|
Ukhaidir
The Fortress of Al-Ukhaidir ( ar, حصن الأخيضر) or Abbasid palace of Ukhaider is located roughly 50 km south of Karbala, Iraq. It is a large, rectangular fortress erected in 775 AD with a unique defensive style. Constructed by the Abbasid caliph As-Saffah's nephew Isa ibn Musa, Ukhaidir represents Abbasid architecture, Abbasid architectural innovation in the structures of its courtyards, residences and mosque. Excavations at Ukhaidir were conducted in the early 20th century by Gertrude Bell, who wrote the first major report on the remains. Ukhaidir was an important stop on regional trade routes, similar to Atshan and Mujdah. The complex comprises a primary hall, a large Iwan, a reception hall and servants quarters. The fortress exemplifies Abbasid architecture in Iraq by demonstrating the "despotic and the pleasure-loving character of the dynasty" in its grand size but cramped living quarters. The current name could be related to ''Isma'il ibn Yusuf al-Ukhaidhir'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abbasid Architecture
Abbasid architecture developed in the Abbasid Caliphate between 750 and 1227, primarily in its heartland of Mesopotamia (modern Iraq). The great changes of the Abbasid era can be characterized as at the same time political, geo-political and cultural. The Abbasid period starts with the destruction of the Umayyad ruling family and its replacement by the Abbasids, and the position of power is shifted to the Mesopotamian area, and as a result in a corresponding displacement of the influence of classical and Byzantine artistic and cultural standards in favor of local Mesopotamian models as well as Persian. The Abbasids evolved distinctive styles of their own, particularly in decoration of their buildings. They favoured mud brick and baked brick for construction, allowing for enormous architectural complexes to be built at relatively low cost, as most clearly exemplified by Samarra, a 9th-century capital city made up of vast palaces and monumental mosques spread across some . The arch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
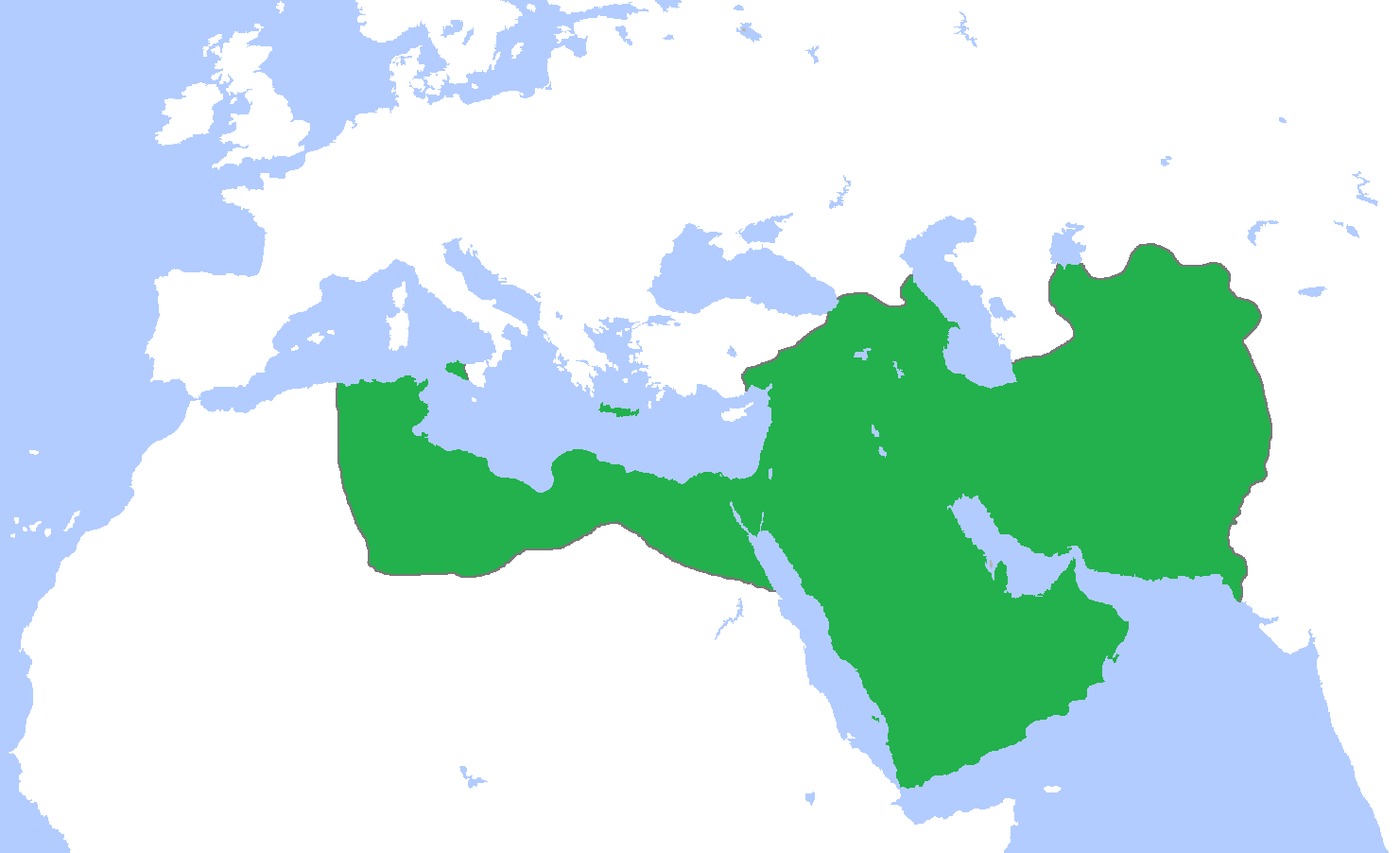
Abbasid Palaces
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttalib (566–653 CE), from whom the dynasty takes its name. They ruled as caliphs for most of the caliphate from their capital in Baghdad in modern-day Iraq, after having overthrown the Umayyad Caliphate in the Abbasid Revolution of 750 CE (132 AH). The Abbasid Caliphate first centered its government in Kufa, modern-day Iraq, but in 762 the caliph Al-Mansur founded the city of Baghdad, near the ancient Babylonian capital city of Babylon. Baghdad became the center of science, culture and invention in what became known as the Golden Age of Islam. This, in addition to housing several key academic institutions, including the House of Wisdom, as well as a multiethnic and multi-religious environment, garnered it a worldwide reputation as the "C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abbasid
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttalib (566–653 CE), from whom the dynasty takes its name. They ruled as caliphs for most of the caliphate from their capital in Baghdad in modern-day Iraq, after having overthrown the Umayyad Caliphate in the Abbasid Revolution of 750 CE (132 anno Hegirae, AH). The Abbasid Caliphate first centered its government in Kufa, modern-day Iraq, but in 762 the caliph Al-Mansur founded the city of Baghdad, near the ancient Babylonian Empire, Babylonian capital city of Babylon. Baghdad became the center of Science in the medieval Islamic world, science, Islamic culture, culture and List of inventions in the medieval Islamic world, invention in what became known as the Islamic Golden Age, Golden Age of Islam. This, in addition to housing several ke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gertrude Bell
Gertrude Margaret Lowthian Bell, CBE (14 July 1868 – 12 July 1926) was an English writer, traveller, political officer, administrator, and archaeologist. She spent much of her life exploring and mapping the Middle East, and became highly influential to British imperial policy-making as an Arabist due to her knowledge and contacts built up through extensive travels. During her lifetime, she was highly esteemed and trusted by British officials such as High Commissioner for Mesopotamia Percy Cox, giving her great influence. She participated in both the 1919 Paris Peace Conference (briefly) and the 1921 Cairo Conference, which helped decide the territorial boundaries and governments of the post-War Middle East as part of the partition of the Ottoman Empire. Bell believed that the momentum of Arab nationalism was unstoppable, and that the British government should ally with nationalists rather than stand against them. Along with T. E. Lawrence, she advocated for independe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isa Ibn Musa
ʿĪsā ibn Mūsā ibn Muḥammad ibn ʿAlī ibn ʿAbd Allāh ibn al-ʿAbbās () (–783/4) was a nephew of the first two Abbasid caliphs, as-Saffah () and al-Mansur (), and for a long time heir-apparent of the Caliphate, until he was superseded by al-Mansur's son al-Mahdi (). Life Isa ibn Musa was born in AH 103 (721/2 CE). In summer 750, immediately after the end of the Abbasid Revolution, Isa was appointed by his uncle as-Saffah as governor of Kufa, the first seat of the Abbasid government. He would retain the post for fifteen years—according to Hugh N. Kennedy, the second longest tenure in the Abbasid period after that of Dawud ibn Yazid al-Muhallabi in the early 9th century. In 754, -Saffah was nearing his death, and as his designated heir Abu Ja'far (al-Mansur) was on pilgrimage in Mecca at the time, the Caliph appointed Isa, then about 34 years old, as the second heir, in the event anything should happen to al-Mansur. This move was necessary to prevent Abu Muslim, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karbala Governorate
Karbala Governorate ( ar, كربلاء ''Karbalāʾ'') is a governorate in central Iraq. Its administrative center is the city of Karbala, a holy city for Shia Muslims for housing the shrine of the revered Imam Hussein. The population is majority Shia. The governorate includes part of the artificial Lake Milh. Provincial Government *Governor: Aqil Al-Turaihi *Deputy Governor: Jawad al-Hasnaw*Provincial Council Chairman (PCC): Abdul al-Al al-Yasser Districts * Ain Al-Tamur District, Ain Al-Tamur * Al-Hindiya * Karbala Karbala or Kerbala ( ar, كَرْبَلَاء, Karbalāʾ , , also ;) is a city in central Iraq, located about southwest of Baghdad, and a few miles east of Lake Milh, also known as Razzaza Lake. Karbala is the capital of Karbala Governorat ... References Governorates of Iraq Shia Islam {{Iraq-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qarmatians
The Qarmatians ( ar, قرامطة, Qarāmiṭa; ) were a militant Isma'ilism, Isma'ili Shia Islam, Shia movement centred in Al-Ahsa Oasis, al-Hasa in Eastern Arabia, where they established a Utopia#Religious utopias, religious-utopian Socialism, socialist state in 899 CE. Its members were part of a movement that adhered to a syncretism, syncretic branch of Sevener Isma'ilism, Ismaili Shia Islam, and were ruled by a dynasty founded by Abu Sa'id al-Jannabi, a Persians, Persian from Bandar Ganaveh, Jannaba in coastal Fars province, Fars. They rejected the claim of Fatimid Caliphate, Fatimid caliph Abdallah al-Mahdi Billah to Imamate in Shia doctrine, imamate and clung to their belief in the coming of the Mahdi, and they revolted against the Fatimid and Abbasid Caliphates. Mecca was sacked by a Qarmatian leader, Abu Tahir al-Jannabi, outraging the Muslim world, particularly with their theft of the Black Stone and desecration of the Zamzam Well with corpses during the Hajj season of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castles In Iraq
A castle is a type of fortified structure built during the Middle Ages predominantly by the nobility or royalty and by military orders. Scholars debate the scope of the word ''castle'', but usually consider it to be the private fortified residence of a lord or noble. This is distinct from a palace, which is not fortified; from a fortress, which was not always a residence for royalty or nobility; from a ''pleasance'' which was a walled-in residence for nobility, but not adequately fortified; and from a fortified settlement, which was a public defence – though there are many similarities among these types of construction. Use of the term has varied over time and has also been applied to structures such as hill forts and 19th-20th century homes built to resemble castles. Over the approximately 900 years when genuine castles were built, they took on a great many forms with many different features, although some, such as curtain walls, arrowslits, and portcullises, were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military History Of The Abbasid Caliphate
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct military uniform. It may consist of one or more military branches such as an army, navy, air force, space force, marines, or coast guard. The main task of the military is usually defined as defence of the state and its interests against external armed threats. In broad usage, the terms ''armed forces'' and ''military'' are often treated as synonymous, although in technical usage a distinction is sometimes made in which a country's armed forces may include both its military and other paramilitary forces. There are various forms of irregular military forces, not belonging to a recognized state; though they share many attributes with regular military forces, they are less often referred to as simply ''military''. A nation's military may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Heritage Sites In Iraq
In its most general sense, the term "world" refers to the totality of entities, to the whole of reality or to everything that is. The nature of the world has been conceptualized differently in different fields. Some conceptions see the world as unique while others talk of a "plurality of worlds". Some treat the world as one simple object while others analyze the world as a complex made up of many parts. In ''scientific cosmology'' the world or universe is commonly defined as " e totality of all space and time; all that is, has been, and will be". '' Theories of modality'', on the other hand, talk of possible worlds as complete and consistent ways how things could have been. ''Phenomenology'', starting from the horizon of co-given objects present in the periphery of every experience, defines the world as the biggest horizon or the "horizon of all horizons". In ''philosophy of mind'', the world is commonly contrasted with the mind as that which is represented by the mind. ''Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buildings And Structures Completed In 775
A building, or edifice, is an enclosed structure with a roof and walls standing more or less permanently in one place, such as a house or factory (although there's also portable buildings). Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, and have been adapted throughout history for a wide number of factors, from building materials available, to weather conditions, land prices, ground conditions, specific uses, prestige, and aesthetic reasons. To better understand the term ''building'' compare the list of nonbuilding structures. Buildings serve several societal needs – primarily as shelter from weather, security, living space, privacy, to store belongings, and to comfortably live and work. A building as a shelter represents a physical division of the human habitat (a place of comfort and safety) and the ''outside'' (a place that at times may be harsh and harmful). Ever since the first cave paintings, buildings have also become objects or canvasses of much artistic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UNESCO World Heritage
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, scientific or other form of significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural heritage around the world considered to be of outstanding value to humanity". To be selected, a World Heritage Site must be a somehow unique landmark which is geographically and historically identifiable and has special cultural or physical significance. For example, World Heritage Sites might be ancient ruins or historical structures, buildings, cities, deserts, forests, islands, lakes, monuments, mountains, or wilderness areas. A World Heritage Site may signify a remarkable accomplishment of humanity, and serve as evidence of our intellectual history on the planet, or it might be a place of great natural beauty. As ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)



