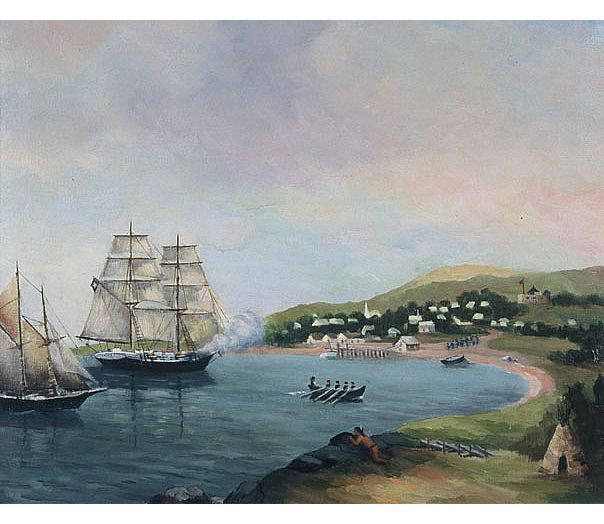|
USS Delaware (1776)
USS ''Delaware'' was a 24-gun sailing frigate of the United States Navy that had a short career in the American Revolutionary War as the British Royal Navy captured her in 1777. The Royal Navy took her in as an "armed ship", and later classed her a sixth rate. The Royal Navy sold her in 1783. British owners named her ''United States'' and then French interests purchased her and named her ''Dauphin''. She spent some years as a whaler and then in March 1795 she was converted at Charleston, South Carolina, to French privateer. Her subsequent fate is unclear. US Navy She was built under the 13 December 1775 order of the Continental Congress in the yard of Warwick Coates of Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, under the direction of the Marine Committee. Upon her launching in July 1776, Captain C. Alexander took command. ''Delaware'' served in the Delaware River, joining with Commodore John Hazelwood's Pennsylvania state ships in operations that delayed the British Fleet in approaching P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warwick Coates
Warwick ( ) is a market town, civil parish and the county town of Warwickshire in the Warwick District in England, adjacent to the River Avon. It is south of Coventry, and south-east of Birmingham. It is adjoined with Leamington Spa and Whitnash. It has ancient origins and an array of historic buildings, notably from the Medieval, Stuart and Georgian eras. It was a major fortified settlement from the early Middle Ages, the most notable relic of this period being Warwick Castle, a major tourist attraction. Much was destroyed in the Great Fire of Warwick in 1694 and then rebuilt with fine 18th century buildings, such as the Collegiate Church of St Mary and the Shire Hall. The population was estimated at 37,267 at the 2021 Census. History Neolithic Human activity on the site dates back to the Neolithic, when it appears there was a sizable settlement on the Warwick hilltop. Artifacts found include more than 30 shallow pits containing early Neolithic flints and pottery and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Hazelwood
John Hazelwood (1726 – March 1, 1800) served as a Commodore in the Pennsylvania Navy and Continental Navy and was among the most noted naval officers during the American Revolutionary War. Born in England about 1726, he became a mariner and settled in Philadelphia early in life, became married and had several children. Promoted to Commodore during the Philadelphia campaign, he also became commander of Fort Mifflin while it was under siege by the British. Throughout the campaign Hazelwood and General Washington were in frequent communication with letters. During the weeks spent engaging the British navy on the Delaware River Hazelwood innovated many naval tactics, kept the British navy at bay for weeks and played a major role in the development of riverine warfare for the American navies. Recommended by Washington and his council, Hazelwood was chosen to lead a large fleet of American ships and riverboats up river to safety. For his bravery and distinguished service Congres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simon & Schuster
Simon & Schuster () is an American publishing company and a subsidiary of Paramount Global. It was founded in New York City on January 2, 1924 by Richard L. Simon and M. Lincoln Schuster. As of 2016, Simon & Schuster was the third largest publisher in the United States, publishing 2,000 titles annually under 35 different imprints. History Early years In 1924, Richard Simon's aunt, a crossword puzzle enthusiast, asked whether there was a book of ''New York World'' crossword puzzles, which were very popular at the time. After discovering that none had been published, Simon and Max Schuster decided to launch a company to exploit the opportunity.Frederick Lewis Allen, ''Only Yesterday: An Informal History of the 1920s'', p. 165. . At the time, Simon was a piano salesman and Schuster was editor of an automotive trade magazine. They pooled , equivalent to $ today, to start a company that published crossword puzzles. The new publishing house used "fad" publishing to publish bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newspapers
A newspaper is a periodical publication containing written information about current events and is often typed in black ink with a white or gray background. Newspapers can cover a wide variety of fields such as politics, business, sports and art, and often include materials such as opinion columns, weather forecasts, reviews of local services, obituaries, birth notices, crosswords, editorial cartoons, comic strips, and advice columns. Most newspapers are businesses, and they pay their expenses with a mixture of subscription revenue, newsstand sales, and advertising revenue. The journalism organizations that publish newspapers are themselves often metonymically called newspapers. Newspapers have traditionally been published in print (usually on cheap, low-grade paper called newsprint). However, today most newspapers are also published on websites as online newspapers, and some have even abandoned their print versions entirely. Newspapers developed in the 17th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Pennsylvania Gazette
''The Pennsylvania Gazette'' was one of the United States' most prominent newspapers from 1728 until 1800. In the several years leading up to the American Revolution the paper served as a voice for colonial opposition to British colonial rule, especially as it related to the Stamp Act, and the Townshend Acts. History The newspaper was first published in 1728 by Samuel Keimer and was the second newspaper to be published in Pennsylvania under the name ''The Universal Instructor in all Arts and Sciences: and Pennsylvania Gazette'', alluding to Keimer's intention to print out a page of Ephraim Chambers' '' Cyclopaedia, or Universal Dictionary of Arts and Sciences'' in each copy. On October 2, 1729, Samuel Keimer, the owner of the ''Gazette'', fell into debt and before fleeing to Barbados sold the newspaper to Benjamin Franklin and his partner Hugh Meredith, who shortened its name, as well as dropping Keimer's grandiose plan to print out the ''Cyclopaedia''. Franklin not only p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mary Hayley
Mary Hayley née Wilkes (30 October 1728 – 9 May 1808) was an English businesswoman. She parlayed an inheritance from her first husband into a sizeable estate with her second husband. Upon the latter's death, she took over the business and successfully operated a shipping firm from 1781 to 1792 before living out her life in Bath. Hayley was born in 1728 in London to the prosperous distiller Israel Wilkes junior and was a sister to the politician John Wilkes. Kind-hearted but opinionated, she lived an unconventional life and was known for her astute observation and discussion, based upon her wide reading. Refusing to bow to custom, she attended trials at the Old Bailey and travelled throughout Britain to satisfy her wide-ranging curiosity. Marrying a widower, Samuel Storke junior, in 1752, she became a widow within the year with a young step-son. As her husband's sole heir, she inherited his business and soon after his death married his chief clerk, George Hayley. He turned out ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noah Stoddard
Captain Noah Stoddard (1755–1850) of Fairhaven, Massachusetts was an American privateer who distinguished himself during the American Revolution by leading the Raid on Lunenburg (1782). In the raid, Stoddard led four other privateer vessels and attacked the British settlement at Lunenburg, Nova Scotia on July 1, 1782. In Nova Scotia, the assault on Lunenburg was the most spectacular raid of the war.Gwyn, p. 75 American Revolution Stoddard was involved in the first naval engagement of the American Revolution, Battle off Fairhaven, when patriots retrieved two vessels that had been captured by the British sloop of war, ''Falcon'', in Buzzards Bay. On May 14, 1775, American Captain Daniel Egery and Capt. Nathaniel Pope of Fairhaven in the sloop ''Success'' (40 guns, 30 men) retrieved two vessels captured by the British crew of Captain John Linzee (Lindsey), Royal Navy commander of HMS ''Falcon'' (14 guns, 110 men). Stoddard and the others took the first naval prisoners of the war, 13 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sandy Hook, New Jersey
Sandy Hook is a barrier spit in Middletown Township, Monmouth County, New Jersey, United States. The barrier spit, approximately in length and varying from wide, is located at the north end of the Jersey Shore. It encloses the southern entrance of Lower New York Bay south of New York City, protecting it from the open waters of the Atlantic Ocean to the east. The Dutch called the area "Sant Hoek", with the English "Hook" deriving from the Dutch "Hoek" (corner, angle), meaning "spit of land". For over three centuries mariners tasked with guiding ships across the Sandy Hook bar have been known as Sandy Hook pilots. Most of Sandy Hook is owned and managed by the National Park Service as the Sandy Hook Unit of Gateway National Recreation Area. Description Geologically, Sandy Hook is a large sand spit or barrier spit, the extension of a barrier peninsula along the coast of New Jersey, separated from the mainland by the estuary of the Shrewsbury River. On its western side, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
League (unit)
A league is a unit of length. It was common in Europe and Latin America, but is no longer an official unit in any nation. Derived from an ancient Celtic unit and adopted by the Romans as the ''leuga'', the league became a common unit of measurement throughout western Europe. It may have originally represented, roughly, the distance a person could walk in an hour. Since the Middle Ages, many values have been specified in several countries. Different definitions Ancient Rome The league was used in Ancient Rome, defined as 1½ Roman miles (7,500 Roman feet, modern 2.2 km or 1.4 miles). The origin is the ''leuga Gallica'' ''(also: leuca Callica)'', the league of Gaul. Argentina The Argentine league (''legua'') is or 6,666 ''varas'': 1 ''vara'' is . English-speaking world On land, the league is most commonly defined as three miles (4.83km), though the length of a mile could vary from place to place and depending on the era. At sea, a league is . English usage also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USS Hancock (1776)
The second ''Hancock'' was one of the first 13 frigates of the Continental Navy. A resolution of the Continental Congress of British North America 13 December 1775 authorized her construction; she was named for the patriot and Continental congressman John Hancock. In her career she served under the American, British and French flags. As ''Hancock'' ''Hancock'' was built at Newburyport, Massachusetts, and placed under command of Captain John Manley 17 April 1776. After a long delay in fitting out and manning, she departed Boston, Massachusetts, on 21 May 1777 in company with Continental frigate and the Massachusetts privateer ''American Tartar'' for a cruise in the North Atlantic. ''American Tartar'' parted from the two frigates shortly thereafter. On 29 May the frigates captured a small brig loaded with cordage and duck. The next day they encountered a convoy of transports escorted by British 64-gun ship which set sail to close ''Hancock''. Manley was saved by clever ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lloyd's Register
Lloyd's Register Group Limited (LR) is a technical and professional services organisation and a maritime classification society, wholly owned by the Lloyd’s Register Foundation, a UK charity dedicated to research and education in science and engineering. The organisation dates to 1760. Its stated aims are to enhance the safety of life, property, and the environment, by helping its clients (including by validation, certification, and accreditation) to improve the safety and performance of complex projects, supply chains and critical infrastructure. In July 2012, the organisation converted from an industrial and provident society to a company limited by shares, named Lloyd’s Register Group Limited, with the new Lloyd’s Register Foundation as the sole shareholder. At the same time the organisation gave to the Foundation a substantial bond and equity portfolio to assist it with its charitable purposes. It will benefit from continued funding from the group’s operating arm, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ebb Tide
Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravitational forces exerted by the Moon (and to a much lesser extent, the Sun) and are also caused by the Earth and Moon orbiting one another. Tide tables can be used for any given locale to find the predicted times and amplitude (or "tidal range"). The predictions are influenced by many factors including the alignment of the Sun and Moon, the phase and amplitude of the tide (pattern of tides in the deep ocean), the amphidromic systems of the oceans, and the shape of the coastline and near-shore bathymetry (see '' Timing''). They are however only predictions, the actual time and height of the tide is affected by wind and atmospheric pressure. Many shorelines experience semi-diurnal tides—two nearly equal high and low tides each day. Other locations have a diurnal tide—one high and low tide each day. A "mixed tide"—two uneven magnitude tides a day—is a third regular category. Tides va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |