|
Ucenni
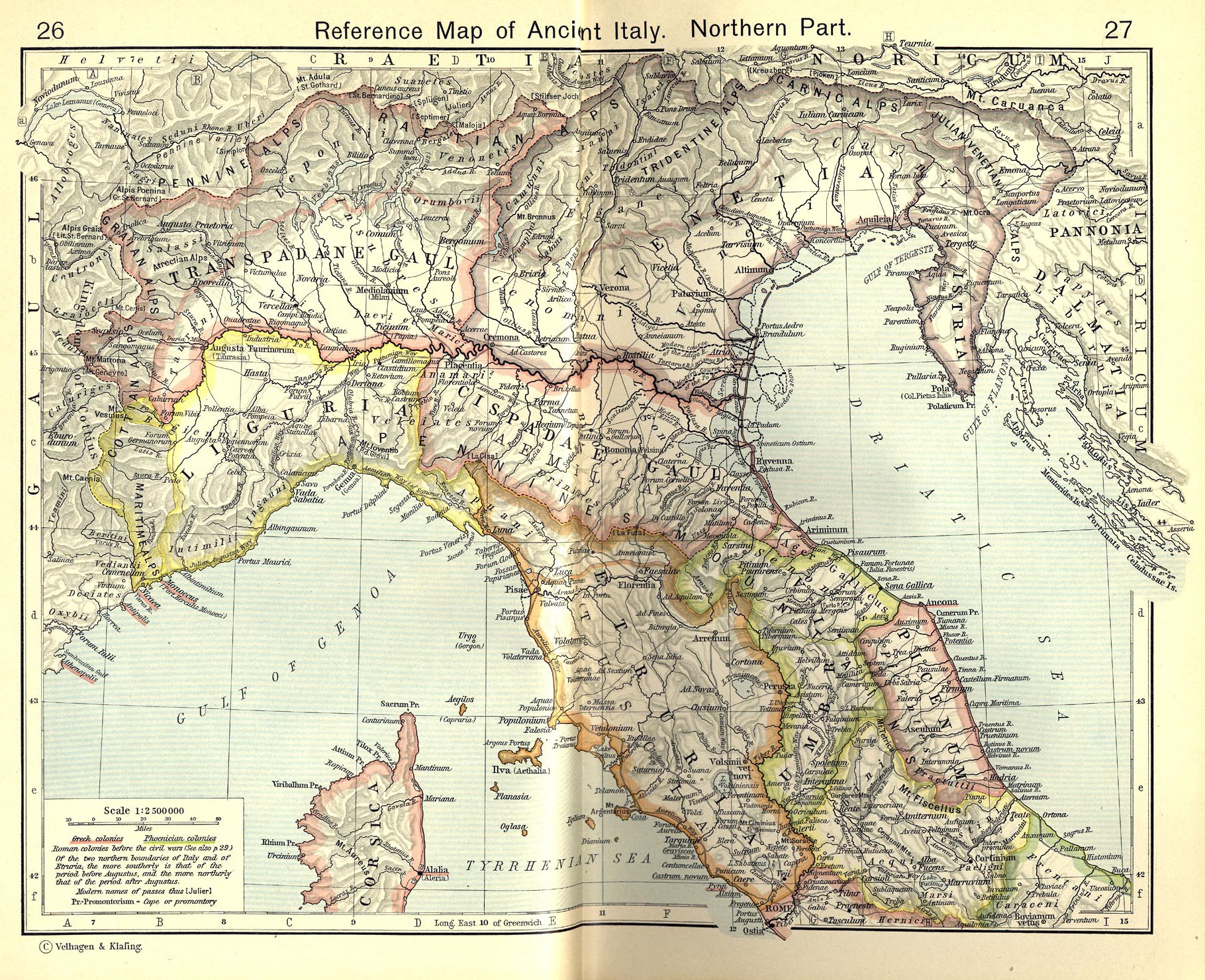
The Ucennii, Ucenni or Iconii were a Gallic tribe dwelling in the Romanche valley, in the Alps, during the Iron Age. Name They are mentioned as ''Ucenni'' (var. ''uceni'', ''ucermi'') by Pliny (1st c. AD) and on the Tropaeum Alpium, Pliny. ''Naturalis Historia'', 3:20; CIL 5:7817. as ''Ucennos'' (var. , , ) by Florus., s.v. ''Ucennii''. The form (Ἰκόνιοι) given by Strabo (early 1st c. AD) is most likely a variant of the ethnic name. The meaning of the name remains obscure, although it is most likely of Celtic origin. It can be compared with the toponym ''Ucena'' in Galatia. Geography The Ucenni lived in the Romanche valley, in the region of Oisans. Their territory was located south of the Graioceli, west of the Belaci, Segovii and Brigianii, north of the Tricorii, and west of the Vertamocorii and Allobroges., Map 17: Lugdunum. Settlements are known at Catorissium (Le Bourg-d'Oisans), Mellosedum (Mont-de-Lans), and Durotincum (near La Grave and Villar-d'Arêne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Segovii
The Segovii (Gaulish: *''Segouioi'', 'the victorious, powerful') were a Gallic tribe dwelling in the Alpes Cottiae, around present-day Cesana Torinese and Montgenèvre, during the Iron Age. Name They are attested as ''Segoviorum'' on the Arch of Susa., s.v. ''Segovii''. The ethnonym ''Segovii'' is a latinized form of Gaulish *''Segouioi''. It derives from the root ''sego''-, meaning 'victory, force'. It is comparable with the feminine forms ''Segouia'' (Segovia) and ''Segauias'' (now Göfis). Geography The Segovii dwelled around the towns of Gaesao/Tyrium (modern Cesana Torinese) and Druantium (Montgenèvre; also named *''Alpis Cottia'' and ''Summae Alpes''). Their territory was located south of the Belaci, north of the Brigianii and Quariates, and east of the Ucenni., Map 17: Lugdunum. The settlement of Ad Fines (modern Fenils) may have been the border between the territories of the Segovii and Belaci. History They are mentioned on the Arch of Susa, erected by Cott ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropaeum Alpium
The Tropaeum Alpium (Latin 'Trophy of the Alps', French: ''Trophée des Alpes''), is a Roman trophy (''tropaeum'') celebrating the emperor Augustus's decisive victory over the tribes who populated the Alps. The monument's ruins are in La Turbie (France), a few kilometers from the Principality of Monaco. Construction The Trophy was built c. 6 BC in honor of Augustus to celebrate his definitive victory over the 45 tribes who populated the Alps. The Alpine populations were defeated during the military campaign to subdue the Alps conducted by the Romans between 16 and 7 BC. The monument was built of stone from the Roman quarry located about 800 metres away, where traces of sections of carved columns are visible in the stone. The monument as partially restored is 35 meters high. When built, according to the architect, the base measured 35 meters in length, the first platform 12 meters in height, and the rotunda of 24 columns with its statue of an enthroned Augustus is 49 metres hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allobroges
The Allobroges (Gaulish: *''Allobrogis'', 'foreigner, exiled'; grc, Ἀλλοβρίγων, Ἀλλόβριγες) were a Gallic people dwelling in a large territory between the Rhône river and the Alps during the Iron Age and the Roman period. The Allobroges came relatively late to Gaul compared to most other tribes of Gallia Narbonensis; they first appear in historical records in connection with Hannibal's crossing of the Alps in 218 BC. Their territory was subsequently annexed to Rome in 121 BC by Gnaeus Domitius Ahenobarbus and Quintus Fabius Maximus Allobrogicus. An attempted revolt was crushed by in 61 BC. However, they had rejected the second Catilinarian conspiracy in 63 BC. During the Gallic Wars, the Allobroges did not side with Vercingetorix at the Battle of Alesia in 52 BC. Name Attestations They are mentioned as ''A̓llobrígōn'' ( Ἀλλοβρίγων) by Polybius (2nd c. BC) and Strabo (early 1st c. AD),Polybius. ''Historíai'3:49–51 Strabo4:1:11 [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graioceli
The Graioceli were a small Gallic tribe dwelling in the valley of Maurienne, in the modern region of Savoie, during the Iron Age. Name They are mentioned as ''Graioceli'' (var. ''graiocaeli, gaioceli'') by Caesar (mid-1st c. BC)., s.v. ''Graioceli''. The etymology of the ethnonym ''Graioceli'' remains unclear. It possibly contains a divine name *''Graios'' (found in ''Herculi''/''Herculeio Graio'') attached to the Gaulish root ''ocel''-, meaning 'peak, summit, promontory'. The same stem is also present in the name of the ''Alpes Graiae''. Geography The Graioceli dwelled in the Maurienne Valley, around the modern towns of Saint-Jean-de-Maurienne and Saint-Jean-d'Arves. Their territory was located the southeast of the Allobroges, south of the Ceutrones, north of the Ucennii, and west of the Medulli., Map 17: Lugdunum. History In the mid-first century BC, the Graioceli are mentioned by Julius Caesar as a tribe hostile to Rome. In what appears to be a concerted attack, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gauls
The Gauls ( la, Galli; grc, Γαλάται, ''Galátai'') were a group of Celtic peoples of mainland Europe in the Iron Age and the Roman period (roughly 5th century BC to 5th century AD). Their homeland was known as Gaul (''Gallia''). They spoke Gaulish, a continental Celtic language. The Gauls emerged around the 5th century BC as bearers of La Tène culture north and west of the Alps. By the 4th century BC, they were spread over much of what is now France, Belgium, Switzerland, Southern Germany, Austria, and the Czech Republic, by virtue of controlling the trade routes along the river systems of the Rhône, Seine, Rhine, and Danube. They reached the peak of their power in the 3rd century BC. During the 4th and 3rd centuries BC, the Gauls expanded into Northern Italy ( Cisalpine Gaul), leading to the Roman–Gallic wars, and into the Balkans, leading to war with the Greeks. These latter Gauls eventually settled in Anatolia, becoming known as Galatians. After the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Villar-d'Arêne
Villar-d'Arêne (; oc, Vilars d'Arena) is a commune in the Hautes-Alpes department in southeastern France, between Grenoble and Briançon. It is in the French Alps, in Massif des Écrins. Near this village located in the Romanche valley, there is La Grave and Col du Lautaret. The access of the valley and its communes is departmental route 1091 (ex- national route 91) (Grenoble – Le Bourg-d'Oisans – Briançon). Population Sights *mountains as Massif des Ecrins, La Meije *Écrins National Park *Jardin botanique alpin du Lautaret *Tradition of boiled bread ("pain bouilli" or "pain noir"), a rye bread made with boiled water, in village's oven See also *Communes of the Hautes-Alpes department The following is a list of the 162 communes of the Hautes-Alpes department of France. The communes cooperate in the following intercommunalities (as of 2020): [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Grave
La Grave (; oc, La Grava) is a commune in the Hautes-Alpes department in southeastern France. It is a small ski resort in the French Alps, dominated by La Meije (3982 m). It was the birthplace of Nicolas de Nicolay; adventurer and Geographer Ordinary to Henry II of France. Skiing The area is unpisted and although patrolled, has no formal avalanche control. The area is dangerous to ski unless supported by a guide, including much glacier travel at the very top. La Grave is visited by off-piste and extreme skiers. The vertical drop totals 2,150 metres, although it is possible to ski below the resort to the road and increase the vertical descent to 2,300 metres. Mechanical access to the mountain is limited to a closed, two-stage, pulse gondola system. The first lift starts at 1,450 metres, runs through one intermediate station (known as P1 at 1,800 metres) then terminates at Peyrou d'Amont (2,400 metres). The second stage of the gondola runs directly from Peyrou d'Amont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mont-de-Lans
Mont-de-Lans () is a former commune in the Isère department in southeastern France. On 1 January 2017, it was merged into the new commune Les Deux Alpes. 28 September 2016 Population See also *Communes of the Isère department
The following is a list of the 512 communes in the French department of Isère.
The communes cooperate in the following intercommunalities (as of 2020):
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Le Bourg-d'Oisans
Le Bourg-d'Oisans () is a commune in the Isère department in southeastern France. It is located in the Oisans region of the French Alps. Le Bourg-d'Oisans is located in the valley of the Romanche river, on the road from Grenoble to Briançon, and on the south side of the Col de la Croix de Fer. It is often on the route of the Tour de France, as the town sits at the base of the road climbing to Alpe d'Huez with 21 hairpin bends. It is surrounded by several well-known mountain resorts, including the Alpe d'Huez and Les Deux Alpes. The Écrins National Park lies to the southeast of Le Bourg-d'Oisans. Population See also *Communes of the Isère department * Livet-et-Gavet *Alpe d'Huez L'Alpe d'Huez () is a ski resort in southeastern France at . It is a mountain pasture in the Central French Western Alps, in the commune of Huez, which is part of the department of Isère in the region of Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes. It is part of ... References Communes of Isèr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertamocorii (Narbonensis)
The Vertamocorii (Gaulish: *''Wertamocorī'') were a Celtic people that lived in Cisalpine Gaul around Novara, in Eastern Piedmont (Italy). The Vertamocorii are reported by Pliny in the third book of Naturalis Historia, where they are said to be the founders of the city of Novara: and indicates their Gaulish origin (the Vocontii were a people of Gallia Narbonensis) and not Ligurian. See also * Ancient peoples of Italy This list of ancient peoples living in Italy summarises groupings existing before and during the Roman expansion and conquest of Italy. Many of the names are either scholarly inventions or exonyms assigned by the ancient writers of works in anc ... References External links Teuta Vertamocori - Group of historical reconstruction from Novara Historical Celtic peoples Gauls Ancient peoples of Italy Novara {{Italy-hist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brigianii
The Brigianii (Gaulish: *''Brigianioi'') were a Gallic tribe dwelling around present-day Briançon during the Iron Age and the Roman period. Name They are mentioned as ''Brigianii'' by Pliny (1st c. AD), and as ''Brigiani'', ''Brigantionis'' and ''Bricianiorum'' on inscriptions. CIL 5:7817, 12:94, 80., s.v. ''Brigianii''. Their name may be based on the Gaulish root ''brig''- ('high, elevated'), or on ''brīgo''- ('might, strength'). Geography The Gallitae lived in the region of , in the center of the Cottian Kingdom. Their territory was located north of the Caturiges, west of the Quariates, east of the Tricorii, south of the Segovii., Map 17: Lugdunum. Their chief town was known as Brigantio (modern Briançon Briançon (, ) is the sole subprefecture of the Hautes-Alpes department in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region in Southeastern France. It is the highest city in France at an altitude of , based on the national definition as a community cont ...), meaning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |