|
USS Savo Island
USS ''Savo Island'' (CVE-78) was the twenty-fourth of fifty s built for the United States Navy during World War II. She was named to memorialize the U.S. casualties of the Battle of Savo Island, which was fought as part of the Guadalcanal campaign. The ship was launched in December 1943, commissioned in February 1944, and served as a frontline carrier throughout the Mariana and Palau Islands campaign and the Philippines campaign. During the Battle of Okinawa, she provided air cover for the replenishment carrier fleet. Postwar, she participated in Operation Magic Carpet, repatriating U.S. servicemen from throughout the Pacific. She was decommissioned in December 1946, when she was mothballed in the Atlantic Reserve Fleet. Ultimately, she was sold for scrapping in February 1960. Design and description ''Savo Island'' was a ''Casablanca''-class escort carrier, the most numerous type of aircraft carriers ever built, and designed specifically to be mass-produced using prefabric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SO3C Seamew
The Curtiss SO3C Seamew was developed by the Curtiss-Wright Corporation as a replacement for the SOC Seagull as the United States Navy's standard floatplane scout. Curtiss named the SO3C the ''Seamew'' but in 1941 the US Navy began calling it by the name ''Seagull'', the same name as the aircraft it replaced (the Curtiss SOC a biplane type), causing some confusion. The British Royal Navy kept the Curtiss name, ''Seamew'', for the SO3Cs that they ordered. One of the US Navy's main design requirements was that the SOC Seagull's replacement had to be able to operate both from ocean vessels with a single center float and from land bases with the float replaced by a wheeled landing gear. Design and development From the time it entered service the SO3C suffered two serious flaws: inflight stability problems and problems with the unique Ranger air-cooled, inverted V-shaped inline engine. The stability problem was mostly resolved with the introduction of upturned wingtips and a larger r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mariana And Palau Islands Campaign
The Mariana and Palau Islands campaign, also known as Operation Forager, was an offensive launched by United States forces against Imperial Japanese forces in the Mariana Islands and Palau in the Pacific Ocean between June and November 1944 during the Pacific War. The United States offensive, under the overall command of Chester W. Nimitz, followed the Gilbert and Marshall Islands campaign and was intended to neutralize Japanese bases in the central Pacific, support the Allied drive to retake the Philippines, and provide bases for a strategic bombing campaign against Japan. The United States invasion force was supported by a massive combat force. The Fifth Fleet was commanded by Admiral Raymond A. Spruance. Task Force 58, commanded by Vice Admiral Marc Mitscher, consisted of 15 carriers, 7 battleships, 11 cruisers, 86 destroyers and over 900 planes. The invasion force, commanded by Vice Admiral Richmond K. Turner, consisted of 56 attack transports, 84 landing craft and ov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
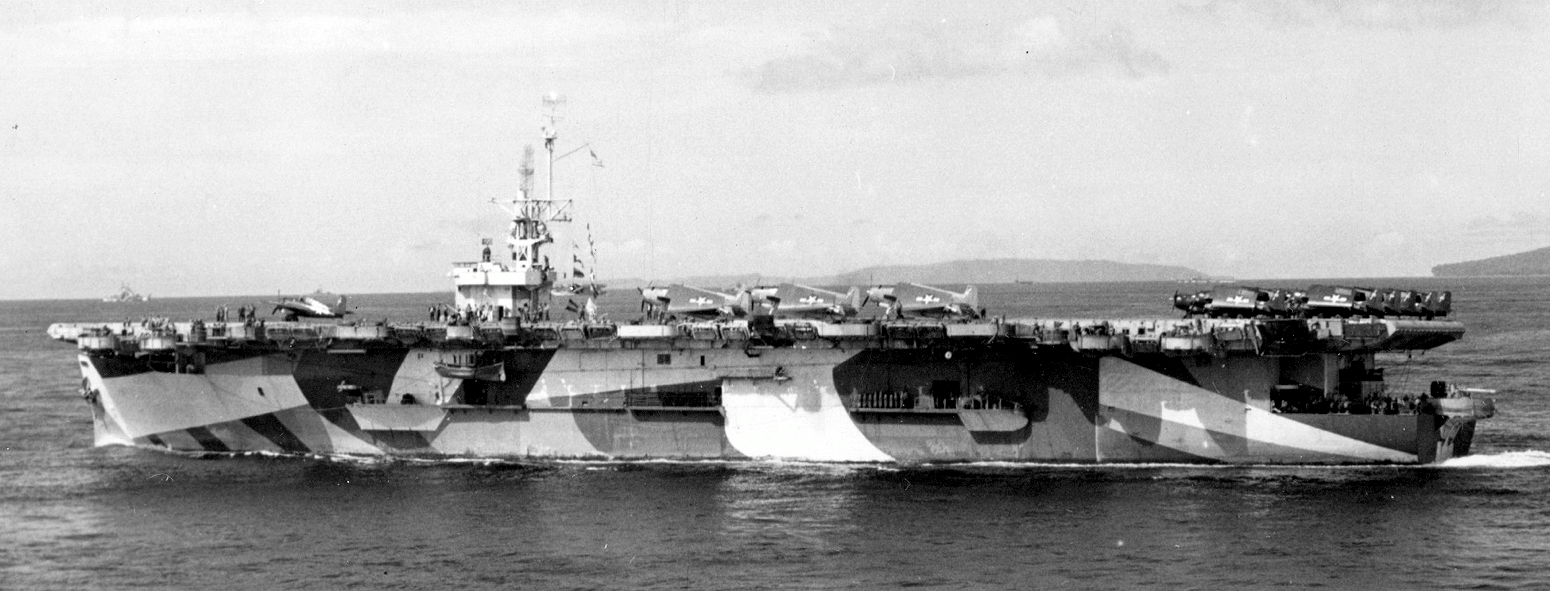
Inboard And Outboard Profiles Of A Casablanca-class Escort Carrier, 1946
An inboard motor is a marine propulsion system for boats. As opposed to an outboard motor where an engine is mounted outside the hull of the craft, an ''inboard motor'' is an engine enclosed within the hull of the boat, usually connected to a propulsion screw by a driveshaft. In international shipping the marine diesel engines are the largest most powerful engines ever produced. History The first marine craft to utilize inboard motors were steam engines going back to 1805 and the ''Clermont'' and the '' Charlotte Dundas''. Harbour tugs, and small steam launches had inboard steam engines. In the 1880s the naphtha engine made its appearance and a few boat engines appeared. Such engines had low power and high fuel consumption. The gasoline (petrol) engine pioneer Gottlieb Daimler and Maybach built a four-cycle boat engine and tested it in 1887 on the Neckar River. Sintz in America built several commercially available engines from 1893. Sizes Inboard motors may be of seve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ship Breaking
Ship-breaking (also known as ship recycling, ship demolition, ship dismantling, or ship cracking) is a type of ship disposal involving the breaking up of ships for either a source of parts, which can be sold for re-use, or for the extraction of raw materials, chiefly scrap. Modern ships have a lifespan of 25 to 30 years before corrosion, metal fatigue and a lack of parts render them uneconomical to operate. Ship-breaking allows the materials from the ship, especially steel, to be recycled and made into new products. This lowers the demand for mined iron ore and reduces energy use in the steelmaking process. Fixtures and other equipment on board the vessels can also be reused. While ship-breaking is sustainable, there are concerns about the use by poorer countries without stringent environmental legislation. It is also labour-intensive, and considered one of the world's most dangerous industries. In 2012, roughly 1,250 ocean ships were broken down, and their average age was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reserve Fleet
A reserve fleet is a collection of naval vessels of all types that are fully equipped for service but are not currently needed; they are partially or fully decommissioned. A reserve fleet is informally said to be "in mothballs" or "mothballed"; an equivalent expression in unofficial modern US naval usage is "ghost fleet". In earlier times, especially in British usage, the ships were said to be "laid up in ordinary". Overview Such ships are held in reserve against a time when it may be necessary to call them back into service. They are usually tied up in backwater areas near naval bases or shipyards in order to speed the reactivation process. They may be modified for storage during such a period, for instance by having rust-prone areas sealed off or wrapped in plastic or, in the case of sailing warships, the masts removed. While being held in the reserve fleet, ships typically have a minimal crew (known informally as a skeleton crew) to ensure that they stay in somewhat usable co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ship Commissioning
Ship commissioning is the act or ceremony of placing a ship in active service and may be regarded as a particular application of the general concepts and practices of project commissioning. The term is most commonly applied to placing a warship in active duty with its country's military forces. The ceremonies involved are often rooted in centuries-old naval tradition. Ship naming and launching endow a ship hull with her identity, but many milestones remain before she is completed and considered ready to be designated a commissioned ship. The engineering plant, weapon and electronic systems, galley, and other equipment required to transform the new hull into an operating and habitable warship are installed and tested. The prospective commanding officer, ship's officers, the petty officers, and seamen who will form the crew report for training and familiarization with their new ship. Before commissioning, the new ship undergoes sea trials to identify any deficiencies needing corre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
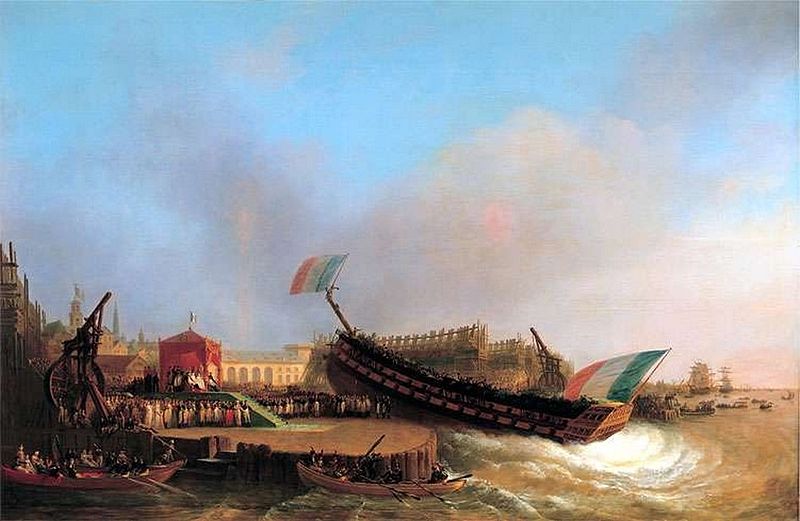
Ceremonial Ship Launching
Ceremonial ship launching involves the performance of ceremonies associated with the process of transferring a vessel to the water. It is a nautical tradition in many cultures, dating back thousands of years, to accompany the physical process with ceremonies which have been observed as public celebration and a solemn blessing, usually but not always, in association with the launch itself. Ship launching imposes stresses on the ship not met during normal operation and, in addition to the size and weight of the vessel, represents a considerable engineering challenge as well as a public spectacle. The process also involves many traditions intended to invite good luck, such as christening by breaking a sacrificial bottle of champagne over the bow as the ship is named aloud and launched. Methods There are three principal methods of conveying a new ship from building site to water, only two of which are called "launching". The oldest, most familiar, and most widely used is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guadalcanal Campaign
The Guadalcanal campaign, also known as the Battle of Guadalcanal and codenamed Operation Watchtower by American forces, was a military campaign fought between 7 August 1942 and 9 February 1943 on and around the island of Guadalcanal in the Pacific theater of World War II. It was the first major land offensive by Allied forces against the Empire of Japan. On 7 August 1942, Allied forces, predominantly United States Marines, landed on Guadalcanal, Tulagi, and Florida in the southern Solomon Islands, with the objective of using Guadalcanal and Tulagi as bases in supporting a campaign to eventually capture or neutralize the major Japanese base at Rabaul on New Britain. The Japanese defenders, who had occupied those islands since May 1942, were outnumbered and overwhelmed by the Allies, who captured Tulagi and Florida, as well as the airfield – later named Henderson Field – that was under construction on Guadalcanal. Surprised by the Allied offensive, the Japanese made ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage of its active battle fleet alone exceeding the next 13 navies combined, including 11 allies or partner nations of the United States as of 2015. It has the highest combined battle fleet tonnage (4,635,628 tonnes as of 2019) and the world's largest aircraft carrier fleet, with eleven in service, two new carriers under construction, and five other carriers planned. With 336,978 personnel on active duty and 101,583 in the Ready Reserve, the United States Navy is the third largest of the United States military service branches in terms of personnel. It has 290 deployable combat vessels and more than 2,623 operational aircraft . The United States Navy traces its origins to the Continental Navy, which was established during the American Revo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Magic Carpet
Operation Magic Carpet was the post-World War II operation by the War Shipping Administration to repatriate over eight million American military personnel from the European, Pacific, and Asian theaters. Hundreds of Liberty ships, Victory ships, and troop transports began repatriating soldiers from Europe in June 1945. Beginning in October 1945, over 370 navy ships were used for repatriation duties in the Pacific. Warships, such as aircraft carriers, battleships, hospital ships, and large numbers of assault transports were used. The European phase of Operation Magic Carpet concluded in February 1946 while the Pacific phase continued until September 1946. Planning As early as mid-1943, the United States Army had recognized that, once the war was over, bringing the troops home would be a priority. More than 16 million Americans were in uniform; and more than eight million of them were scattered across all theaters of war worldwide. Army Chief of Staff General George Marshall es ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Okinawa
The , codenamed Operation Iceberg, was a major battle of the Pacific War fought on the island of Okinawa by United States Army (USA) and United States Marine Corps (USMC) forces against the Imperial Japanese Army (IJA). The initial invasion of Okinawa on 1 April 1945 was the largest amphibious assault in the Pacific Theater of World War II. The Kerama Islands surrounding Okinawa were preemptively captured on 26 March, (L-6) by the 77th Infantry Division. The 82-day battle lasted from 1 April until 22 June 1945. After a long campaign of island hopping, the Allies were planning to use Kadena Air Base on the large island of Okinawa as a base for Operation Downfall, the planned invasion of the Japanese home islands, away. The United States created the Tenth Army, a cross-branch force consisting of the U.S. Army 7th, 27th, 77th and 96th Infantry Divisions with the USMC 1st, 2nd, and 6th Marine Divisions, to fight on the island. The Tenth was unique in that it had its own Tact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)
_underway_c1947.jpg)
_underway_2009.jpg)


