,000 for the project and made Gibson the director of the project, which originally included native Hawaiians but they soon were off the project and Gibson ran the project by himself. Gibson contacted Thomas R. Gould, a Boston sculptor living abroad in Florence, Italy to create the statue. Features Even though photographs of Polynesians had been sent to him so that Gould could make an appropriate likeness, he seemed to ignore them. A Roman nose and more European features were adopted. This is most likely due to the fact that Gould was in Italy studying Roman sculpture. The sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by '' Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in which case it is known as latent tuberculosis. Around 10% of latent infections progress to active disease which, if left untreated, kill about half of those affected. Typical symptoms of active TB are chronic cough with blood-containing mucus, fever, night sweats, and weight loss. It was historically referred to as consumption due to the weight loss associated with the disease. Infection of other organs can cause a wide range of symptoms. Tuberculosis is spread from one person to the next through the air when people who have active TB in their lungs cough, spit, speak, or sneeze. People with Latent TB do not spread the disease. Active infection occurs more often in people with HIV/AIDS and in those who smoke. Diagnosis of active TB is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamakua
Hāmākua is a district on the northeast coast of Hawaii (island), Hawaii's Big Island, administered by the Hawaii County, Hawaii, County of Hawaii in the state of Hawaii, Hawaii. It is also the name given for the coastline in the region, the "Hāmākua Coast". Description Hāmākua's coast is approximately long, along the Pacific Ocean around , ending at Waipio Valley, Waipio Valley and the uninhabited Waimanu Valley. The term Hāmākua Coast is used loosely to describe the region between Hilo, Hawaii, Hilo and Waipio, although the modern Hāmākua zoning district begins north of Laupāhoehoe, Hawai'i, Laupāhoehoe and west of 'Ō'ōkala, Hawaii, Ōōkala. The rainfall due to the prevailing northeasterly tropical trade winds produces steep erosional valleys and cliffs, showing evidence of frequent landslides. The lush vegetation and lack of sandy beaches contrasts sharply with other regions of the island. The dominating geographic feature in Hāmākua is the volcanic mountain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overthrow Of The Hawaiian Kingdom
The overthrow of the Hawaiian Kingdom was a ''coup d'état'' against Queen Liliʻuokalani, which took place on January 17, 1893, on the island of Oahu and led by the Committee of Safety, composed of seven foreign residents and six non-aboriginal Hawaiian Kingdom subjects of American descent in Honolulu. The Committee prevailed upon American minister John L. Stevens to call in the U.S. Marines to protect the national interest of the United States of America. The insurgents established the Republic of Hawaii, but their ultimate goal was the annexation of the islands to the United States, which occurred in 1898. The 1993 Apology Resolution by the U.S. Congress concedes that "the overthrow of the Kingdom of Hawaii occurred with the active participation of agents and citizens of the United States and ..the Native Hawaiian people never directly relinquished to the United States their claims to their inherent sovereignty as a people over their national lands, either through the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liliʻuokalani
Liliʻuokalani (; Lydia Liliʻu Loloku Walania Kamakaʻeha; September 2, 1838 – November 11, 1917) was the only queen regnant and the last sovereign monarch of the Hawaiian Kingdom, ruling from January 29, 1891, until the overthrow of the Hawaiian Kingdom on January 17, 1893. The composer of " Aloha ʻOe" and numerous other works, she wrote her autobiography '' Hawaiʻi's Story by Hawaiʻi's Queen'' during her imprisonment following the overthrow. Liliʻuokalani was born on September 2, 1838, in Honolulu, on the island of Oʻahu. While her natural parents were Analea Keohokālole and Caesar Kapaʻakea, she was ''hānai'' (informally adopted) at birth by Abner Pākī and Laura Kōnia and raised with their daughter Bernice Pauahi Bishop. Baptized as a Christian and educated at the Royal School, she and her siblings and cousins were proclaimed eligible for the throne by King Kamehameha III. She was married to American-born John Owen Dominis, who later became the Governor o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Governors Of Kauai
The Governor of Kauai ( haw, Kiaaina o Kauai) was the royal governor or viceroy of the island of Kauai and island of Niihau during the Kingdom of Hawaii. The Governor of Kauai was usually a Hawaiian chief or prince and could even be a woman. The governor had authority over the islands of Kauai and Niihau, and it was up to the governor to appoint lieutenant governors to assist them. The governor had replaced the old alii aimokus of the islands, but the sovereignty remained with the king. The first governor was the last king of Kaumualii, and it was not until his death in 1824 that Queen Kaahumanu and King Kamehameha II took control from his sons. The island governors were under the jurisdiction of the Ministers of the Interiors. Role In the 1840 Constitution of the Kingdom of Hawaii it states: ''There shall be four governors over these Hawaiian Islands - one for Hawaii - one for Maui and the Islands adjacent - one for Oahu, and one for Kauai and the adjacent Islands. All th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lanihau
Lanihau (June 19, 1852 – October 24, 1914) was a Hawaiian high chiefess of the Hawaiian Kingdom. She served as the Keeper of the Royal Mausoleum (Mauna ʻAla), Royal Mausoleum of Mauna ʻAla from 1885 to 1886 and was the last Governors of Kauai, Governess (female governor) of the islands of Kauai and Niihau from 1886 to 1888. During her tenure, she was given the honorific Excellency, Her Excellency, the Governess of Kauai. Name She was sometimes referred to as A. Lanihau in official documents. In the Hawaiian language, the name Lanihau means "cool heaven". An ''ahupuaʻa'' (land division) of the same name was located in the district of Kona District, Hawaii, Kona on the island of Hawaii (island), Hawaii. Lanihau was also the name of a short-lived son of Kalanimoku and his wife Likelike (wife of Kalanimoku), Likelike who died in 1821. She has also been referred to as Ana Lanihau Koakanu, Mary Lanihau or Lanihau Opeka. Family Lanihau was the daughter of Pius F. Koakanu (some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legislature Of The Hawaiian Kingdom
The Legislature of the Hawaiian Kingdom () was the bicameral (later unicameral) legislature of the Hawaiian Kingdom. A royal legislature was first provided by the 1840 Constitution and the 1852 Constitution was the first to use the term Legislature of the Hawaiian Islands, and the first to subject the monarch to certain democratic principles. Prior to this the monarchs ruled under a Council of Chiefs (ʻAha Aliʻi). Structure The Legislature from 1840 to 1864 was bicameral and originally consisted of a lower House of Representatives and an upper House of Nobles as provided for under the Constitutions of the Kingdom of 1840 and 1852, until abolished by the 1864 Constitution which then provided for a unicameral Legislature. House of Nobles The members of the upper House of Nobles (Hale ʻAhaʻōlelo Aliʻi) were appointed by the Monarch with the advice of his Privy Council. It also served as the court of impeachment for any royal official. Members were usually Hawaiian ali� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Green Hoapili
John Green Hoapili ( – May 1, 1896) was a judge and politician of the Kingdom of Hawaii. He served as a legislator for many years. He commonly referred to by his initials, J. G. Hoapili. Life and career John Green Hoapili was born 1833, at Ke Au Hou, North Kona, on the island of Hawaii, the son of Kanehoa and his wife Kapaleililahu. His siblings were David Makainui-o-Kuakini and Hoapiliwahine Davis. His family descended from the ancient kings and high chiefs of Hawaii and Maui. He was considered a kinsman of King Kalākaua, who ruled Hawaii from 1874 to 1891. in 1866, Hoapili was elected to the House of Representative, the lower house of the legislature of the kingdom. He sat in on the legislative assembly of 1866 and the extra session of 1867 during the reign of King Kamehameha V. After serving his first legislative term, he became district magistrate and a district judge for his home district of North Kona and also South Kona, which was a profession he held for a period of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1887 Constitution Of The Hawaiian Kingdom
The 1887 Constitution of the Hawaiian Kingdom was a legal document prepared by anti-monarchists to strip the Hawaiian monarchy of much of its authority, initiating a transfer of power to American, European and native Hawaiian elites. It became known as the Bayonet Constitution for the use of intimidation by the armed militia which forced King Kalākaua to sign it or be deposed. Rebellion of 1887 On June 30, 1887, a meeting of residents including the armed militia of the Honolulu Rifles, a group of white soldiers that were secretly the Hawaiian League's military arm, and politicians who were members of the Reform Party of the Hawaiian Kingdom, demanded from King Kalākaua the dismissal of his Cabinet, headed by the controversial Walter M. Gibson. Their concerns about Gibson stemmed from the fact that he supported the king's authority. The meeting was called to order by Sanford B. Dole (cousin of then 9-year-old James Dole) and chaired by Peter Cushman Jones, the president of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
.jpg)