|
USS Gertrude (1863)
USS ''Gertrude'' was the British blockade-running steamship ''Gertrude'' captured by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was placed in service by the Navy as a gunboat and assigned to patrol the southern coast of the United States for ships attempting to run the Union blockade of Southern ports. She was later the American merchant ship ''Gussie Telfair'' until wrecked in 1880. Service history The iron-hulled steamer ''Gertrude'' was built in Whiteinch, Glasgow, Scotland as Yard No.100 at the Clydeholm yard of Barclay, Curle & Company as an American Civil War blockade runner and launched on 25 November 1862. Along with her sistership '' Emma'', she was built for Thomas Stirling Begbie, a London shipowner and merchant. ''Gertrude'' was measured as 278 grt and 191 nrt, with dimensions 164.4 feet length overall, 21.2 feet beam and 12.2 feet depth. She was powered by 2-cylinder oscillating engine of 100nhp, made by John Scott's Greenock Foundry Company, Greenock. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barclay Curle
Seawind Barclay Curle is a British shipbuilding company. History The company was founded by Robert Barclay at Stobcross in Glasgow, Scotland during 1818.Grace's Guide: Barclay Curle In 1862, the company built a large engineering works at Stobcross in Glasgow. In 1876, the company moved their yard down the river to . It was incorporated in 1884 as ''Barclay Curle''. In 1912, Barclay Curle acquired the nearby Elderslie Shipyard in from John Shearer & Sons, to take the excess orders that the firm's existing Clydeholm yard in Whiteinch could not hand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Scott (shipbuilder)
John Scott (5 September 1830, Greenock – 19 May 1903, Ayrshire) was a Scottish engineer and shipbuilder. Life He was born at Greenock on 5 September 1830, and was eldest son in the family of five sons and six daughters of Charles Cuningham Scott of Halkshill, Largs, Ayrshire, and his wife, Helen Rankin. His father was partner of Messrs. Scott & Co., a leading firm of shipbuilders on the Clyde, which was founded by an ancestor in 1710. After education at Edinburgh Academy and then studying at Glasgow University, John served an apprenticeship to his father, and, on attaining his majority, was admitted to partnership in the firm. In 1868, he became its responsible head, in association with his brother, Robert Sinclair Scott, and directed its affairs for thirty-five years. The ships constructed in the Scott yard during his charge of it included many notable vessels for the mercantile marine as well as for the British navy ; others, such as the battleships ''HMS Canopus (1897 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2020, it is the second-largest U.S. state by both List of U.S. states and territories by area, area (after Alaska) and List of U.S. states and territories by population, population (after California). Texas shares borders with the states of Louisiana to the east, Arkansas to the northeast, Oklahoma to the north, New Mexico to the west, and the Mexico, Mexican States of Mexico, states of Chihuahua (state), Chihuahua, Coahuila, Nuevo León, and Tamaulipas to the south and southwest; and has a coastline with the Gulf of Mexico to the southeast. Houston is the List of cities in Texas by population, most populous city in Texas and the List of United States cities by population, fourth-largest in the U.S., while San Antonio is the second most pop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
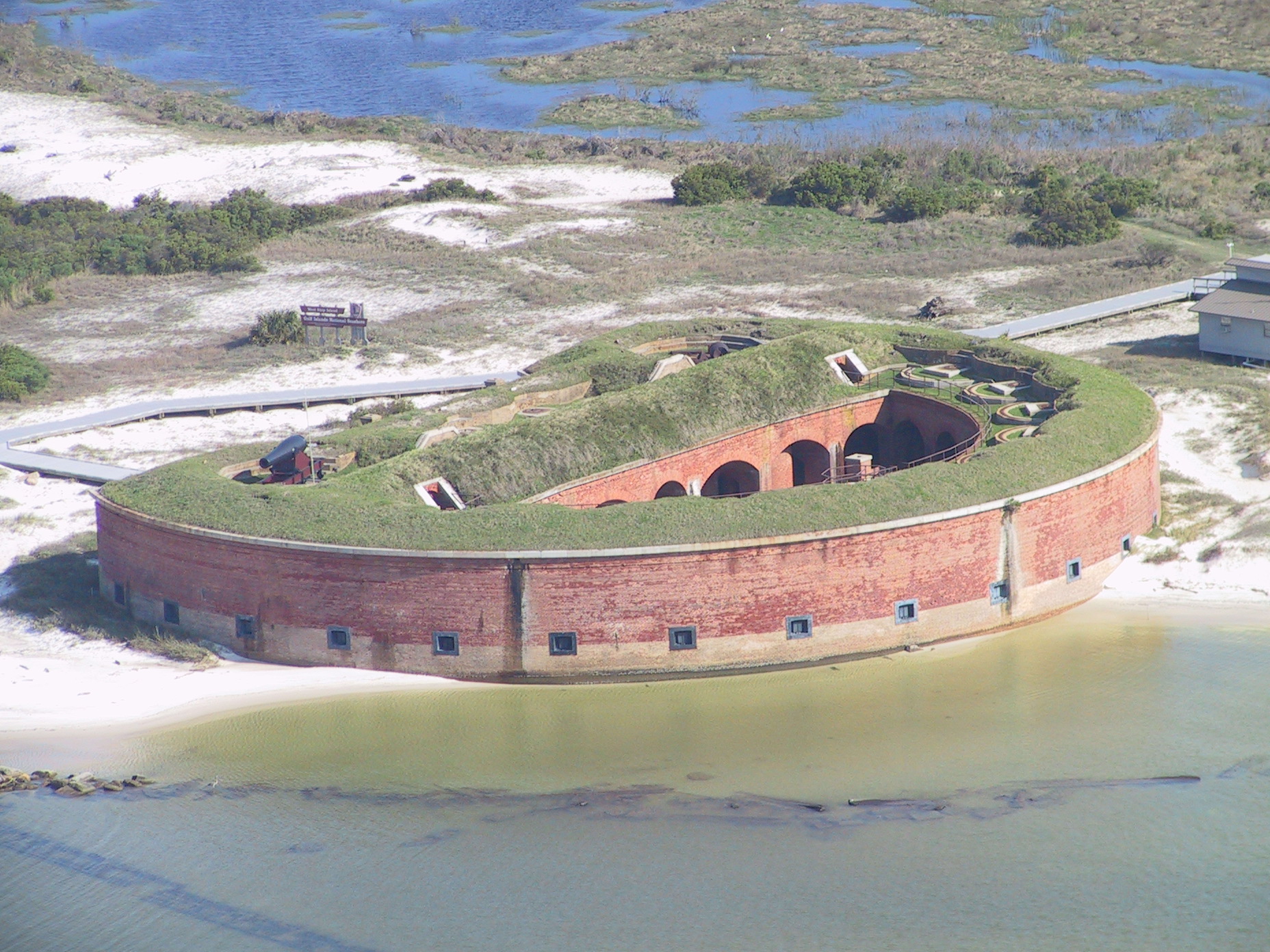
Ship Island, Mississippi
Ship Island is a barrier island off the Gulf Coast of Mississippi, one of the Mississippi–Alabama barrier islands. Hurricane Camille split the island into two separate islands (West Ship Island and East Ship Island) in 1969. In early 2019, the US Army Corps of Engineers completed the first stage of a project rejoining the two islands and recreating one Ship Island. Ship Island is the site of Fort Massachusetts (built 1859–66), as a Third System fortification. Part of the island is included in the Gulf Islands National Seashore. History Having the only deep-water harbor between Mobile Bay and the Mississippi River, the island served as a vital anchorage for ships bearing explorers, colonists, sailors, soldiers, defenders and invaders. The French, Spanish, British, Confederate and Union flags have all flown over Ship Island. French explorer Pierre Le Moyne d'Iberville charted Ship Island on 10 February 1699, "Hancock County, Then and Now", Hancock County Histor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Orleans, Louisiana
New Orleans ( , ,New Orleans Merriam-Webster. ; french: La Nouvelle-Orléans , es, Nueva Orleans) is a Consolidated city-county, consolidated city-parish located along the Mississippi River in the southeastern region of the U.S. state of Louisiana. With a population of 383,997 according to the 2020 U.S. census, it is the List of municipalities in Louisiana, most populous city in Louisiana and the twelfth-most populous city in the southeastern United States. Serving as a List of ports in the United States, major port, New Orleans is considered an economic and commercial hub for the broader Gulf Coast of the United States, Gulf Coast region of the United States. New Orleans is world-renowned for its Music of New Orleans, distinctive music, Louisiana Creole cuisine, Creole cuisine, New Orleans English, uniq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mobile, Alabama
Mobile ( , ) is a city and the county seat of Mobile County, Alabama, United States. The population within the city limits was 187,041 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, down from 195,111 at the 2010 United States census, 2010 census. It is the fourth-most-populous city in Alabama, after Huntsville, Alabama, Huntsville, Birmingham, Alabama, Birmingham, and Montgomery, Alabama, Montgomery. Alabama's only saltwater port, Mobile is located on the Mobile River at the head of Mobile Bay on the north-central Gulf Coast. The Port of Mobile has always played a key role in the economic health of the city, beginning with the settlement as an important trading center between the French colonization of the Americas, French colonists and Native Americans in the United States, Native Americans, down to its current role as the 12th-largest port in the United States.Drechsel, Emanuel. ''Mobilian Jargon: Linguistic and Sociohistorical Aspects of a Native American Pidgin''. New York: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Farragut
David Glasgow Farragut (; also spelled Glascoe; July 5, 1801 – August 14, 1870) was a flag officer of the United States Navy during the American Civil War. He was the first rear admiral, vice admiral, and admiral in the United States Navy. Farragut, 1879, p. 3 Hickman, 2010, p. 216 He is remembered for his order at the Battle of Mobile Bay, usually paraphrased as "Damn the torpedoes, full speed ahead" in U.S. Navy tradition. Stein, 2005, p. 5 Spears, 1905, p. 328 Born near Knoxville, Tennessee, Farragut was fostered by naval officer David Porter after the death of his mother. When he was 11 years old, Farragut served in the War of 1812 under the command of his adoptive father. He received his first command in 1823, at the age of 22, and went on to participate in anti-piracy operations in the Caribbean Sea. He then served in the Mexican–American War under the command of Matthew C. Perry, participating in the blockade of Tuxpan. After the war, he oversaw the construction of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Gulf Blockading Squadron
The Union blockade in the American Civil War was a naval strategy by the United States to prevent the Confederate States of America, Confederacy from trading. The blockade was proclaimed by President Abraham Lincoln in April 1861, and required the monitoring of of Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic and Gulf of Mexico, Gulf coastline, including 12 major ports, notably New Orleans and Mobile, Alabama, Mobile. Those Blockade runners of the American Civil War, blockade runners fast enough to evade the Union Navy could carry only a small fraction of the supplies needed. They were operated largely by foreign citizens, making use of neutral ports such as Havana, Cuba, Havana, Nassau, Bahamas, Nassau and Bermuda. The Union commissioned around 500 ships, which destroyed or captured about 1,500 blockade runners over the course of the war. Proclamation of blockade and legal implications On April 19, 1861, President Lincoln issued a ''Proclamation of Blockade Against Southern Ports'': Whereas an in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New York Navy Yard
The Brooklyn Navy Yard (originally known as the New York Navy Yard) is a shipyard and industrial complex located in northwest Brooklyn in New York City, New York (state), New York. The Navy Yard is located on the East River in Wallabout Bay, a semicircular bend of the river across from Lower East Side#Corlears Hook, Corlears Hook in Manhattan. It is bounded by Navy Street to the west, Flushing Avenue to the south, Kent Avenue to the east, and the East River on the north. The site, which covers , is listed on the National Register of Historic Places. The Brooklyn Navy Yard was established in 1801. From the early 1810s through the 1960s, it was an active shipyard for the United States Navy, and was also known as the United States Naval Shipyard, Brooklyn and New York Naval Shipyard at various points in its history. The Brooklyn Navy Yard produced wooden ships for the U.S. Navy through the 1870s, and steel ships after the American Civil War in the 1860s. The Brooklyn Navy Yard has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prize Court
A prize court is a court (or even a single individual, such as an ambassador or consul) authorized to consider whether prizes have been lawfully captured, typically whether a ship has been lawfully captured or seized in time of war or under the terms of the seizing ship's letters of marque and reprisal. A prize court may order the sale or destruction of the seized ship, and the distribution of any proceeds to the captain and crew of the seizing ship. A prize court may also order the return of a seized ship to its owners if the seizure was unlawful, such as if seized from a country which had proclaimed its neutrality. History/jurisdiction in various countries Prize courts were common in the 17th through 19th centuries, during times of American or European naval warfare. The United States in 1780 established the Federal Court of Appeals in Cases of Capture to hear appeals of prize cases from state prize courts; this court was ended in 1787, after conclusion of the war. Under cur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the List of United States cities by population density, most densely populated major city in the United States, and is more than twice as populous as second-place Los Angeles. New York City lies at the southern tip of New York (state), New York State, and constitutes the geographical and demographic center of both the Northeast megalopolis and the New York metropolitan area, the largest metropolitan area in the world by urban area, urban landmass. With over 20.1 million people in its metropolitan statistical area and 23.5 million in its combined statistical area as of 2020, New York is one of the world's most populous Megacity, megacities, and over 58 million people live within of the city. New York City is a global city, global Culture of New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eleuthera Island
Eleuthera () refers both to a single island in the archipelagic state of The Commonwealth of the Bahamas and to its associated group of smaller islands. Eleuthera forms a part of the Great Bahama Bank. The island of Eleuthera incorporates the smaller Harbour Island. "Eleuthera" derives from the feminine form of the Greek adjective ἐλεύθερος (''eleútheros''), meaning "free". Known in the 17th century as Cigateo, it lies 80 km (50 miles) east of Nassau. It is long and thin—180 km (110 miles) long and in places little more than 1.6 km (1.0 mile) wide. Its eastern side faces the Atlantic Ocean, and its western side faces the Great Bahama Bank. The topography of the island varies from wide rolling pink sand beaches to large outcrops of ancient coral reefs, and its population is approximately 11,000. The principal economy of the island is tourism. Geography and wildlife The name Eleuthera refers both to the single Bahamian island and is also used to refer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






_(14762199554).jpg)

