|
UHRF1
Ubiquitin-like, containing PHD and RING finger domains, 1, also known as UHRF1, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''UHRF1'' gene. Function This gene encodes a member of a subfamily of RING finger domain, RING-finger type E3 ubiquitin ligases. The protein binds to hemi-methylated DNA during S-phase and recruits the main DNA methyltransferase protein, DNMT1, to regulate chromatin structure and gene expression. Its expression peaks at late G1 phase and continues during G2 and M phases of the cell cycle. It plays a major role in the G1/S transition, and functions in the p53-dependent DNA damage checkpoint. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. It was originally identified as a direct regulator of topoisomerase 2a, but this has subsequently been disproven. Uhrf1 has been extensively studied in vivo using zebrafish. Clinical significance UHRF1 has recently been identified as a novel oncogene in hepatocellular carcinom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNMT1
DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of methyl groups to specific CpG structures in DNA, a process called DNA methylation. In humans, it is encoded by the ''DNMT1'' gene. DNMT1 forms part of the family of DNA methyltransferase enzymes, which consists primarily of DNMT1, DNMT3A, and DNMT3B. Function This enzyme is responsible for maintaining DNA methylation, which ensures the fidelity of this epigenetic patterns across cell divisions. In line with this role, it has a strong preference towards methylating CpGs on hemimethylated DNA. However, Dnmt1 can catalyze de novo DNA methylation in specific genomic contexts, including transposable elements and paternal imprint control regions. Aberrant methylation patterns are associated with certain human tumors and developmental abnormalities. See also * DNA methyltransferase Interactions DNMT1 has been shown to interact with UHRF1,: * DMAP1, * DNMT3A * DNMT3B DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RING Finger Domain
In molecular biology, a RING (short for Really Interesting New Gene) finger domain is a protein structural domain of zinc finger type which contains a C3HC4 amino acid motif which binds two zinc cations (seven cysteines and one histidine arranged non-consecutively). This protein domain contains 40 to 60 amino acids. Many proteins containing a RING finger play a key role in the ubiquitination pathway. Zinc fingers Zinc finger (Znf) domains are relatively small protein motifs that bind one or more zinc atoms, and which usually contain multiple finger-like protrusions that make tandem contacts with their target molecule. They bind DNA, RNA, protein and/or lipid substrates. Their binding properties depend on the amino acid sequence of the finger domains and of the linker between fingers, as well as on the higher-order structures and the number of fingers. Znf domains are often found in clusters, where fingers can have different binding specificities. There are many superfamilie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
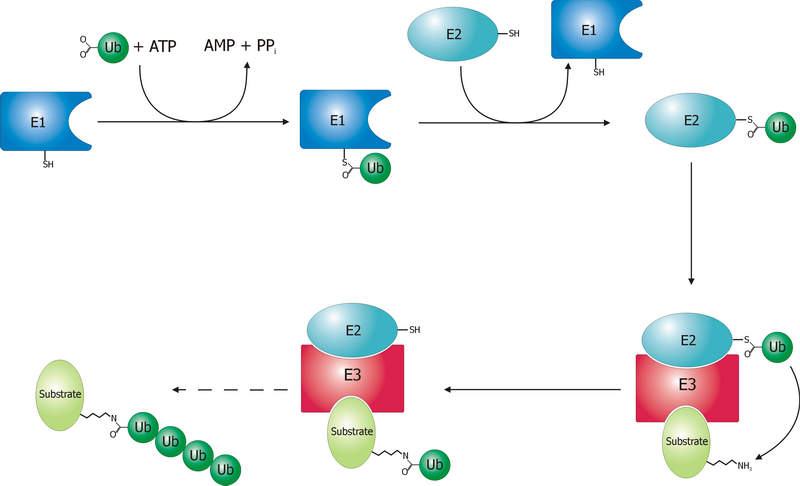
E3 Ubiquitin Ligase
A ubiquitin ligase (also called an E3 ubiquitin ligase) is a protein that recruits an E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme that has been loaded with ubiquitin, recognizes a protein substrate, and assists or directly catalyzes the transfer of ubiquitin from the E2 to the protein substrate. In simple and more general terms, the ligase enables movement of ubiquitin from a ubiquitin carrier to another thing (the substrate) by some mechanism. The ubiquitin, once it reaches its destination, ends up being attached by an isopeptide bond to a lysine residue, which is part of the target protein. E3 ligases interact with both the target protein and the E2 enzyme, and so impart substrate specificity to the E2. Commonly, E3s polyubiquitinate their substrate with Lys48-linked chains of ubiquitin, targeting the substrate for destruction by the proteasome. However, many other types of linkages are possible and alter a protein's activity, interactions, or localization. Ubiquitination by E3 ligases re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Cycle
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a cell that cause it to divide into two daughter cells. These events include the duplication of its DNA (DNA replication) and some of its organelles, and subsequently the partitioning of its cytoplasm, chromosomes and other components into two daughter cells in a process called cell division. In cells with nuclei ( eukaryotes, i.e., animal, plant, fungal, and protist cells), the cell cycle is divided into two main stages: interphase and the mitotic (M) phase (including mitosis and cytokinesis). During interphase, the cell grows, accumulating nutrients needed for mitosis, and replicates its DNA and some of its organelles. During the mitotic phase, the replicated chromosomes, organelles, and cytoplasm separate into two new daughter cells. To ensure the proper replication of cellular components and division, there are control mechanisms known as cell cycle checkpoints after each of the key s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |