|
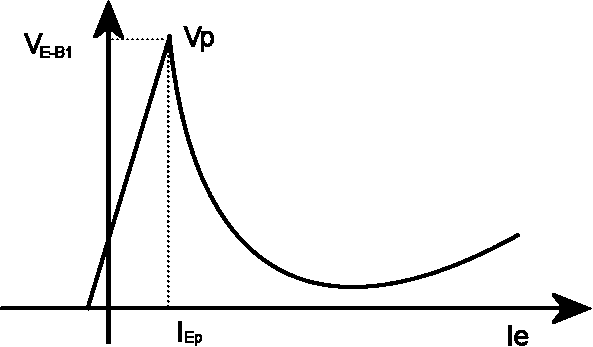
UJT
A unijunction transistor (UJT) is a three-lead electronic semiconductor device with only one junction that acts exclusively as an electrically controlled switch. The UJT is not used as a linear amplifier. It is used in free-running oscillators, synchronized or triggered oscillators, and pulse generation circuits at low to moderate frequencies (hundreds of kilohertz). It is widely used in the triggering circuits for silicon controlled rectifiers. In the 1960s, the low cost per unit, combined with its unique characteristic, warranted its use in a wide variety of applications like oscillators, pulse generators, saw-tooth generators, triggering circuits, phase control, timing circuits, and voltage- or current-regulated supplies.J. F. Cleary (ed.), ''General Electric Transistor Manual'', General Electric, 1964 Chapter 13 "Unijunction Transistor Circuits" The original unijunction transistor types are now considered obsolete, but a later multi-layer device, the programmable unijunction tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UJT Caratteristica
A unijunction transistor (UJT) is a three-lead electronic semiconductor device with only one junction that acts exclusively as an electrically controlled switch. The UJT is not used as a linear amplifier. It is used in free-running oscillators, synchronized or triggered oscillators, and pulse generation circuits at low to moderate frequencies (hundreds of kilohertz). It is widely used in the triggering circuits for silicon controlled rectifiers. In the 1960s, the low cost per unit, combined with its unique characteristic, warranted its use in a wide variety of applications like oscillators, pulse generators, saw-tooth generators, triggering circuits, phase control, timing circuits, and voltage- or current-regulated supplies.J. F. Cleary (ed.), ''General Electric Transistor Manual'', General Electric, 1964 Chapter 13 "Unijunction Transistor Circuits" The original unijunction transistor types are now considered obsolete, but a later multi-layer device, the programmable unijunction tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UJT Struttura
A unijunction transistor (UJT) is a three-lead electronic semiconductor device with only one junction that acts exclusively as an electrically controlled switch. The UJT is not used as a linear amplifier. It is used in free-running oscillators, synchronized or triggered oscillators, and pulse generation circuits at low to moderate frequencies (hundreds of kilohertz). It is widely used in the triggering circuits for silicon controlled rectifiers. In the 1960s, the low cost per unit, combined with its unique characteristic, warranted its use in a wide variety of applications like oscillators, pulse generators, saw-tooth generators, triggering circuits, phase control, timing circuits, and voltage- or current-regulated supplies.J. F. Cleary (ed.), ''General Electric Transistor Manual'', General Electric, 1964 Chapter 13 "Unijunction Transistor Circuits" The original unijunction transistor types are now considered obsolete, but a later multi-layer device, the programmable unijunction tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Negative Resistance
In electronics, negative resistance (NR) is a property of some electrical circuits and devices in which an increase in voltage across the device's terminals results in a decrease in electric current through it. This is in contrast to an ordinary resistor in which an increase of applied voltage causes a proportional increase in current due to Ohm's law, resulting in a positive resistance. While a positive resistance consumes power from current passing through it, a negative resistance produces power. Under certain conditions it can increase the power of an electrical signal, amplifying it. Negative resistance is an uncommon property which occurs in a few nonlinear electronic components. In a nonlinear device, two types of resistance can be defined: 'static' or 'absolute resistance', the ratio of voltage to current v / i, and ''differential resistance'', the ratio of a change in voltage to the resulting change in current \Delta v/\Delta i. The term negative resistance means ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Programmable Unijunction Transistor
A programmable unijunction transistor (PUT) is a three-lead electronic semiconductor device which is similar in its characteristics to a unijunction transistor, except that its behavior can be controlled using external components. In a unijunction transistor, the base region is divided into two parts by the emitter. The two parts of the base form a voltage divider, which sets the operating point of the UJT. That voltage divider can be programmed with two physical resistors connected to the gate terminal of the PUT. This allows the designer some control over the operating point of the PUT. Construction In construction, the programmable unijunction transistor is similar to the silicon controlled rectifier. It consists of four layers, two p-type layers and two n-type layers in equal proportion. Applications * It is used to trigger thyristors. * It is also used as a relaxation oscillator. As of 2012 ON Semiconductor onsemi (stylized in lowercase; legally ON Semiconductor Corporat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thyristor
A thyristor () is a solid-state semiconductor device with four layers of alternating P- and N-type materials used for high-power applications. It acts exclusively as a bistable switch (or a latch), conducting when the gate receives a current trigger, and continuing to conduct until the voltage across the device is reversed biased, or until the voltage is removed (by some other means). There are two designs, differing in what triggers the conducting state. In a three-lead thyristor, a small current on its Gate lead controls the larger current of the Anode to Cathode path. In a two-lead thyristor, conduction begins when the potential difference between the Anode and Cathode themselves is sufficiently large (breakdown voltage). Some sources define silicon-controlled rectifier (SCR) and thyristor as synonymous. Other sources define thyristors as more complex devices that incorporate at least four layers of alternating N-type and P-type substrate. The first thyristor devices were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N-type Semiconductor
An extrinsic semiconductor is one that has been '' doped''; during manufacture of the semiconductor crystal a trace element or chemical called a doping agent has been incorporated chemically into the crystal, for the purpose of giving it different electrical properties than the pure semiconductor crystal, which is called an ''intrinsic semiconductor''. In an extrinsic semiconductor it is these foreign dopant atoms in the crystal lattice that mainly provide the charge carriers which carry electric current through the crystal. The doping agents used are of two types, resulting in two types of extrinsic semiconductor. An ''electron donor'' dopant is an atom which, when incorporated in the crystal, releases a mobile conduction electron into the crystal lattice. An extrinsic semiconductor which has been doped with electron donor atoms is called an n-type semiconductor, because the majority of charge carriers in the crystal are negative electrons. An ''electron acceptor'' dopant is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hall Effect
The Hall effect is the production of a voltage difference (the Hall voltage) across an electrical conductor that is transverse to an electric current in the conductor and to an applied magnetic field perpendicular to the current. It was discovered by Edwin Hall in 1879. A Hall effect can also occur across a void or hole in a semiconductor or metal plate, when current is injected via contacts that lie on the boundary or edge of the void or hole, and the charge flows outside the void or hole, in the metal or semiconductor. This Hall effect becomes observable in a perpendicular applied magnetic field across voltage contacts that lie on the boundary of the void on either side of a line connecting the current contacts. It exhibits apparent sign reversal in comparison to the standard "ordinary Hall effect" in the simply connected specimen, and depends only on the current injected from within the void. Superposition may also be realized in the Hall effect: first imagine the standard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doping (semiconductor)
In semiconductor production, doping is the intentional introduction of impurities into an intrinsic semiconductor for the purpose of modulating its electrical, optical and structural properties. The doped material is referred to as an extrinsic semiconductor. Small numbers of dopant atoms can change the ability of a semiconductor to conduct electricity. When on the order of one dopant atom is added per 100 million atoms, the doping is said to be ''low'' or ''light''. When many more dopant atoms are added, on the order of one per ten thousand atoms, the doping is referred to as ''high'' or ''heavy''. This is often shown as ''n+'' for n-type doping or ''p+'' for p-type doping. (''See the article on semiconductors for a more detailed description of the doping mechanism.'') A semiconductor doped to such high levels that it acts more like a conductor than a semiconductor is referred to as a degenerate semiconductor. A semiconductor can be considered i-type semiconductor if it has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Active Component
Passivity is a property of engineering systems, most commonly encountered in analog electronics and control systems. Typically, analog designers use ''passivity'' to refer to incrementally passive components and systems, which are incapable of power gain. In contrast, control systems engineers will use ''passivity'' to refer to thermodynamically passive ones, which consume, but do not produce, energy. As such, without context or a qualifier, the term ''passive'' is ambiguous. An electronic circuit consisting entirely of passive components is called a passive circuit, and has the same properties as a passive component. If a component is ''not'' passive, then it is an active component. Thermodynamic passivity In control systems and circuit network theory, a passive component or circuit is one that consumes energy, but does not produce energy. Under this methodology, voltage and current sources are considered active, while resistors, capacitors, inductors, transistors, tunnel di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P-type Semiconductor
An extrinsic semiconductor is one that has been '' doped''; during manufacture of the semiconductor crystal a trace element or chemical called a doping agent has been incorporated chemically into the crystal, for the purpose of giving it different electrical properties than the pure semiconductor crystal, which is called an ''intrinsic semiconductor''. In an extrinsic semiconductor it is these foreign dopant atoms in the crystal lattice that mainly provide the charge carriers which carry electric current through the crystal. The doping agents used are of two types, resulting in two types of extrinsic semiconductor. An ''electron donor'' dopant is an atom which, when incorporated in the crystal, releases a mobile conduction electron into the crystal lattice. An extrinsic semiconductor which has been doped with electron donor atoms is called an n-type semiconductor, because the majority of charge carriers in the crystal are negative electrons. An ''electron acceptor'' dopant is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
555 Timer IC
The 555 timer IC is an integrated circuit (chip) used in a variety of timer, delay, pulse generation, and oscillator applications. Derivatives provide two ( 556) or four ( 558) timing circuits in one package. The design was first marketed in 1972 by Signetics. Since then, numerous companies have made the original bipolar timers, as well as similar low-power CMOS timers. In 2017, it was said that over a billion 555 timers are produced annually by some estimates, and that the design was "probably the most popular integrated circuit ever made". History The timer IC was designed in 1971 by Hans Camenzind under contract to Signetics. In 1968, he was hired by Signetics to develop a phase-locked loop (PLL) IC. He designed an oscillator for PLLs such that the frequency did not depend on the power supply voltage or temperature. Signetics subsequently laid off half of its employees due to the 1970 recession, and development on the PLL was thus frozen. Camenzind proposed the dev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |