|
Ultrasound Computer Tomography
Ultrasound computer tomography (USCT), sometimes also ''Ultrasound computed tomography'', ''Ultrasound computerized tomography'' or just ''Ultrasound tomography'', is a form of medical ultrasound tomography utilizing ultrasound waves as physical phenomenon for imaging. It is mostly in use for soft tissue medical imaging, especially breast imaging. Description ''Ultrasound computer tomographs'' use ultrasound waves for creating images. In the first measurement step a defined ultrasound wave is generated with typically Piezoelectric ultrasound transducers, transmitted in direction of the measurement object and received with other or the same ultrasound transducers. While traversing and interacting with the object the ultrasound wave is changed by the object and carries now information about the object. After being recorded the information from the modulated waves can be extracted and used to create an image of the object in a second step. Unlike X-ray or other physical properties ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Ultrasound
Medical ultrasound includes diagnostic techniques (mainly imaging techniques) using ultrasound, as well as therapeutic applications of ultrasound. In diagnosis, it is used to create an image of internal body structures such as tendons, muscles, joints, blood vessels, and internal organs, to measure some characteristics (e.g. distances and velocities) or to generate an informative audible sound. Its aim is usually to find a source of disease or to exclude pathology. The usage of ultrasound to produce visual images for medicine is called medical ultrasonography or simply sonography. The practice of examining pregnant women using ultrasound is called obstetric ultrasonography, and was an early development of clinical ultrasonography. Ultrasound is composed of sound waves with frequencies which are significantly higher than the range of human hearing (>20,000 Hz). Ultrasonic images, also known as sonograms, are created by sending pulses of ultrasound into tissue using a pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scattering Theory
In mathematics and physics, scattering theory is a framework for studying and understanding the scattering of waves and particles. Wave scattering corresponds to the collision and scattering of a wave with some material object, for instance sunlight scattered by rain drops to form a rainbow. Scattering also includes the interaction of billiard balls on a table, the Rutherford scattering (or angle change) of alpha particles by gold nuclei, the Bragg scattering (or diffraction) of electrons and X-rays by a cluster of atoms, and the inelastic scattering of a fission fragment as it traverses a thin foil. More precisely, scattering consists of the study of how solutions of partial differential equations, propagating freely "in the distant past", come together and interact with one another or with a boundary condition, and then propagate away "to the distant future". The direct scattering problem is the problem of determining the distribution of scattered radiation/particle flux basing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institute Of Electrical And Electronics Engineers
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) is a 501(c)(3) professional association for electronic engineering and electrical engineering (and associated disciplines) with its corporate office in New York City and its operations center in Piscataway, New Jersey. The mission of the IEEE is ''advancing technology for the benefit of humanity''. The IEEE was formed from the amalgamation of the American Institute of Electrical Engineers and the Institute of Radio Engineers in 1963. Due to its expansion of scope into so many related fields, it is simply referred to by the letters I-E-E-E (pronounced I-triple-E), except on legal business documents. , it is the world's largest association of technical professionals with more than 423,000 members in over 160 countries around the world. Its objectives are the educational and technical advancement of electrical and electronic engineering, telecommunications, computer engineering and similar disciplines. History Origins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malcolm Slaney
Malcolm Slaney is an American electrical engineer, whose research has focused on machine perception and multimedia analysis. He is a Fellow of the IEEE for "contributions to perceptual signal processing and tomographic imaging". He is a consulting professor at the Stanford University Center for Computer Research in Music and Acoustics and an affiliate faculty member in the Electrical Engineering Department at the University of Washington. Slaney attended Purdue University for his bachelor's, master's, and PhD degrees in electrical engineering. He is currently a Research Scientist in the Machine Hearing group at Google. Previously, he worked at Bell Labs, Schlumberger Palo Alto Research, Apple Computer, Interval Research Corporation, IBM Research – Almaden, Yahoo! Research Yahoo!, once one of the most popular web sites in the United States, is as of September 2021 a content sub-division of the namesake company Yahoo (2017–present), Yahoo Inc., owned by Apollo Global Mana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avinash Kak
Avinash C. Kak (born 1944) is a professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering at Purdue University who has conducted pioneering research in several areas of information processing. His most noteworthy contributions deal with algorithms, languages, and systems related to networks (including sensor networks), robotics, and computer vision. Born in Srinagar, Kashmir, he did his Bachelors in BE at University of Madras and Phd in Indian Institute of Technology Delhi. He joined the faculty of Purdue University in 1971. His brother is the computer scientist Subhash Kak and sister the literary theorist Jaishree Odin. Robotics and computer vision His contributions include the 3D-POLY, which is the fastest algorithm for recognizing 3D objects in depth maps In 1992, Kosaka and Kak published FINALE, which is considered to be a computationally efficient and highly robust approach to vision-based navigation by indoor mobile robots. In 2003, a group of researchers that included Kak develo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TU München
The Technical University of Munich (TUM or TU Munich; german: Technische Universität München) is a public research university in Munich, Germany. It specializes in engineering, technology, medicine, and applied and natural sciences. Established in 1868 by King Ludwig II of Bavaria, the university now has additional campuses in Garching, Freising, Heilbronn, Straubing, and Singapore, with the Garching campus being its largest. The university is organized into eight schools and departments, and is supported by numerous research centers. It is one of the largest universities in Germany, with 50,000 students and an annual budget of €1,770.3 million (including university hospital). A ''University of Excellence'' under the German Universities Excellence Initiative, TUM is considered the top university in Germany according to major rankings as of 2022 and is among the leading universities in the European Union. Its researchers and alumni include 18 Nobel laureates and 23 Leibniz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qualitative Data
Qualitative properties are properties that are observed and can generally not be measured with a numerical result. They are contrasted to quantitative properties which have numerical characteristics. Some engineering and scientific properties are qualitative. A test method can result in qualitative data about something. This can be a categorical result or a binary classification Binary classification is the task of classifying the elements of a set into two groups (each called ''class'') on the basis of a classification rule. Typical binary classification problems include: * Medical testing to determine if a patient has c ... (e.g., pass/fail, go/no go, Conformity, conform/non-conform). It can sometimes be an engineering judgement. The data that all share a qualitative property form a nominal category. A variable which codes for the presence or absence of such a property is called a binary categorical variable, or equivalently a dummy variable (statistics), dummy variable. In b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues (physiology). Medical imaging seeks to reveal internal structures hidden by the skin and bones, as well as to diagnose and treat disease. Medical imaging also establishes a database of normal anatomy and physiology to make it possible to identify abnormalities. Although imaging of removed organs and tissues can be performed for medical reasons, such procedures are usually considered part of pathology instead of medical imaging. Measurement and recording techniques that are not primarily designed to produce images, such as electroencephalography (EEG), magnetoencephalography (MEG), electrocardiography (ECG), and others, represent other technologies that produce data susceptible to representation as a parameter graph versus time or maps that contain data about the measurement loca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantitative Property
Quantitative research is a research strategy that focuses on quantifying the collection and analysis of data. It is formed from a deductive approach where emphasis is placed on the testing of theory, shaped by empiricist and positivist philosophies. Associated with the natural, applied, formal, and social sciences this research strategy promotes the objective empirical investigation of observable phenomena to test and understand relationships. This is done through a range of quantifying methods and techniques, reflecting on its broad utilization as a research strategy across differing academic disciplines. The objective of quantitative research is to develop and employ mathematical models, theories, and hypotheses pertaining to phenomena. The process of measurement is central to quantitative research because it provides the fundamental connection between empirical observation and mathematical expression of quantitative relationships. Quantitative data is any data that is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spherical Wave
The (two-way) wave equation is a second-order linear partial differential equation for the description of waves or standing wave fields — as they occur in classical physics — such as mechanical waves (e.g. water waves, sound waves and seismic waves) or electromagnetic waves (including light waves). It arises in fields like acoustics, electromagnetism, and fluid dynamics. Single mechanical or electromagnetic waves propagating in a pre-defined direction can also be described with the first-order one-way wave equation which is much easier to solve and also valid for inhomogenious media. Introduction The (two-way) wave equation is a second-order partial differential equation describing waves, including traveling and standing waves; the latter can be considered as linear superpositions of waves traveling in opposite directions. This article mostly focuses on the scalar wave equation describing waves in scalars by scalar functions of a time variable (a variable representing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
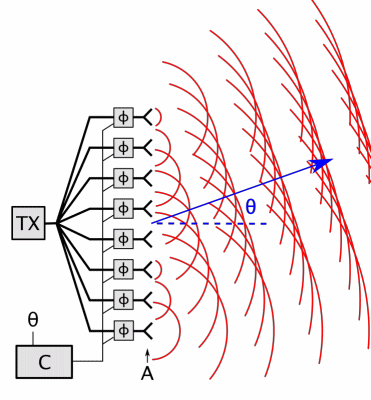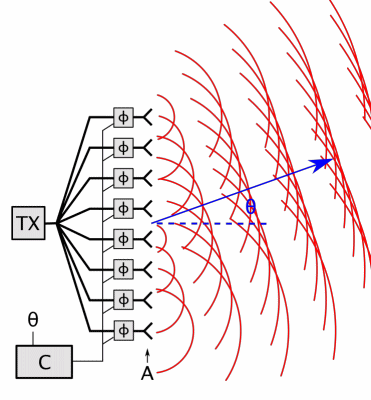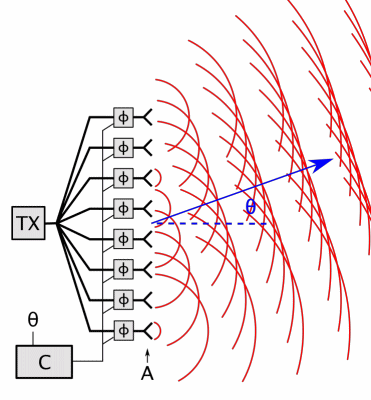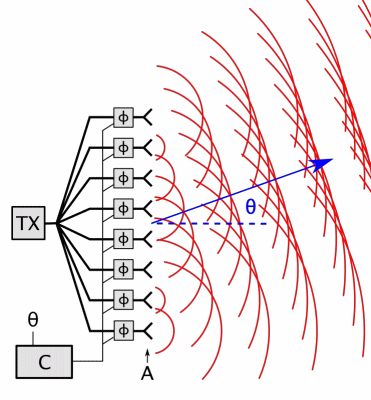
Beamforming
Beamforming or spatial filtering is a signal processing technique used in sensor arrays for directional signal transmission or reception. This is achieved by combining elements in an antenna array in such a way that signals at particular angles experience constructive interference while others experience destructive interference. Beamforming can be used at both the transmitting and receiving ends in order to achieve spatial selectivity. The improvement compared with omnidirectional reception/transmission is known as the directivity of the array. Beamforming can be used for radio or sound waves. It has found numerous applications in radar, sonar, seismology, wireless communications, radio astronomy, acoustics and biomedicine. Adaptive beamforming is used to detect and estimate the signal of interest at the output of a sensor array by means of optimal (e.g. least-squares) spatial filtering and interference rejection. Techniques To change the directionality of the array when transm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phased Array
In antenna theory, a phased array usually means an electronically scanned array, a computer-controlled array of antennas which creates a beam of radio waves that can be electronically steered to point in different directions without moving the antennas. In a simple array antenna, the radio frequency current from the transmitter is fed to multiple individual antenna elements with the proper phase relationship so that the radio waves from the separate elements combine ( superpose) to form beams, to increase power radiated in desired directions and suppress radiation in undesired directions. In a phased array, the power from the transmitter is fed to the radiating elements through devices called ''phase shifters'', controlled by a computer system, which can alter the phase or signal delay electronically, thus steering the beam of radio waves to a different direction. Since the size of an antenna array must extend many wavelengths to achieve the high gain needed for narrow bea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |