|
UQ-CSL V451
V451 was a COVID-19 vaccine candidate developed by the University of Queensland and the Australian pharmaceutical company CSL Limited. The vaccine candidate used the University of Queensland's molecular clamp technology and the MF59 adjuvant. Description V451 is a protein subunit vaccine. As part of the vaccine's design, researchers added "a fragment of one protein found on the HIV virus" as a "ground-breaking molecular clamp technology". Terminated trial The development of the vaccine was cancelled on 11 December 2020 during its Phase I trial, after a number of trial participants were found to give false positive test results for HIV antibodies when they did not in fact have HIV. This was due to the HIV virus fragment used as a molecular clamp leading to "a partial antibody response" to HIV. This is an undesirable outcome as it will interfere with future HIV screening tests for affected participants. Nine days prior to the termination, on 2 December, the first e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SARS-CoV-2
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‑CoV‑2) is a strain of coronavirus that causes COVID-19 (coronavirus disease 2019), the respiratory illness responsible for the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. The virus previously had a provisional name, 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV), and has also been called the human coronavirus 2019 (HCoV-19 or hCoV-19). First identified in the city of Wuhan, Hubei, China, the World Health Organization declared the outbreak a public health emergency of international concern on January 30, 2020, and a pandemic on March 11, 2020. SARS‑CoV‑2 is a positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus that is contagious in humans. SARS‑CoV‑2 is a virus of the species ''severe acute respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus'' (SARSr-CoV), related to the SARS-CoV-1 virus that caused the 2002–2004 SARS outbreak. Despite its close relation to SARS-CoV-1, its closest known relatives, with which it forms a sister group, are the derived SARS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
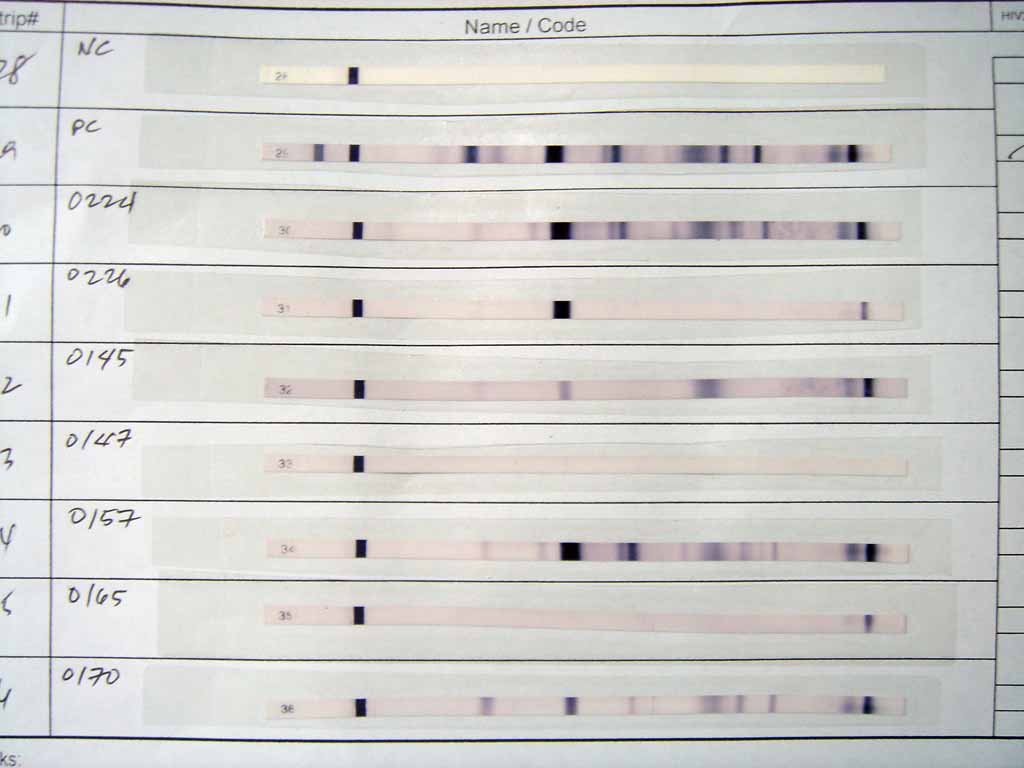
HIV Antibodies
The human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) are two species of ''Lentivirus'' (a subgroup of retrovirus) that infect humans. Over time, they cause acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), a condition in which progressive failure of the immune system allows life-threatening opportunistic infections and cancers to thrive. Without treatment, average survival time after infection with HIV is estimated to be 9 to 11 years, depending on the HIV subtype. In most cases, HIV is a sexually transmitted infection and occurs by contact with or transfer of blood, pre-ejaculate, semen, and vaginal fluids. Non-sexual transmission can occur from an infected mother to her infant during pregnancy, during childbirth by exposure to her blood or vaginal fluid, and through breast milk. Within these bodily fluids, HIV is present as both free virus particles and virus within infected immune cells. Research has shown (for both same-sex and opposite-sex couples) that HIV is untransmittable through con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clinical Trials
Clinical trials are prospective biomedical or behavioral research studies on human participants designed to answer specific questions about biomedical or behavioral interventions, including new treatments (such as novel vaccines, drugs, dietary choices, dietary supplements, and medical devices) and known interventions that warrant further study and comparison. Clinical trials generate data on dosage, safety and efficacy. They are conducted only after they have received health authority/ethics committee approval in the country where approval of the therapy is sought. These authorities are responsible for vetting the risk/benefit ratio of the trial—their approval does not mean the therapy is 'safe' or effective, only that the trial may be conducted. Depending on product type and development stage, investigators initially enroll volunteers or patients into small pilot studies, and subsequently conduct progressively larger scale comparative studies. Clinical trials can vary i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Australian COVID-19 Vaccines
Australian(s) may refer to: Australia * Australia, a country * Australians, citizens of the Commonwealth of Australia ** European Australians ** Anglo-Celtic Australians, Australians descended principally from British colonists ** Aboriginal Australians, indigenous peoples of Australia as identified and defined within Australian law * Australia (continent) ** Indigenous Australians * Australian English, the dialect of the English language spoken in Australia * Australian Aboriginal languages * ''The Australian'', a newspaper * Australiana, things of Australian origins Other uses * Australian (horse), a racehorse * Australian, British Columbia, an unincorporated community in Canada See also * The Australian (other) * Australia (other) * * * Austrian (other) Austrian may refer to: * Austrians, someone from Austria or of Austrian descent ** Someone who is considered an Austrian citizen, see Austrian nationality law * Austrian German dialect * Someth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford–AstraZeneca COVID-19 Vaccine
The Oxford–AstraZeneca COVID19 vaccine, sold under the brand names Covishield and Vaxzevria among others, is a viral vector vaccine for prevention of COVID-19. Developed in the United Kingdom by Oxford University and British-Swedish company AstraZeneca, using as a vector the modified chimpanzee adenovirus ChAdOx1. The vaccine is given by intramuscular injection. Studies carried out in 2020 showed that the efficacy of the vaccine is 76.0% at preventing symptomatic COVID-19 beginning at 22 days following the first dose, and 81.3% after the second dose. A study in Scotland found that, for symptomatic COVID-19 infection after the second dose, the vaccine is 81% effective against the Alpha variant (lineage B.1.1.7), and 61% against the Delta variant (lineage B.1.617.2). The vaccine is stable at refrigerator temperatures and has a good safety profile, with side effects including injection-site pain, headache, and nausea, all generally resolving within a few days. More rarely, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medicines And Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency
The Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) is an executive agency of the Department of Health and Social Care in the United Kingdom which is responsible for ensuring that medicines and medical devices work and are acceptably safe. The MHRA was formed in 2003 with the merger of the Medicines Control Agency (MCA) and the Medical Devices Agency (MDA). In April 2013, it merged with the National Institute for Biological Standards and Control (NIBSC) and was rebranded, with the MHRA identity being used solely for the regulatory centre within the group. The agency employs more than 1,200 people in London, York and South Mimms, Hertfordshire. Structure The MHRA is divided into three main centres: * MHRA Regulatory – the regulator for the pharmaceutical and medical devices industries * Clinical Practice Research Datalink – licences anonymised health care data to pharmaceutical companies, academics and other regulators for research * National Institute for Biolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pfizer–BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccine
The Pfizer–BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine ( INN: tozinameran), sold under the brand name Comirnaty, is an mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccine developed by the German biotechnology company BioNTech. For its development, BioNTech collaborated with American company Pfizer to carry out clinical trials, logistics, and manufacturing. It is authorized for use in people aged five years and older in some jurisdictions, twelve years and older in some jurisdictions, and for people sixteen years and older in other jurisdictions, to provide protection against COVID-19, caused by infection with the SARS-CoV-2 virus. The vaccine is given by intramuscular injection. It is composed of nucleoside-modified mRNA (modRNA) encoding a mutated form of the full-length spike protein of SARS-CoV-2, which is encapsulated in lipid nanoparticles. Initial advice indicated that vaccination required two doses given 21 days apart, but the interval was later extended to up to 42 days in the US, and up to four months i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emergency Use Authorization
An Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) in the United States is an authorization granted to the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) under sections of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act as added to and amended by various Act of Congress, Acts of Congress, including by the Pandemic and All-Hazards Preparedness Reauthorization Act of 2013 (PAHPRA), as codified by , to allow the use of a drug prior to approved drug, approval. It does not constitute ''approval'' of the drug in the full statutory meaning of the term, but instead authorizes the FDA to facilitate availability of an unapproved product, or an unapproved use of an approved product, during a declared state of emergency from one of several agencies or of a "material threat" by the Secretary of Homeland Security. Use EUAs have historically been infrequent. A review article by Rizk et al. provides a summary of the US experience in 2020 with pharmacological EUA approvals during the COVID-19 pandemic. It also provides a descripti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HIV Screening
HIV tests are used to detect the presence of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), the virus that causes acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), in serum, saliva, or urine. Such tests may detect antibodies, antigens, or RNA. AIDS diagnosis AIDS is diagnosed separately from HIV. Terminology The window period is the time from infection until a test can detect any change. The average window period with HIV-1 antibody tests is 25 days for subtype B. Antigen testing cuts the window period to approximately 16 days and nucleic acid testing (NAT) further reduces this period to 12 days. Performance of medical tests is often described in terms of: * Sensitivity: The percentage of the results that will be positive when HIV is present * Specificity: The percentage of the results that will be negative when HIV is not present. All diagnostic tests have limitations, and sometimes their use may produce erroneous or questionable results. * False positive: The test incorrectly i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
False Positive Rate
In statistics, when performing multiple comparisons, a false positive ratio (also known as fall-out or false alarm ratio) is the probability of falsely rejecting the null hypothesis for a particular test. The false positive rate is calculated as the ratio between the number of negative events wrongly categorized as positive (false positives) and the total number of actual negative events (regardless of classification). The false positive rate (or "false alarm rate") usually refers to the expectancy of the false positive ratio. Definition The false positive rate is FPR=\frac where \mathrm is the number of false positives, \mathrm is the number of true negatives and N=\mathrm+\mathrm is the total number of ground truth negatives. The level of significance that is used to test each hypothesis is set based on the form of inference ( simultaneous inference vs. selective inference) and its supporting criteria (for example FWER or FDR), that were pre-determined by the researche ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intramuscular Injection
Intramuscular injection, often abbreviated IM, is the injection of a substance into a muscle. In medicine, it is one of several methods for parenteral administration of medications. Intramuscular injection may be preferred because muscles have larger and more numerous blood vessels than subcutaneous tissue, leading to faster absorption than subcutaneous or intradermal injections. Medication administered via intramuscular injection is not subject to the first-pass metabolism effect which affects oral medications. Common sites for intramuscular injections include the deltoid muscle of the upper arm and the gluteal muscle of the buttock. In infants, the vastus lateralis muscle of the thigh is commonly used. The injection site must be cleaned before administering the injection, and the injection is then administered in a fast, darting motion to decrease the discomfort to the individual. The volume to be injected in the muscle is usually limited to 2–5 milliliters, depending on in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phase I Trial
The phases of clinical research are the stages in which scientists conduct experiments with a health intervention to obtain sufficient evidence for a process considered effective as a medical treatment. For drug development, the clinical phases start with testing for safety in a few human subjects, then expand to many study participants (potentially tens of thousands) to determine if the treatment is effective. Clinical research is conducted on drug candidates, vaccine candidates, new medical devices, and new diagnostic assays. Summary Clinical trials testing potential medical products are commonly classified into four phases. The drug development process will normally proceed through all four phases over many years. If the drug successfully passes through Phases I, II, and III, it will usually be approved by the national regulatory authority for use in the general population. Phase IV trials are 'post-marketing' or 'surveillance' studies conducted to monitor safety over se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)
_2021_C.jpg)
_E.jpg)